Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
A |
|---|
Absolute Magnitude | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio:
Short Definition:
Absolute magnitude is the measurement of the brightness of celestial bodies using inverse logarithmic calculations in astronomical calculations and expressed as a mathematical value. This process involves mathematically expressing their luminosity, as a hypothesis, by placing objects at an equal distance from the observer (10 parsecs that equals to 32.6 light years).
Detailed Definition:
Absolute magnitude is also called absolute visual magnitude, which is a hypothesis that predicts the mathematical calculation of the luminosity of different celestial bodies, taking into account fixed distances, and comparing the luminosities of these objects. The mathematical formula used to calculate this luminosity is as follows; Mv: Absolute magnitude m: Apparent magnitude d: Distance in 10 parsecs Mv = m – 2.5 log [d/10]² The apparent magnitude here, on an inverse scale, indicates how bright celestial objects appear to our eyes. Because it's an inverted scale, high numbers indicate dim objects and low numbers indicate bright objects. The brightest object known and measured on this scale has a value of -10, while the star Sirius has a luminosity of 1.4, and our sun has a luminosity of 4.8.
Etymology:
Absolute -from old Latin (absolūtus) (Absolute – Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/absolute) Magnitude -from old Latin (Magnus) (Magnitude – Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/magnitude)
Sample Sentence(s):
‘’When comet 289P/Blanpain was discovered in 1819, its absolute magnitude was estimated as {\displaystyle M_{1}=8.5}{\displaystyle M_{1}=8.5}’’ (Wikipedia contributors. (2023, January 13). Absolute magnitude. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Absolute_magnitude) ‘’Colour–magnitude diagram, in astronomy, graph showing the relation between the absolute magnitudes (brightnesses) of stars and their colours, which are closely related to their temperatures and spectral types.’’ (The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (1998, July 20). Colour–magnitude diagram | astronomy. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/colour-magnitude-diagram) Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages:
French:
Magnitude absolue German:
Absolute Helligkeit Polish:
wielkość absolutna Swedish:
Absolut magnitud Turkish: Mutlak Kadir
Links to Videos/Articles:
Absolute magnitude | astronomy. (n.d.-a). Encyclopaedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/absolute-magnitude Absolute Magnitude | COSMOS. (n.d.-a). https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/a/Absolute+Magnitude Apparent and Absolute Magnitudes. (n.d.-b). https://www.phys.ksu.edu/personal/wysin/astro/magnitudes.html Michel van Biezen. (2014, April 9). Astronomy - Measuring Distance, Size, and Luminosity (18 of 30) Absolute Magnitude [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yfsUhOPCMaM | |||
Accretion disc | |||
|---|---|---|---|
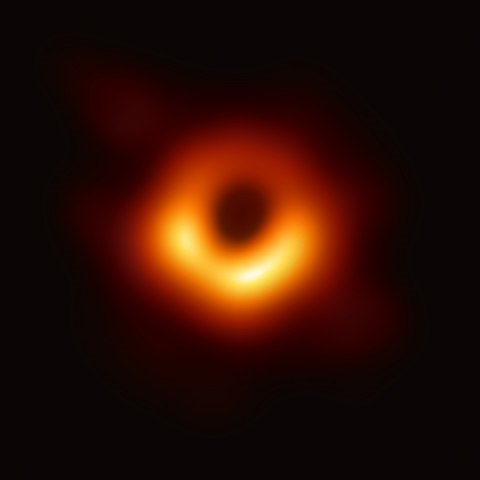

Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Black_hole_-_Messier_87_crop_max_res.jpg Short Definition: An accretion disk is a structure, which is an amalgamation of gas, plasma or particles around the black hole. It is attracted by the gravitational pull and orbits the black hole while it slowly spirals into it, so it is a phenomenon that describes the way how a big celestial body amasses matter like black holes. Detailed Definition: One can not observe black holes or their event horizon, but since black holes have accretion disks, which are a type of structure and accumulations of gas, plasma or particles that were attracted by the huge gravitational pull of black holes. Humans are able to see those accretion disks, because the spinning matter is so fast, which in turn generates heat and emits x-rays and gamma rays. The high amount of angular momentum makes it impossible for the matter to simply fall into the black hole like it would on earth or one would think. Angular momentum decreases despite there being no friction in space, because of turbulence, which is caused by the fact that rotation increases the effect of magnetic fields. Temperatures in the accretion disks tend to vary quite a bit, which is determined by the composition of the accretion disk and its source. Temperatures can go from a few thousand to a few million Kelvin. Etymology: Accretion from Latin ad+ crescere-->accrescere--->accretionem Disk from Latin discus
Sample Sentence(s):
The accretion disk is the natural consequence of how gravitational pull attracts matter and makes it impossible to simply fall into the black hole. Many people think they saw a picture of a black hole, but in reality they only saw a picture of its accretion disk.
French: disque d’accrétion German: Akkretionsscheibe Polish: Dysk akrecyjny Swedish: Accretionsskiva Links to Videos/Articles: GMS: Black Hole Accretion Disk Visualization (nasa.gov) | |||
Additive manufacturing | ||
|---|---|---|
DefinitionsShort Definition Detailed Definition Etymology Sample Sentence(s)Extensive use of additive manufacturing in aerospace industry will result in more frequent launches, as this technology greatly shortens the expenses. The most common and well-known example of additive manufacturing is 3-D printing models from melted plastic. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner LanguagesFrench la fabrication additive German Italian Polish Swedish Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other LanguagesRussian аддитивное производство Ukrainian Links to Videos/Articles:2. Additive manufacturing, explained | MIT Sloan. (2017b, December 7). MIT Sloan. Retrieved [ 06.14.2023 ], from https://mitsloan.mit.edu/ideas-made-to-matter/additive-manufacturing-explained 3. SAE Media Group. (2020, January 17). 3D Printing and Space Exploration: How NASA Will Use Additive Manufacturing. Tech Briefs. Retrieved [ 06.20.2023 ], from https://www.techbriefs.com/component/content/article/tb/stories/blog/35871 | ||
Aerolite | ||
|---|---|---|
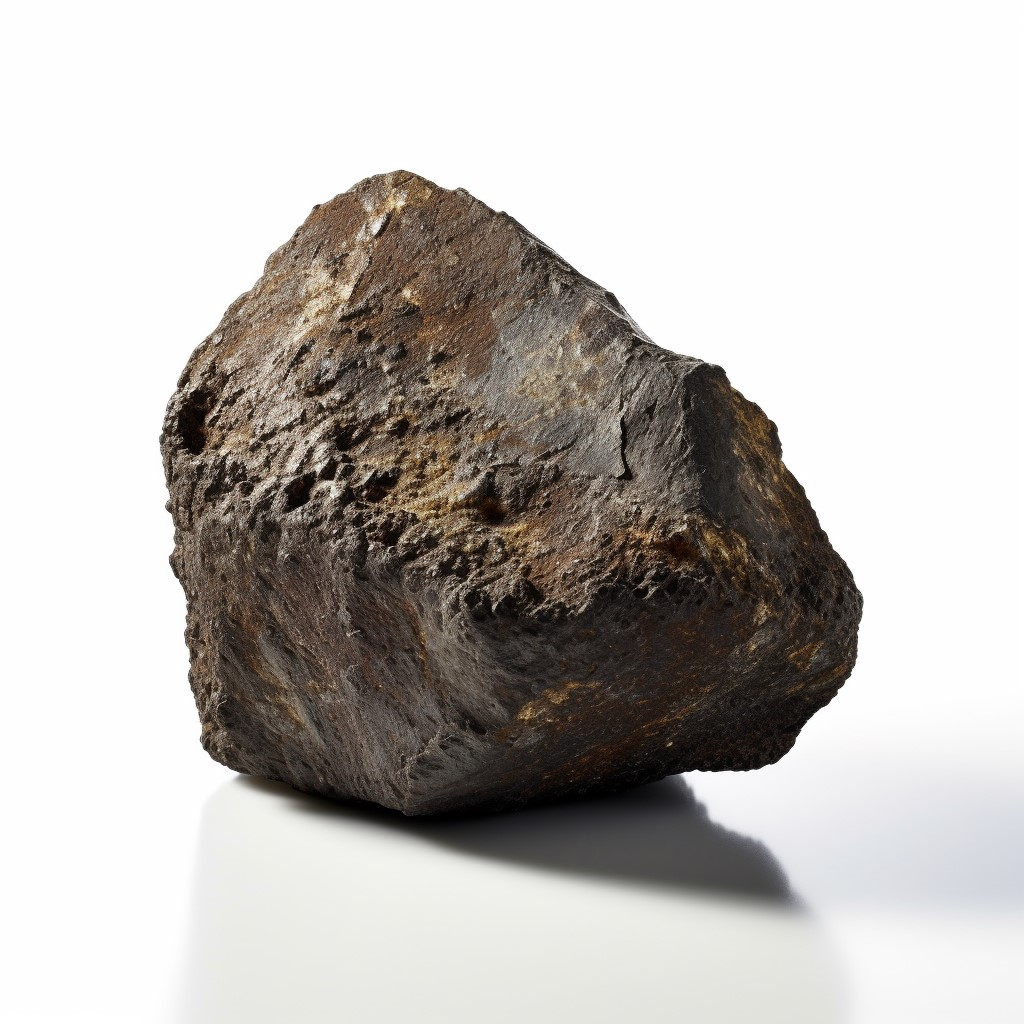 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 31). AI image of an aerolite meteorite. midjourney. midjourney.com Short definition: An Aerolite is a stony meteorite that
comes from the asteroid belt. Detailed Definition: In astronomy, an aerolite
is a type of meteorite that is composed primarily of rock and minerals. They
are believed to originate from the asteroid belt, a region between Mars and
Jupiter where many small bodies orbit the Sun. Aerolites are formed from the
debris of collisions between asteroids and are made up of a variety of minerals,
including silicates and oxides. They are different from iron meteorites, which
are composed primarily of iron and nickel. Etymology: aero - air+ -lite - (used to from names of rocks and minerals) Sample Sentence(s):
"The museum's collection includes a small aerolite from the asteroid belt." "The aerolite that landed in the farmer's field was later determined to be a piece of the asteroid Vesta." "Many scientists study aerolites to learn more about the composition of the early solar system." Translations: French: aérolithe German: Steinmeteorit Polish: aerolit Links to videos/articles: https://www.britannica.com/science/stony-meteorite | ||
Almucantar | ||
|---|---|---|
Media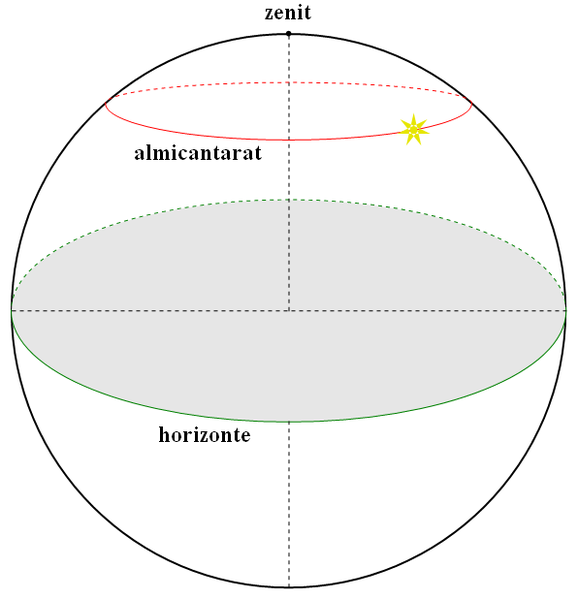 DefinitionsAlmucantar (also known as almucantarat, almacantara) is a circle of the celestial sphere parallel to the horizon. Stars belonging to the same almucantar have the same altitude. Detailed Definition
Almucantar is commonly defined by the arc on the celestial sphere, characterized by the zenith angle, which represents half of its angular magnitude. The almucantar plane refers to a plane within the celestial sphere that is formed by the almucantar. A solar almucantar specifically denotes an almucantar plane used for measuring the irradiance of the Sun. Etymology
From French almucantarat, from Arabic almuqanṭarāt"circles of celestial latitude" , from qanṭara"arch" Sample Sentence(s)The Sun and the Moon seized their almucantar and remained there for a moment, dividing the world into day and night.
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner LanguagesFrench
l'almicantarat German
der Almukantarat Italian
l’almucantarat Polish
almukantar, almukantarat Swedish
almicantarat Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other LanguagesRussian
альмукантарат
Ukrainian
альмукантарат
Links to Videos/Articles:The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (1998a, July 20). Almucantar | astronomy. Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved [ 06.14.2023 ], from https://www.britannica.com/science/almucantar | ||
Analog habitat | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Mars Desert Research Station - an analog habitat in the middle of a desert in Utah Source: Wikipedia An analog habitat is a facility that is set up to imitate martian or lunar conditions on earth. Detailed Definition: An analog habitat is a base meant to simulate a space habitat or colony. It is designed to test and study the feasibility of living in such a habitat. Analog habitats are used to test technologies and systems that could be used in a real space habitat, and to study the psychological and social effects of living in a closed environment without the risks and cost of an actual space mission. Etymology: From Latin habitō (“I live or I dwell”). Sample Sentence(s): An analog habitat was set up in the middle of a desert. Translations: French: habitat analogique German: analoger Lebensraum Polish: habitat analogowy Swedish: analog livsmiljö Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352309321000018 | |||
Antimatter | ||
|---|---|---|
Media: 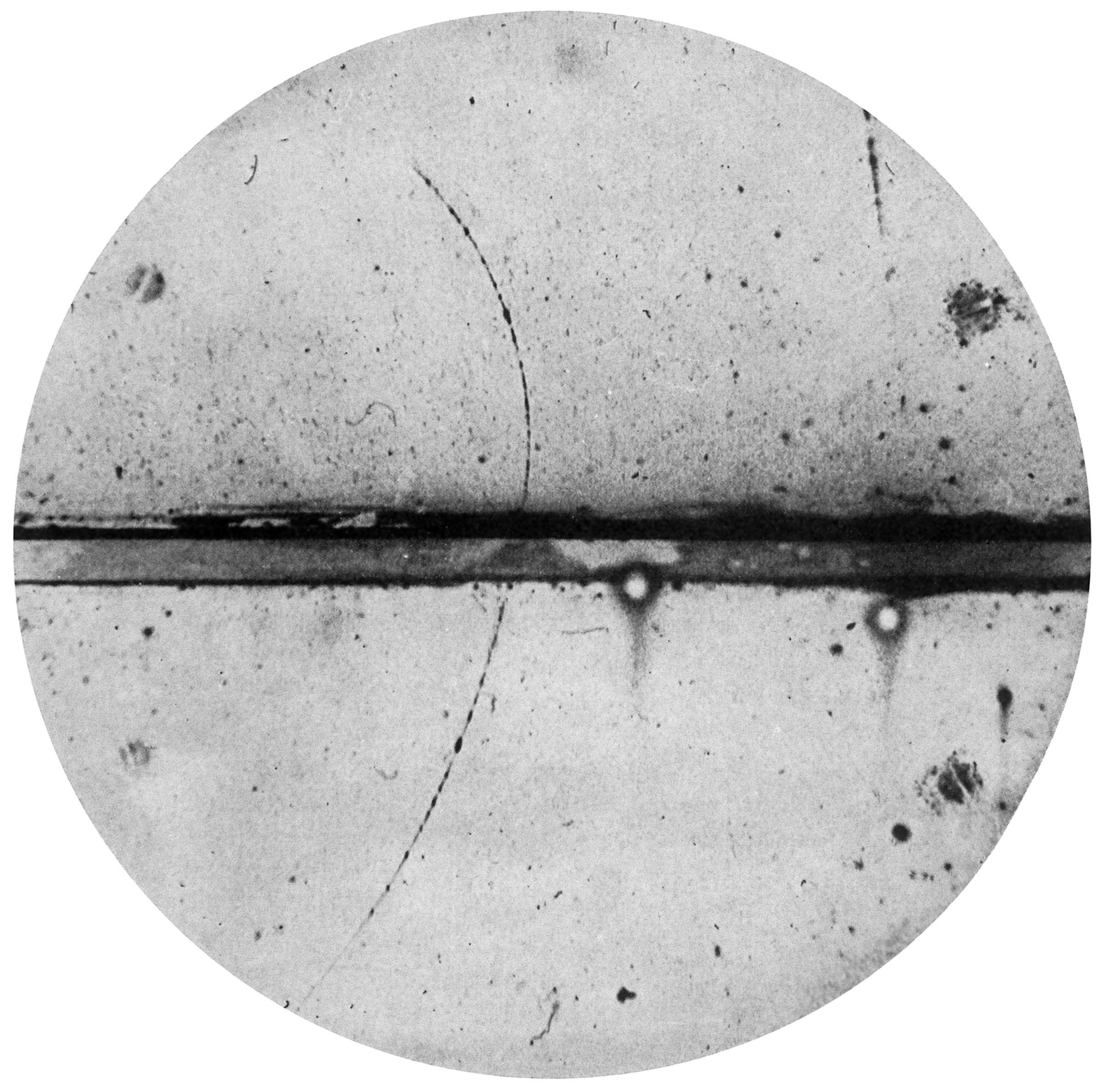 Media: Carl D. Anderson (1905–1991) - Anderson, Carl D. (1933). "The Positive Electron". Physical Review 43 (6): 491–494. DOI:10.1103/PhysRev.43.491. Short Definition: Antimatter is a type of matter which takes on exactly reverse properties to normal matter, considering charge, parity and time in a symmetric matter. Properties such as mass and acceleration are the same to regular matter, even though some are exactly opposite. Where in normal matter electrons have negative charge, antimatter has its own 'positrons' which behave the same as electrons but are positively charged. Detailed Definition: Antimatter is a type of matter which has certain properties flipped. As matter is all around us and is a building block of our universe, antimatter also has a place in our universe. This type of matter has an obvious relation with regular matter. When the two come into contact, they are both annihilated and turn into pure energy. Antimatter has been in our universe since the beginning according to the Big Bang theory. There is far less antimatter in the universe than regular matter, but it constantly gets created through radiation, decay and even lightnings, to shortly after being destroyed by contact with electrons. Antimatter is a well-defined concept in physics and is used in medical PET (Positron emission tomography) scans to form images of our bodies. The term is connected to many other concepts with 'anti-' prefix, as Antimatter is a general concept describing particles with inverse properties to the regular ones. Etymology: The prefix 'anti' from Greek, meaning 'something opposite' and 'matter' from Anglo-French 'materie' meaning 'a substance'. Sample Sentence(s): 1. At CERN, physicists make antimatter to study in experiments. The starting point is the Antiproton Decelerator, which slows down antiprotons so that physicists can investigate their properties. 2. Antimatter and regular matter annihilate each other at contact into pure energy. Translations: French - Antimatière German - Antimaterie Italian - Antimateria Polish - antymateria Swedish - Antimateria | ||
Aphelion | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Vitalik1986 (2011, March 26). Perihelios-aphelion. wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=14702160 Short definition: The point in the orbit of a planet or other celestial body that is farthest from the sun. Detailed Definition: Aphelion is the point in the orbit of a celestial body where it is farthest from the sun. It is the opposite of perihelion, which is the point in the orbit where the celestial body is closest to the sun. The distance between a celestial body and the sun varies during its orbit due to the elliptical shape of the orbit. The aphelion is the point where the distance is at a maximum. Etymology: aphelios - far from the sun aph - from and helion - the sun Sample Sentence(s):
"Mars reaches its aphelion in July, when it is about 250 million miles from the sun." "The aphelion of Earth's orbit occurs in July, when it is about 3.1 million miles farther from the sun than at perihelion in January." "The aphelion of Pluto's orbit is about 49.3 billion kilometres, while its perihelion is about 29.7 billion kilometres." Translations: French: aphélie German: Aphel Polish: aphelium Links to videos/articles: https://www.britannica.com/science/aphelion https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/videos/whats-up-january-2021 | ||
Apogee | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: Short Definition: An apogee is a point in an elliptical orbit, which is considered to be the farthest point from Earth. Detailed Definition: There are two sides in any elliptical orbit, with the names referring to the primary body in the orbit. The closest and farthest points are referred to by, respectively, the prefixes peri- and apo-. The suffix is determined by the primary body, which in the case of Earth is -gee. Therefore, an apogee is the term describing the farthest point on the elliptical orbit of Earth. A satellite is at its slowest when travelling through the apogee. Etymology: "apogee" - French apogée, Latin apogaeum, Greek apogaion - point at which the Moon is farthest from the Earth "apo-" - Greek apo, Avestan apa, Latin ab - off, away, away from "Gaia" / "ge" - Greek Gaia / gaia - a titan, personification of Earth Sample Sentence(s): A satellite that travel around a celestial body is at its slowest whenever the satellite is at its apogee. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Apogée German: Höhepunkt Polish: apogeum Swedish: Höjdpunkt Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.allthescience.org/what-is-an-apogee.htm | |||
Ariane 5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
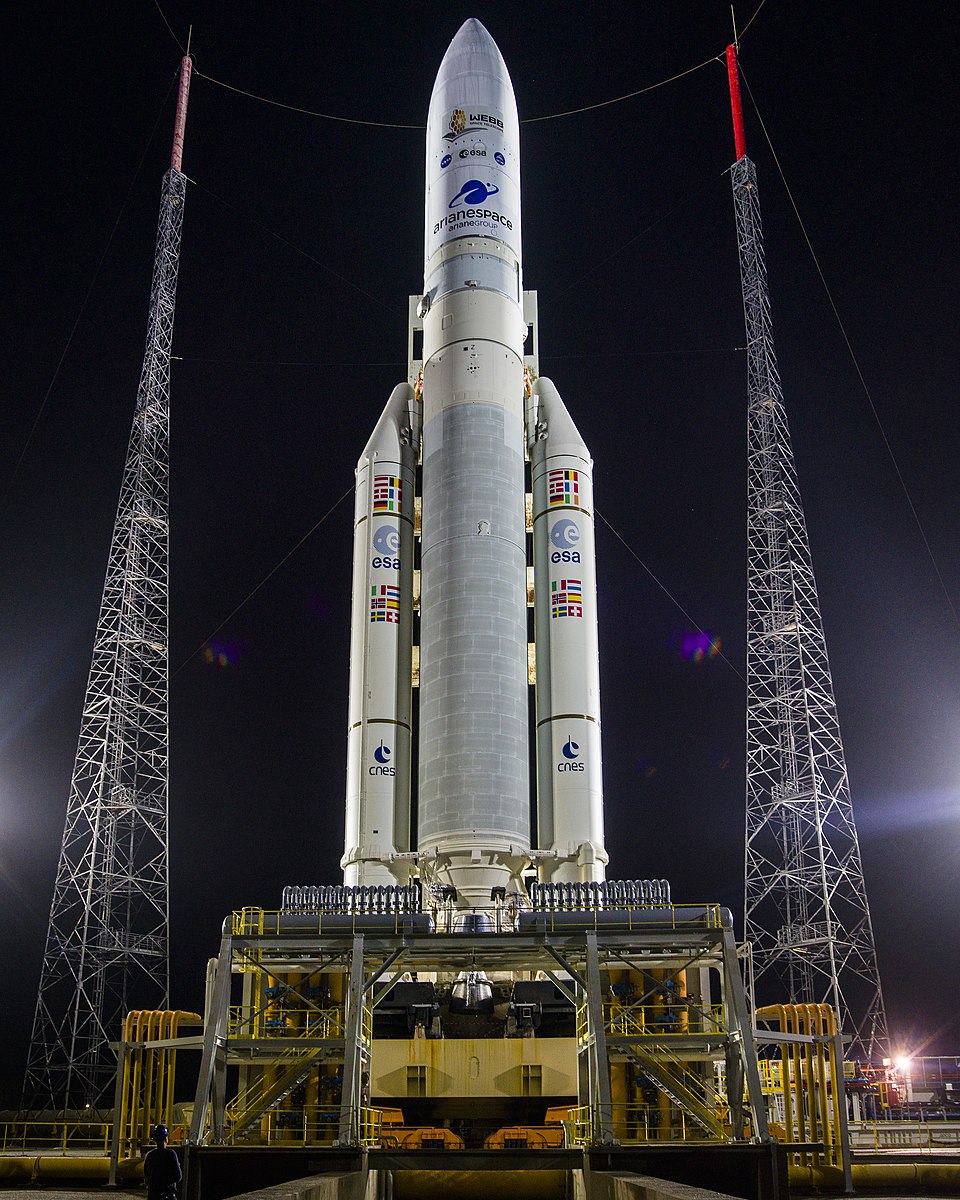 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Ariane_5_with_James_Webb_Space_Telescope_Prelaunch_(51773093465).jpg Author: Unknown Year: (n.d.) Title: Ariane 5 with James Webb Space Telescope Prelaunch Description: Ariane 5 rocket with the James Webb Space Telescope before launch Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Ariane_5_with_James_Webb_Space_Telesco pe_Prelaunch_(51773093465).jpg Author: Unknown Year: (n.d.) Title: Ariane 5 with James Webb Space Telescope Prelaunch Description: Ariane 5 rocket with the James Webb Space Telescope before launch Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Ariane_5_with_James_Webb_Space_Telesco pe_Prelaunch_(51773093465).jpg Definitions Short Definition Ariane V is a heavy-lift space launch vehicle developed by the European Space Agency. It is designed to deliver payloads, including satellites and space probes, into geostationary transfer orbit. The Ariane V rocket consists of two main stages, multiple solid rocket boosters, and a cryogenic upper stage, allowing it to launch large and heavy payloads into space. Detailed Definition Ariane V is a powerful rocket designed in 2021 to send satellites and spacecraft into space. It was created by the European Space Agency, ESA and is part of a family of rockets called Ariane. The rocket has two main parts, or stages, that work together to launch the payload into space. The first stage has two powerful engines that burn solid fuel for about two minutes. After that, they detach and the second stage takes over. The second stage has a liquid fuel engine that takes the payload higher and faster until it reaches the desired orbit. Ariane V is very reliable and has been used for many different types of missions, such as launching communication satellites, Earth observation satellites, and scientific missions. Ariane V can carry very heavy payloads, which makes it a perfect choice for launching big commercial satellites. Etymology Ariane is a name that comes from Greek mythology, specifically from the story of Theseus and the Minotaur. In the story, Theseus, a Greek hero, is sent to Crete to defeat the Minotaur, a monster with the head of a bull and the body of a man. He is aided in his mission by Ariane, she gives Theseus a ball of thread to help him navigate through the maze where the Minotaur lived. With her help, Theseus was able to kill the monster and escape the maze. The name Ariane was chosen for the European Space Agency's rocket family because it represents the idea of finding a way through complex and difficult challenges, just as Theseus found his way through the labyrinth with Ariane's help. The rockets in the Ariane family are designed to help humans explore space, which is one of the most complex and challenging endeavours for humans. Sample Sentence(s) Among the many European satellites launched by Ariane have been Giotto, the probe to Halley’s Comet; Hipparcos, the stellar distance-measuring satellite; Rosetta, a comet rendezvous mission; and Envisat, a large Earth-observing satellite. Author: Britannica Year: (n.d.) Title of the article: Ariane (European launch vehicles) Title of the website or source: Encyclopedia Britannica Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023 URL: https://www.britannica.com/technology/Ariane- European-launch-vehicles The European Space Agency's Ariane V rocket was successfully launched into space, carrying a satellite that will provide internet access to remote areas. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French: Ariane V German: Ariane V Italian: Ariane V Polish: Ariane V Swedish: Ariane V Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Lang... Russian: Ариан 5 Links to Videos/Articles: ● https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Transportation/Launch_veh icles/Ariane_5 ● https://youtu.be/UaYZieeCX68 | |||
Asteroid | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Burned Pineapple Productions (2018, June 14). asteroid. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/51686021@N07/42075207904 Short definition: An asteroid is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the sun, also known as a “minor planet”. They can be rocky, metallic, or icy bodies with no atmosphere and range in a wide spectrum of sizes and shapes. Long definition: An asteroid is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the sun, also known as a “minor planet”. They can be rocky, metallic, or icy bodies with no atmosphere and vary greatly in shape and size, from 1000 km to 1 m across. The three largest asteroids (Ceres, Vesta and Pallas) look very much like miniature planets by being almost spherical and containing some partly differentiated interiors. They are thought to be surviving protoplanets. Nevertheless, a wide majority of asteroids are smaller and irregularly shaped and are thought to be shattered remnants of planetesimals, which are bodies that never grew large enough to become planets within the formation of the solar system (solar nebula) or fragments of bigger bodies. The physical composition of asteroids is in most cases still poorly understood and varies from asteroid to asteroid. They are classified by their emission spectra and are divided generally in three big groups: C-type, M-type, and S-Type, named after their compositions carbon-rich, metallic, and salicaceous, respectively. In the main asteroid belt there are two primary types of asteroids: dark, volatile-rich asteroid consisting of the C-type and P-type, and dense, volatile-poor asteroids consisting of the S-type and M-type asteroids.Etymology: From Greek asteroeidēs ‘starlike’, from astēr ‘star’. Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Astrobiology | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 11). Artistic AI Illustration of Astrobiology. midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition:Astrobiology is an interdisciplinary field of research concerned with the origin, evolution, distribution and future of life in the universe. It encompasses research in astronomy, biology, chemistry, geology, and physics. Detailed Definition:The goal of this study is to understand more about the origin and evolution of life on Earth, planetary system formation, organic compounds in space, and whether or not life exists or might exist elsewhere. Especially the frozen moons of the outer solar system, particularly Europa and Enceladus, as well as Mars, are of significant astrobiological interest. These solar system bodies are the focus of current and future multinational space missions, for example in the DLR. Etymology:
astro - Ancient Greek - ἄστρον (astron) "star" bio – Ancient Greek - βίος (bíos) “life” logy – Ancient Greek -λογία (logía) “branch of study” or “to speak” Sample Sentence(s):
“The research field of astrobiology is gaining more and more importance in the last decades.” “Did you see the documentary on astrobiology last week?” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:
https://www.dlr.de/me/en/desktopdefault.aspx/tabid-2016/ | ||
Astronomy | |||
|---|---|---|---|
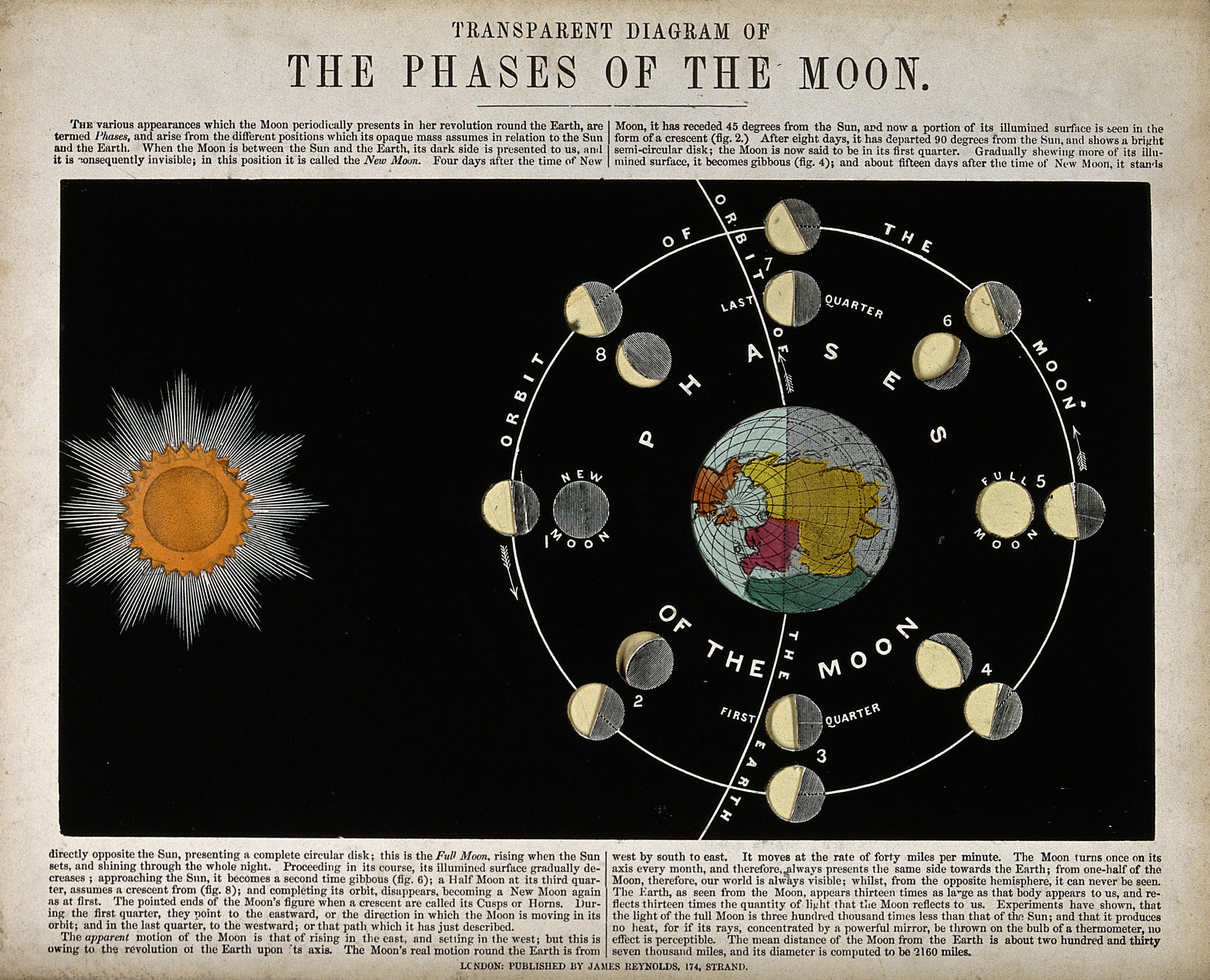 Image/Video/Audio: Diagram: Phases of the Moon Image/Video/Audio Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/8b/Astronomy%3B_a_diagram_of_the_phases_of_the_moon._Engraving._Wellcome_V0024718.jpg Short Definition:
Astronomy is a positive science that includes the discovery, observation, interpretation and recording of all objects and phenomena in space. Before 17th century, astronomy, which worked only to observe and interpret the positions and motion capabilities of observable celestial bodies due to technological inadequacies, after advanced its agenda in all space with the advancement of technology. Detailed Definition:
Astronomy, which aims to investigate first our galaxy and then the whole space in the light of the physics and chemistry sciences that have developed since the 19th century, it also includes to investigate structures and movements of celestial bodies, the formation of galaxies and the chemical analysis of this formation, and the distances and brightness levels of these objects and phenomena. There are 4 main sub-branches of today's contemporary astronomy. These are; Astrophysics: Examines the harmony and application of defined laws of physics in space. Astrometry: It deals with mapping the locations of space objects and their distances from each other. Astrogeology: It deals with the elucidation and understanding of the structure and reserves of materials in space. Astrobiology: Examines possible extraterrestrial life. All these sub-domains contain more of an observable method besides being experimental due to he lack of possibilities we have today in regards with technology.
Etymology:
‘Astron’ (star) – From Ancient Greek ‘Nomos’ (rule, law) – From Ancient Greek
Sample Sentence(s):
''Astronomy has expanded to include astrophysics, the application of physical and chemical knowledge to an understanding of the nature of celestial objects and the physical processes that control their formation, evolution, and emission of radiation.'' (Evans, J. (2023, January 5). Astronomy | Definition, History, Discoveries, & Facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/astronomy) ‘’Astrology can be fun to think about, but it’s different from astronomy. Astrology is not science!’’ (Cloudflare CAPTCHA. (n.d.). https://www.amnh.org/explore/ology/astronomy/what-is-astronomy) Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French:
Astronomie German:
Astronomie Polish:
astronomia Swedish:
Astronomi Turkish: Astronomi
Links to Videos/Articles:
Astronomic. (2015, July 7). Astronomy: Explained | Astronomic [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XinkicMVzLs Cloudflare CAPTCHA. (n.d.). https://www.amnh.org/explore/ology/astronomy/what-is-astronomy E., E. (2022, May 12). 17 branches of astronomy. Earth How. https://earthhow.com/what-is-astronomy/ Evans, J. (2023, January 5). Astronomy | Definition, History, Discoveries, & Facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/astronomy | |||
Atmosphere | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Gatley, R. (2018, January 27). Cruising at 47000 feet over Kazakhstan. Shot with an 8mm fisheye lens.. unsplash. https://unsplash.com/photos/oxgK2f_rxDc Definition:The mass of gas that surrounds an astronomical body, such as a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of this body. Etymology:From Greek ατμός (atmos)'vapor' + σφαιρα (sphaira)'sphere' Translations:
| |||
Aurora | ||
|---|---|---|
 Image/Video/Audio Source: Hemmingsen, J.A. (2016, January 8). aurora borealis in Ersfjordbotn. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/64104971@N02/24226248576 Short Definition: An aurora is a phenomenon caused by the Sun (star). A bust of electrified gas (solar wind) from the star approaches planets. Small particles travel down the magnetic field lines towards both poles. Particles from the star interact with gas particles in the atmosphere, causing the creation of the light in the sky. Depending on the atmosphere composition, the colour of the aurora might be different. Oxygen glows green and red, nitrogen blue and purple. Auroras can appear on every celestial object that has an atmosphere and magnetic field. On Earth, the aurora near the North Pole is called an aurora borealis (northern light) and one near the South Pole is called an aurora australis (southern light). Etymology: “Aurorae are considered to be one of the seven natural wonders of the world.” (source: https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/a/Aurora) Translations: French: German: Polish: Swedish: Spanish: Links to Videos/Articles: | ||
B |
|---|
Barycenter | ||
|---|---|---|
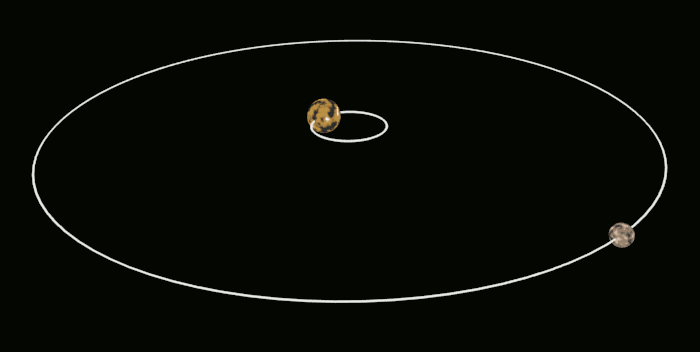 Source: Hoover, S. (2013, July 21). wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=28974343 Short Definition:
Barycenter is a theoretical point that has several meanings according to the field in which it is employed:
Detailed Definition:The barycenter is a theoretical point usually with a mathematical value, which has different meanings depending on the field to which it is applied. From its etymology, Barycenter is usually used to express the center or average of a distribution of objects, values or data.
Originally, the mathematician and physicist Archimède introduced and described the notion of barycenter around 300 B.C.E. He first approached it from a physical perspective by stating: “Every heavy body has a well-defined centre of gravity in which all the weight of the body can be considered concentrated." In astronomy, this notion describes the point around which a celestial body and its/their satellite(s) rotate. The illustration below depicts the barycenter with the red cross in the middle as well as the two bodies of different mass orbiting around it. Etymology:Barycenter comes from ancient Greek. Bary: βάρος (báros, “weight”) + center which comes from the Latin of centrum or even earlier from ancient Greek as kentron, κέντρον (single point). Sample Sentence:"How well we understand the Solar System’s barycenter is critical as we attempt to sense even the smallest tingle to the web.” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://youtu.be/7hMfCCqSdFc
| ||
Big Bang | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 24). Artistic AI Illustration of the Big Bang. midjourney. midjourney.com Definition:
According to the Big Bang Theory, this is the starting point of the known, observable universe, when a rapid expansion of matter took place. According to the standard cosmological model (Big Bang Theory), the Big Bang occurred about 13.8 billion years ago. The model describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature, and offers an explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, like the lighter elements, such as hydrogen and helium. Etymology:From English big “of considerable size or extent” and bang “to (cause something to) make a sudden very loud noise or noises.” The term was introduced in 1948 by the British astronomer Fred Hoyle. In a radio broadcast, Mr Hoyle made disparaging remarks about the hypothesis of the expanding universe and mocked its starting point as the "big bang", without suspecting that he was giving birth to a term that would become part of humankind's common vocabulary. Translations:
| |||
Binary stars | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Sources: Center for High Angular Resolution Astronomy (2008, August 21). Beta Lyrae - CHARA (inverted colors). wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=86270181 Short Definition: A system composed of two stars in which both share a common centre of revolution or one revolves around the other. Detailed Definition: A binary star is a pair of stars in orbit around their common centre of gravity. The term is different from a double star, which refers to any two stars close together in the sky. If components in binary star systems are close enough, they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stellar atmospheres. In some cases, binary systems can exchange mass, evolving in a way which is unattainable for single stars. Etymology: The term binary was first used in the context of space terminology by Sir William Herschel in 1802, in one of his works regarding the observation of double stars. Binary - "dual, twofold, double," mid-15c., from Late Latin binarius Sample Sentence(s): One of the examples of a binary star is Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Étoile binaire German: Doppelstern Polish: Gwiazdy podwójne Swedish: Binär Stjärna Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pIFiCLhJmig https://www.scienceabc.com/nature/universe/what-are-binary-stars.html | |||
Biomining | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 24). AI illustration of microorganisms on ore. midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition:A process involving the extraction of a resource using biological tools. For example, with bacteria or algea. Detailed Definition:Biomining is an environmentally friendly and energy efficient way of extracting useful elements by using microbes to break down rocks to make soil or provide nutrients. Microbes are tiny organisms, such as bacteria and fungi, that have a wide variety of functions. Some microbes have abilities that could be beneficial to humans, such as biomining. Etymology:Bio: From Ancient Greek βίο- (bo-), combining form and stem of βίος (bíos, “life”). Mining: Any activity that extracts or unearths minerals. Sample Sentence:You can use biomining to extract minerals from asteroids using bacteria or fungi." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.sciencedirect.com/referencework/9780080885049/comprehensive-biotechnology | ||
Black Hole | ||
|---|---|---|

Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Black_hole_-_Messier_87_crop_max_res.jpg Short definition: A Black Hole is a region of spacetime where the gravitational field is so strong that nothing, not even light or other electromagnetic waves can escape its event horizon. An event horizon is “the point of no return”, meaning the boundary beyond which nothing can escape. Detailed definition: Since Black Holes can’t be observed directly with telescopes, they’re usually detected by other means, such as observing their gravitational influence on their surroundings. Most Black Holes are formed from large stars that die in a supernova explosion - these Black Holes are usually around 20 times as massive as the Sun. However, there also exist Black Holes that are incredibly large, called Supermassive Black Holes, which can be millions or even billions times as massive as the Sun. Scientists believe that at the centre of almost every big galaxy lies a Supermassive Black Hole, for example Sagittarius A* at the centre of the Milky Way. Etymology: Presumably in December 1967, a student suggested the phrase "black hole" at a lecture by John Wheeler; Wheeler adopted the term for its brevity and "advertising value", and it quickly caught on. (Source: Siegfried, T. (2019, August 9). 50 years later, it’s hard to say who named Black Holes. Science News. https://www.sciencenews.org/blog/context/50-years-later-its-hard-say-who-named-black-holes) Sample sentence(s): Some Black Holes apparently have nonstellar origins. (Source: Lohnes, K. (n.d.). How Do Black Holes Really Work? Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/story/how-do-black-holes-really-work ) Translations: French: Trou noir German: Schwarzes Loch Italian: buco nero Polish: Czarna dziura Swedish: Svart hål Links to Videos/Articles:
The Economist. (2022, July 12). Black holes: why they matter [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/qqMAFtIGaq4 Black Holes | Science Mission Directorate. (n.d.). https://science.nasa.gov/astrophysics/focus-areas/black-holes | ||
Black hole Horizon | |||
|---|---|---|---|
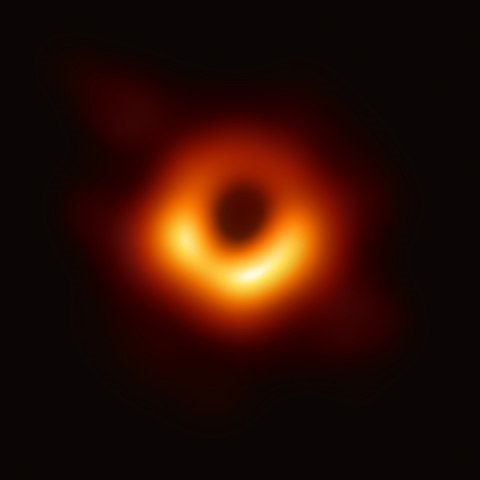 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Black_hole_-_Messier_87_crop_max_res.jpg Short Definition: The horizon of a black hole is called event horizon and is an astrophysical phenomenon, which describes the “point of no return” where matter and even light can not cross back according to our understandings of physics. The event horizon is a boundary in spacetime, where the gravitational pull becomes absolute. Detailed Definition: The astrophysical phenomenon of the event horizon defines the boundary of spacetime, where the ability of mass to deform spacetime is absolute. Near this event horizon time seems to work differently, because of gravitational time dilation, which appears to slow down clocks near the horizon more than those farther away and the clock would take an infinite amount of time to reach the black hole in itself. The huge amounts of gravitational pull causes any light to redshift in a process called gravitational redshift. A clock that is falling into a black hole would change from being visible from an outside perspective, to the light of it red shifting and then finally it would disappear from view and all this in a mere minute. On the contrary an indestructible observer that falls into a black hole would experience time normally and it would fall into the black hole in a finite amount of time.
Etymology: Black hole term was coined in astronomy in 1964 Horizon Greekhorizon (kyklos) àboundary
Sample Sentence(s): From an outside perspective an object falling into the black hole horizon would take an infinite amount of time to reach it.
The black hole horizon is the point of no
return, where matter or light are not able to cross back.
French:
Horizon du trou noir
German:
Schwarzes Loch-Horizont
Polish:
Horyzont czarnej dziury
Swedish:
Horisont för svarta hål
Links to Videos/Articles: | |||
Blazar | |||
|---|---|---|---|
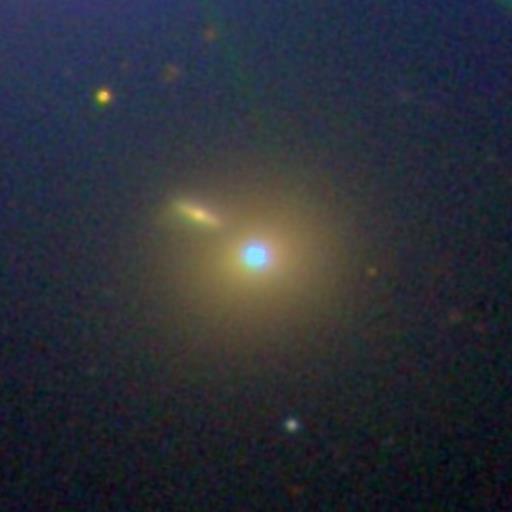 Sloan Digital Sky Survey image of blazar Markarian 421. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Markarian_421#/media/File:SDSS_Mrk_421.jpg Short Definition: A blazar is a type of active galaxy nucleus with a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light, which direction is nearly towards an observer. Due to the jet almost directly shooting towards Earth, a blazar appears much brighter on observations than in case of facing another direction. Blazars are a source of powerful radiation in all electromagnetic spectrum, especially in high-energy gamma rays. Blazars are among the most energetic phenomena in the universe and are an important subject to research. Detailed Definition: Blazars are an extremely bright, starlike object characterized by rapid changes in luminosity and a flat spectrum caused by a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light directed at the observer. Blazars emit electromagnetic radiation over a very wide range of frequencies, but mostly distinguished by amount of radio and gamma rays. Due to blazar's instabilities its properties change over time, specifically the variability and intensity of their observable brightness, which is distinguishing blazars from another class of active galactic nucleus, quasars. Blazars are important topics of research in astronomy and astrophysics. Blazar research includes investigation of the properties of accretion disks and jets, the central supermassive black holes and surrounding host galaxies, and the emission of high-energy photons, cosmic rays, and neutrinos. Etymology: Coined by 1978 by astronomer Edward Spiegel from BL Lac object and quasar. Sample Sentence(s): "Blazars are thought to be active galactic nuclei, with relativistic jets oriented close to the line of sight with the observer." Translations: French: Blazar German: Blazare Polish: Blazar Swedish: Blazar Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/blazar | |||
C |
|---|
Canadian Space Agency | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:Canadian Space Agency is a national space agency of Canada, whose aim is to coordinate spaceflight activities. It is responsible for space exploration (focusing on physical processes in stars), as well as Earth observation and monitoring its resources. Canadian Space Agency was established in 1989 and works on space science and exploration, satellite communications, and it also provides space awareness and promotes the activities of the organisation. International cooperation with other space agencies is also part of the CSA’s mission. The headquarters are located in Longueuil, Canada. Sample Sentence(s):"The Canadian Space Agency is now developing a next generation of satellites." "The Canadian Space Agency is a founding member of the Charter."
Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles: | |||
Chandrasekhar limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|
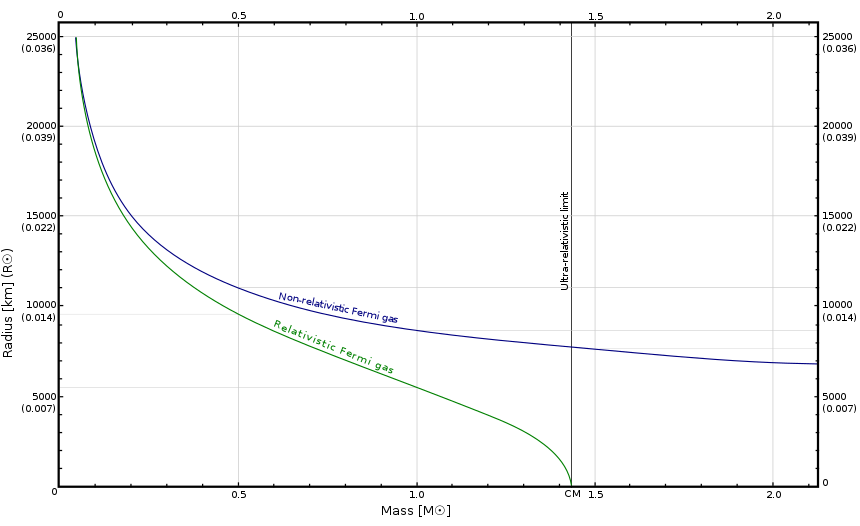 Creator : Unknown Year: (n.d.) Title of image: White Dwarf Mass-Radius Relationship Description of image: Graph illustrating the mass-radius relationship of white dwarf stars Retrieved from URL: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/14/WhiteDwarf_mass-radius_en.svg/860px-WhiteDwarf_mass-radius_en.svg.png Definitions
Sample Sentence(s)
Author : Staff, Space.com Year: (n.d.) Title of the article: Chandrasekhar Limit: Definition, Facts & Equation Title of the Website: Space.com Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023 URL: https://www.space.com/chandrasekhar-limit
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Lang...
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.toppr.com/guides/physics/astronomy/chandrasekhar-limit/ Author(s): Unknown Year: (n.d.) Title of the article: Chandrasekhar Limit Title of the Website: Toppr.com Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, URL: https://www.toppr.com/guides/physics/astronomy/chandrasekhar-limit/
| |||
ClearSpace-1 | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: ESA - ESA commissions world’s first space debris removal Definition:ClearSpace-1 is a mission targeting the removal of the Vega Secondary Payload Adapter (Vega) which is planned for launch in 2025. The mission is brought forward as a service contract with a startup-led commercial consortium, to help establish a new market for in-orbit servicing, as well as debris removal. The ClearSpace-1 ‘chaser’ will be launched into a lower 500-km orbit for commissioning and critical tests before being raised to the target orbit for rendezvous and capture using a quartet of robotic arms under ESA supervision. The combined chaser plus Vespa will then be deorbited to burn up in the atmosphere. Etymology:Sample Sentences(s):Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:ESA - ESA commissions world’s first space debris earth observation for sustainable development (esa.int) removal | ||
Comet | ||
|---|---|---|
Source: Hassell, E. (2020, July 16). Comet NEOWISE over Queen Valley. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/115357548@N08/50120466697 Short Definition: Detailed Definition: comet – Greek - koman (κομᾶν) - to wear the hair long Sample Sentence(s): French: German: Polish: Swedish: Spanish Links to Videos/Articles: | ||
Constellation | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Term/Concept: constellation Image/Video/Audio:  Term/Concept: constellation Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: Sullivan, R. (2017, June 12). Constellations map. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/47430793@N08/35249283965 Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||||||||||
Copernicus Programme | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:A European Earth observation programme aiming at monitoring land, atmosphere and the marine environment, supporting emergency management, ensuring civil security and mitigating the consequences of climate change. The programme was officially established in 2014 by the European Commission and the European Space Agency, serving as a successor of the project GMES (Global Monitoring of Environmental Security), which has existed since 1998. Copernicus Programme utilizes the Sentinel missions for surveillance and observation of land, ocean and atmosphere, as well as a range of contributing missions organized by various countries.Etymology:The programme is named after Nicolaus Copernicus, who was a Renaissance scientist and the author of the heliocentric model of the Universe. Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:
https://www.esa.int/Applications/Observing_the_Earth/Copernicus/Europe_s_Copernicus_programme https://www.copernicus.eu/en/copernicus-services | |||
Cosmic rays | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short definition: Cosmic rays are high energy particles that travel through space at nearly the speed of light. Most cosmic rays are represented by atomic nuclei stripped of their atoms. Detailed definition: Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912. They originate from the Sun, from the Milky Way, and from distant galaxies. Most cosmic rays (89%) are protons of hydrogen, but some of them are nuclei of helium (around 10%) and other, heavier nuclei. Only about 1% of cosmic rays are lone electrons. Once a cosmic ray reaches the Earth’s atmosphere, it collides with other atoms there and bursts them into different particles, namely pions, muons and neutrinos. Etymology: Cosmic comes from Ancient Greek κόσμος (kósmos, “order, proper order of the world”). The term ray likely arose because cosmic rays were initially believed to be electromagnetic radiation. Sample sentence(s): Cosmic rays follow convoluted paths and arrive at the top of the Earth’s atmosphere from all directions. Translations: French: Rayonnement cosmique German: Kosmische Strahlung Italian: Raggi cosmici Polish: Promieniowanie kosmiczne, promienie kosmiczne Swedish: Kosmiska partiklar Links to Videos/Articles:
Cosmic Rays - Introduction. (n.d.). https://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/science/toolbox/cosmic_rays1.html
Vox. (2019, August 30). The mysterious rays shooting at us from space [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/Z9gQLELtbhg | ||
Cosmochemistry | ||
|---|---|---|
Short Definition:The chemistry of cosmic objects or the chemistry of objects in space, such as the chemistry of the Moon, Mars, the Sun, asteroids, quasars, etc. and their effects on each other. Detailed Definition:
Cosmochemistry is the study of the chemical compositions of matter in the universe and the processes that led to those compositions. Cosmochemistry is primarily done by studying the chemical compositions of cosmic objects or the chemistry of objects in space. For example, carbonaceous meteorites were among the earliest formed bodies in the solar system. Their organic carbon is an indicator of chemical processes that occurred before the dawn of life on Earth. By studying carbonaceous meteorites and the origin and fate of their organic compounds, we begin to understand the general process of chemical evolution of organic molecules from interstellar space. Cosmochemistry also advances our knowledge of the physical and chemical processes in the distant past that might have had a significant role in the development of life in the universe.Etymology:Cosmo = kosmos (latin) + Chemistry = Alchemy (Greek), khēmia (Egyptician) Sample Sentence:“The spectral research on sulphur-containing radicals is of great significance in many fields such as atmospheric chemistry, combustion chemistry, cosmochemistry and so on.” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Cosmos | ||
|---|---|---|
Image: Source: Short Definition: The concept of an organized system with pattern and order in the universe. Detailed Definition: The idea of the physical universe as a whole system, one having order and pattern. The understanding of the cosmos has been evolving with new discoveries about the universe. This leads to the definition of cosmology as the history of the study of the cosmos as a whole. Etymology: Cosmos comes from the Latin Kosmos, which means order or world. Sample Sentence(s): The cosmos may now be represented digitally by scientists. Scientists are hunting for hints as to how the universe came into being. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: cosmos German: Kosmos Polish: kosmos Swedish: kosmos Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nationalgeographicla.com/cosmos https://www.researchgate.net/publication/363520256_The_Infinite_Cosmos_Ebo_S | ||
Crater | |||
|---|---|---|---|
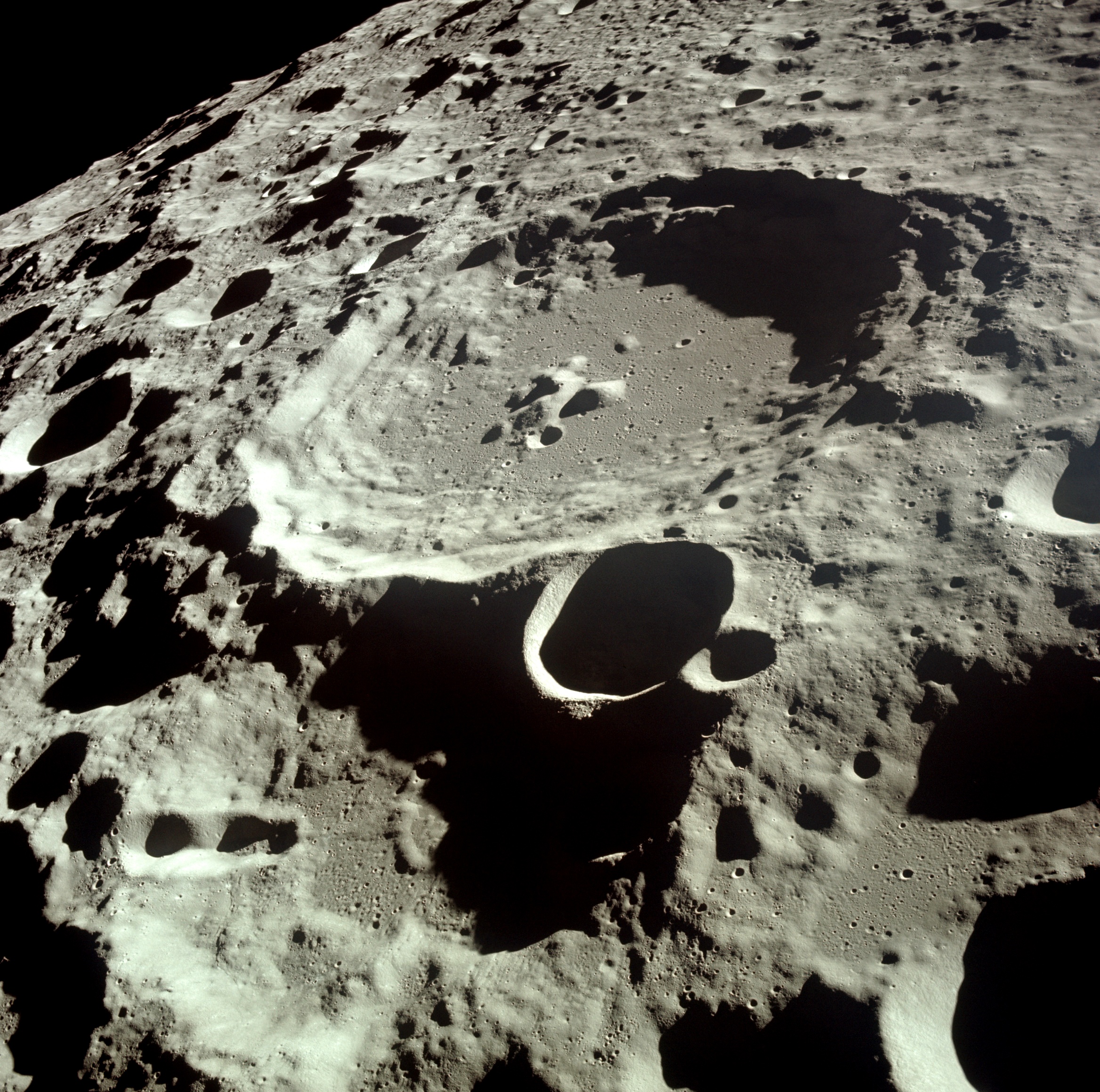 Dedal crater on the Moon Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Moon_Dedal_crater.jpg Short Definition: An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid cosmic body shaped by the hypervelocity collision of a smaller object. Impact craters are the major geographic features on a lot of solid Solar System objects, including the Moon, Mercury, plus the majority of small moons and asteroids. Detailed Definition: An impact crater is a circular distortion on the surface of a celestial body caused by the collision of a meteorite, asteroid or comet. Craters are the most common features of the exterior of rocky and rock-ice bodies in the Solar System. The observed number of craters contains data about the age of the geological structure covered by them. Impact craters should be distinguished from similar structures of other origin, for instance, volcanic craters. Etymology: First coined in 1613, from Latin crātēr (“basin”) and from Ancient Greek κρᾱτήρ (krātḗr, “mixing-bowl, wassail-bowl”). Sample Sentence(s): "Because of the many missions studying Mars since the 1960s, there is good coverage of its surface, which contains large numbers of craters." Translations: French: Cratère German: Krater Polish: krater Swedish: Krater Links to Videos/Articles: | |||
CubeSat | ||
|---|---|---|
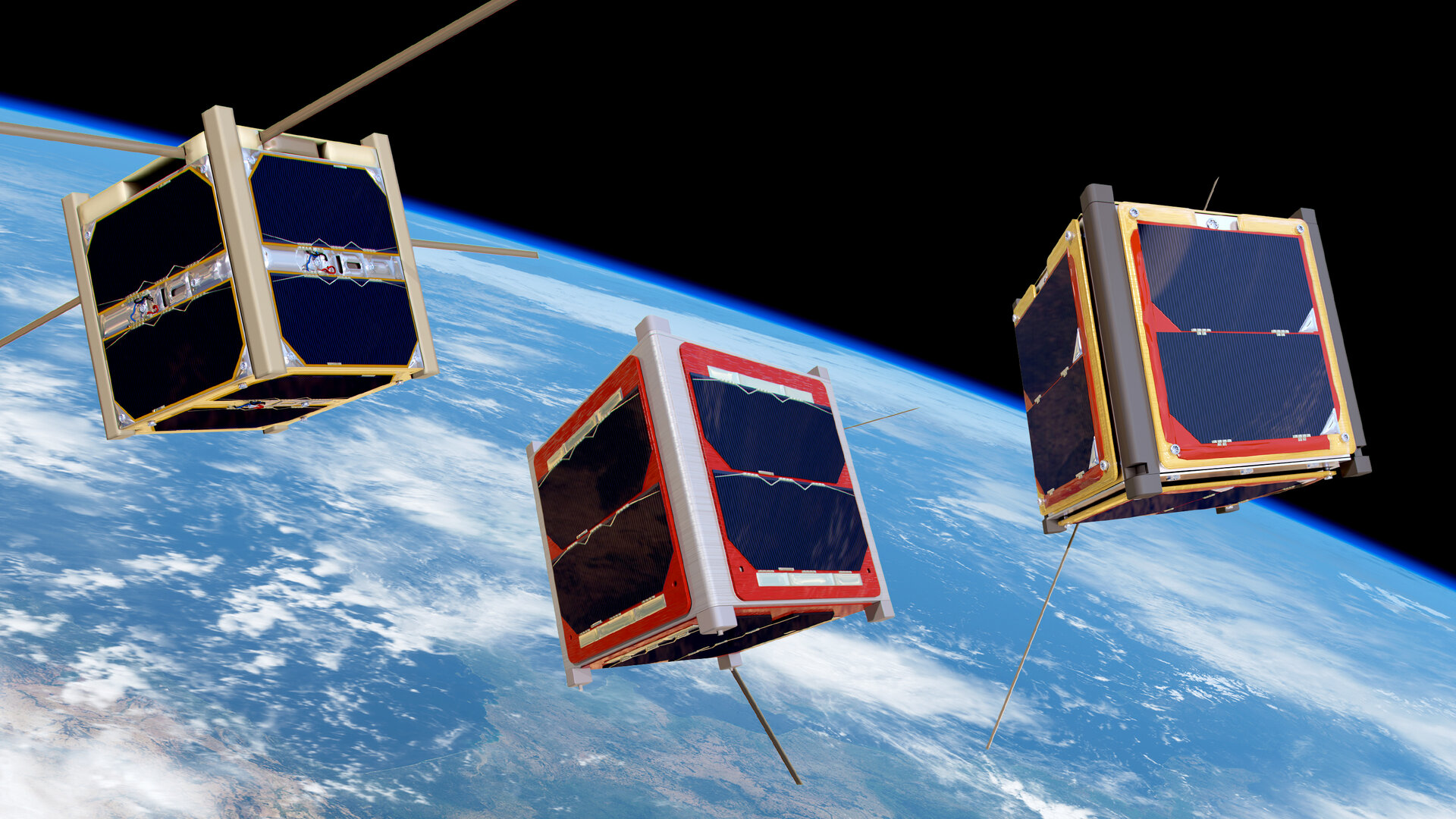 The European Space Agency. (2022, March). CubeSats orbiting Earth. Retrieved from https://www.esa.int/var/esa/storage/images/esa_multimedia/images/2016/04/cubesats_orbiting_earth/15950521-1-eng-GB/CubeSats_orbiting_Earth_pillars.jpg Short definition: CubeSat (Cube Satellite) is a spacecraft that is meant to be a planet's artificial satellite and is designed as a cubic case. The purpose of such case is to carry its payload. Detailed Definition CubeSat is a nanosatellite. It is built as a cube with standard dimension, length of each side is a multiple of 10cm or 1U. They can contain arbitrary payload, usually scientific equipment such as small cameras. Their usual weight is about 1.3 kilograms, what makes them relatively cheap to launch and hence widely accessible. Their accessibility allows smaller players in space industry such as companies and even universities to deploy their space exploration tools into space. Etymology Cube SatelliteCube – from Latin cubusSatellite – from Latin satellitem– an attendant Sample Sentences "These CubeSats are flown as auxiliary payloads on previously planned missions."NASA. (2018, February). CubeSats Overview. Retrieved from https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/cubesats/overview Translations in our Alliance languages: French: CubeSatGerman: CubeSat Italian: CubeSat Polish: CubeSat Swedish: CubeSat Translations in other languages: Russian: КубСат References The European Space Agency. (2022, March). CubeSats. Retrieved from https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Preparing_for_the_Future/Discovery_and_Preparation/CubeSats Cal Poly SLO. (2014, February). CubeSat Design Specification Rev. 13. Retrieved from https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5418c831e4b0fa4ecac1bacd/t/56e9b62337013b6c063a655a/1458157095454/cds_rev13_final2.pdf | ||
D |
|---|
Dark energy | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: https://astronomy.com/news/2020/03/whats-the-difference-between-dark-matter-and-dark-energy Definition:Dark energy (not to be mistaken with dark matter) makes up approximately 68% of the universe, and it is distributed evenly not only in space, but also in time (therefore it has a global effect on the universe as a whole). This is a repulsive force, that accelerates the expansion of the universe. The rate of expansion and its acceleration can be measured by observations based on the Hubble law. The existence of dark energy is proven and its role in the universe can be described thanks to Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity. Example Sentence(s):"Dark energy is generally accepted as contributing to the increased acceleration of the expanding universe, so understanding this relationship will help to refine how physicists and astrophysicists understand it." "And there are still no final answers to the questions surrounding dark energy." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://home.cern/science/physics/dark-matterhttps://astronomy.com/news/2020/03/whats-the-difference-between-dark-matter-and-dark-energy | |||
Dark matter | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: https://astronomy.com/news/2020/03/whats-the-difference-between-dark-matter-and-dark-energy Definition:Dark matter (not to be mistaken with dark energy) makes up about 27% of the universe. Unlike normal matter, dark matter does not interact with electromagnetic forces. This means it does not absorb, reflect or emit light, therefore it can't be seen, but researchers can detect it and map it by measuring gravitational lensing. Because of these properties, it works like an attractive force, holding the universe together. In the 1930s, astronomer Fritz Zwicky studied images of around 1,000 galaxies that make up the Coma Cluster and speculated that some kind of matter must be keeping them together. Astronomers Vera Rubin and Kent Ford found a similar phenomenon when they studied the rotation rates of individual galaxies, with even more evidence of the features mentioned above. The existence of dark matter is so widely accepted that it’s part of the "standard model of cosmology", although there is no solid evidence that it is real. There are many theories suggesting that physics beyond the Standard Model, such as supersymmetry and extra dimensions, exist. If other parallel universes exist, then physical features of each universe would be different, therefore the amount of dark matter in each universe would be different. Dark matter helps scientists gain a better understanding of the composition of our universe and how galaxies are held together. Sample Sentence(s):"You can see the galaxy clusters that Professor Zwicky studied to discover Dark Matter." "Dr. Shepherd's work enhances our profile in the area of Dark Matter exploration significantly." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://home.cern/science/physics/dark-matterhttps://astronomy.com/news/2020/03/whats-the-difference-between-dark-matter-and-dark-energy | |||
Dark Nebula | ||
|---|---|---|
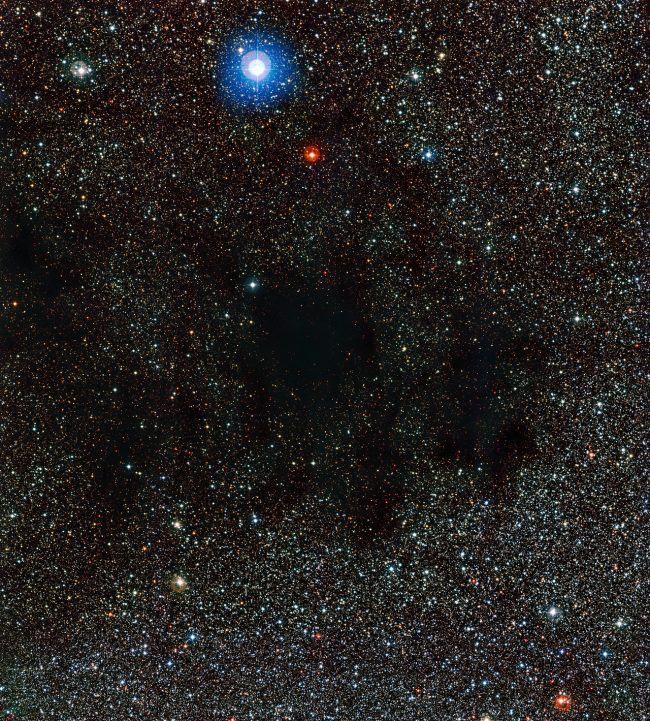 Short DefinitionA dark nebula, also known as an absorption nebula, is a form of interstellar cloud. It is so thick that it obscures visible wavelengths of light from things behind it, such as reflection nebulae or background stars and emission. Interstellar dust grains in molecular clouds' coldest, densest portions produce light extinction. Detailed DefinitionSometimes the light from the background stars or reflection nebulas can be obscured by an interstellar cloud composed of gas, plasma and galaxy dust, creating irregular shapes without defined boundaries. This results in the formation of a black nebula or absorption nebula. The naked eye has seen large dark nebulas, often seen as shadows falling from the sky. The development of stars and meteors is crucial in the black nebula. Because of the difference in density, it is impossible to form stars during condensation. Enormous molecular clouds often surround the black nebulas, while the small ones can be called Bok globulos. Half of the world's famous Bang globules have been discovered to contain new stars. Etymologymid-15c., nebule "a cloud, mist," from Latin nebula, plural nebulae, "mist, vapor, fog, smoke, exhalation," figuratively "darkness, obscurity," from PIE root *nebh- "cloud." Sample Sentence(s) 1. Later, when I looked to my left, there was a black nebula. It had initially been an implacable cloud. 2. In general, the detections best suited the concept of a collision between a star and an interstellar nebula. 3. We've seen enough evidence to believe our solar system began with a cold black nebula spinning in slow motion. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages Swedish: mörk nebulosa 1. Kurzgesagt - In a Nutwchell. 2017. The Last Light Before Eternal Darkness – White Dwarfs & Black Dwarfs. Retrieved on June 6, 2023 from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qsN1LglrX9s&ab_channel=Kurzgesagt%E2%80%93InaNutshell 2. Encyclopedia Britannica Contributors. February 23. 2023. Nebula. Retrieved June 15, 2023 from https://www.britannica.com/science/nebula | ||
DART Mission | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: https://dart.jhuapl.edu/Gallery/media/graphics/lg/DART-infographic_v4.jpg Definition:A mission planned by NASA to test a method of planetary defense by redirecting an asteroid, which could hypothetically pose a threat to Earth, by means of the DART spacecraft deliberately crashing itself into this asteroid. The DART spacecraft was built by Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory and was launched on November 23, 2021 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Its target is the binary near-Earth asteroid Didymos (780 m across) and its secondary body, or “moonlet”, Dimorphos (163 m across). This binary asteroid is situated roughly 11 million kilometers from the Earth and does not pose a threat to the planet, but corresponds to the size of a potentially hazardous celestial body (140 m or more in diameter). As a result of the planned collision at the end of September 2022, the orbit of Dimorphos will change, this change will be observed and measured using telescopes on Earth and the data will be used to predict effectiveness of kinetic impact for the purpose of asteroid deflection as a planetary defense method. (https://blogs.nasa.gov/dart/2021/11/24/nasa-spacex-launch-dart-first-planetary-defense-test-mission/) Etymology:DART stands for “Double Asteroid Redirection Test” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hbL07cZUEMU More detailed information on the project:https://www.nasa.gov/planetarydefense/dart https://dart.jhuapl.edu/ | |||
Deimos | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:The smaller of the two natural satellites/moons of Mars situated farthest from the planet. Etymology:Named after Deimos, the Ancient Greek god of terror, twin brother of Phobos, son of Ares (the equivalent of the Ancient Roman god of war Mars). Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles: | |||
Dusty Vacuum Chamber (Dirty Vacuum Chamber) | ||
|---|---|---|
Source: https://ttu-ir.tdl.org/bitstream/handle/2346/73031/ICES_2017_235.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y Short Definition:An enclosure that constitutes a closed environment developed for the purpose of simulating lunar conditions and allow for the testing of material behaviour in such a space.
Detailed Definition:Sample Sentence(s):Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles: | ||
Dwarf Galaxy | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Picture: Fornax Dwarf Galaxy Image/Video/Audio Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Fornax_dwarf_galaxy.jpg
Short Definition:
A dwarf galaxy is one that contains fewer stars than larger galaxies. A dwarf galaxy is a galaxy made up of material and dark matter ejected from larger galaxies by the force of gravity. Although a dwarf galaxy is defined by astronomers by the number of stars it contains, and hence its size, it is also defined as dwarf by its shape, content, and even appearance.
Detailed Definition:
Dwarf galaxies, formed from fragments of larger galaxies, are the most abundant type of galaxy in the universe. Dwarf galaxies are galaxies that break apart due to their relatively small size to their neighbors, causing stellar streams and galaxy mergers. However dynamic these relationships with neighboring galaxies may be, they are difficult to detect by astronomers due to their low light, mass and small size. The astronomical importance of these dwarf galaxies actually comes from their tendency to form from other large galaxies and merge again with larger galaxies. Their difference from the usual galaxy shape is that they have low metallicity and gas in abundance. This situation is used by astronomers as evidence to interpret the motion and evolution of galaxies. Dwarf galaxies are basically divided into three groups: Dwarf elliptical galaxies, dwarf spheroidal galaxies, and dwarf irregular galaxies.
Etymology:
From Old English ‘Dweorg’ + From Latin ‘Galaxias’
Sample Sentence(s):
‘’The most powerful space telescope currently operating has zoomed in on a lonely dwarf galaxy in our galactic neighborhood, imaging it in stunning detail.’’ (Lea, R. (2022, November 11). James Webb Space Telescope peers into lonely dwarf galaxy with sparkling results. Space.com. https://www.space.com/james-webb-space-telescope-wlm-dwarf-galaxy-image) ‘’This Living Collection starts with an introductory Comment and continues with a series of articles on the science of dwarf galaxies, their properties and their theoretical modelling and simulations.’’ (It’s time for some plane speaking. (2021, December 13). Nature. https://www.nature.com/collections/bgegjajcec error=cookies_not_supported&code=03e197b7-7ba4-4db9-a0c7-ee3cf2730af7)
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French: Galaxie Naine German: Zwerggalaxie Polish: Galaktyka karłowata Swedish: DvärggalaxTurkish: Cüce Gökada
Links to Videos/Articles:
https://esahubble.org/wordbank/dwarf-galaxy/ https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/D/dwarf+galaxy https://www.sciencealert.com/webb-is-giving-us-a-stunning-new-look-into-this-lonely-dwarf-galaxy https://esawebb.org/images/WLMb/ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hcDrvX6vy0k&ab_channel=EuropeanSouthernObservatory%28ESO%29 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gez1RSHQvDE&ab_channel=Engadget | |||
E |
|---|
Eclipse | ||
|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio Source: Short Definition: Detailed Definition: Latin from Greek ekleipsis, from ekleipein‘fail to appear, be eclipsed’ Sample Sentence(s): French: Une éclipse German: Zaćmienie Swedish: En eklips Spanish: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eclipse | ||
Einstein ring | |||
|---|---|---|---|
DefinitionA ring-shaped distortion of light from a galaxy caused by gravitational lensing, while this galaxy passes behind another massive object. It is sometimes also referred to as the Chwolson ring, named after a Soviet scientist Orest Chwolson, who mentioned this phenomenon in his article (in English, his surname is usually transcribed as Khvolson, however, German transliteration Chwolson is used instead, since his article was first published in a German academic journal). EtymologyThe phenomenon is named after Albert Einstein, who predicted it in his theory of general relativity. Translation:
Links to Videos/Articles:Gallery of Einstein rings: https://hubblesite.org/contents/media/images/2005/32/1788-Image.html
| |||
Elementary differentiation (Planetary differentiation) | ||
|---|---|---|
Source: By James St. John - Brachinite (NWA 3151 Meteorite) 3, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=34763072 Short Definition:A process that a planetary body goes through during its formation to acquire its physio-chemical composition. Elementary differentiation can be witnessed on planets, and natural satellites such as the moon. Detailed Definition:Etymology:1. Elementary (Adjective), originating from Latin elementarius, which means “belonging to the constituents of all things”. 2. Differentiation (Verb), originating from Medieval Latin, differentiatus, which means “to distinguish”. Sample Sentence(s):“These high precision measurements (δ56Fe ≈ ± 0.04‰, 2 S.D.) place tight constraints on Fe isotope fractionation during planetary differentiation.” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:
[Gardner-Vandy et Al. (2012)] The Tafassasset primitive achondrite: Insights into initial stages of planetary differentiation Differentiation Planetary, Frank Sohl and Doris Breuer, Encyclopedia of Astrobiology.
| ||
Ephemeris | ||
|---|---|---|
Source: Short definition: An ephemeris is a table or data file that gives the positions of celestial objects at specific times. Detailed Definition: An ephemeris is a detailed table or data file that provides the positions of celestial objects in the sky at specific times. Ephemerides are used in astronomy to predict the future positions of these objects and to understand their orbits and movements. They can be calculated for any point in time and are usually given for a series of times at regular intervals, such as every day or every hour. Initially ephemerides were written, then printed, nowadays, they are digital. Ephemerides of the Solar System play a crucial role in navigating spacecraft. Etymology: ephemeris (Latin) - diary; ephemeris (Greek) - diary, journal Sample Sentence(s): "I consulted an ephemeris to find out when the next solar eclipse would occur." "The astronomer used an ephemeris to predict when the comet would be visible in the sky." "Ephemerides are widely used in astrology." Translations: French: Éphéméride German: Ephemeriden Polish: Efemeryda Swedish: Efemerid Links to videos/articles: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ephemeris https://www.astro.com/swisseph/swepha_e.htm https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/horizons/ | ||
Equation of time | ||
|---|---|---|
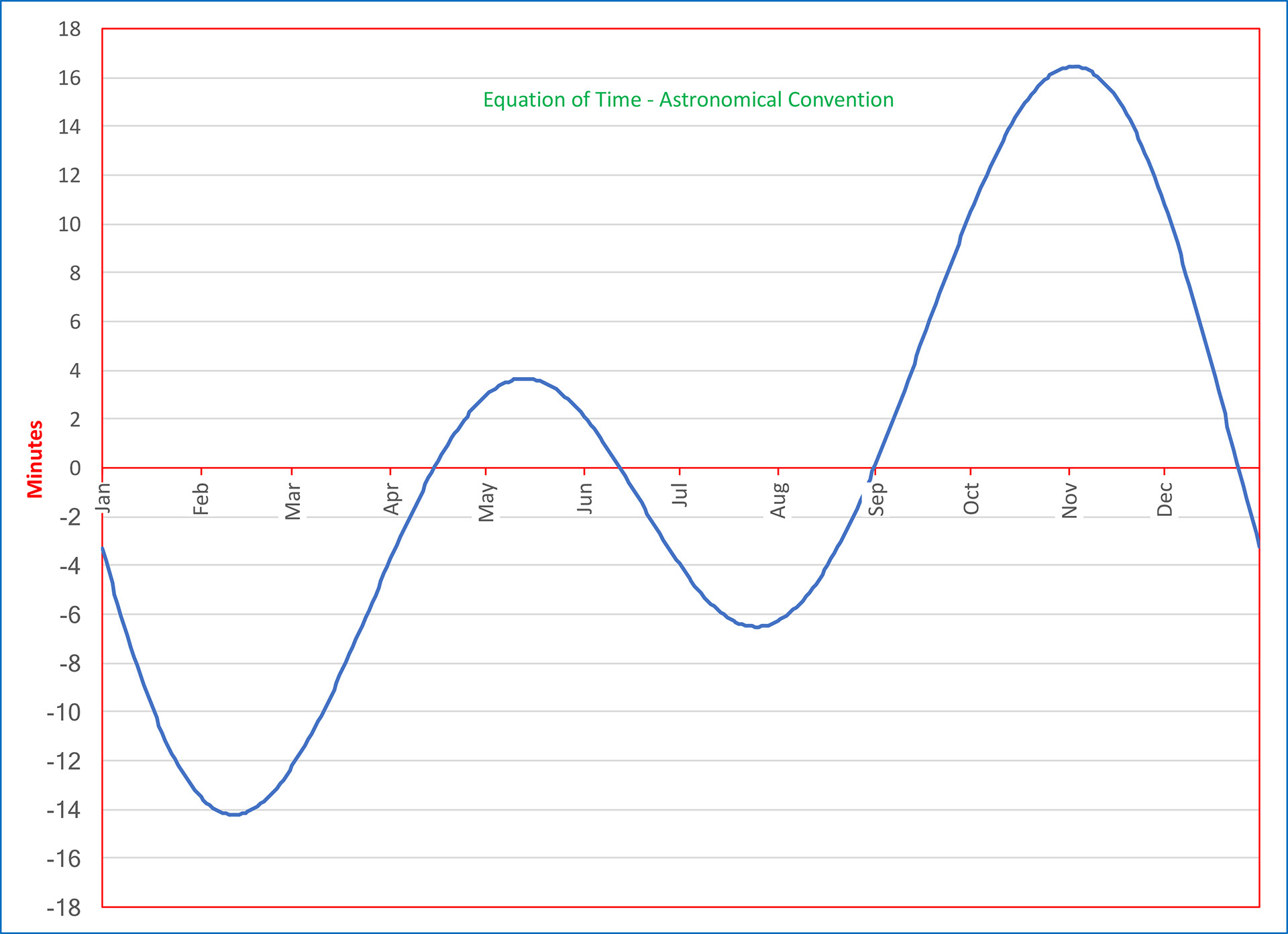 Source: https://pro2-bar-s3-cdn-cf3.myportfolio.com/cf59f354b34391ef9ddbec41a1409bef/ece2a825-e54c-4ea4-a57c-bc1f3e901591_rw_1920.jpg?h=e8d9d5ab3208bd43c08d7702b9ec2c74 Short Definition: The equation of time is a result of the difference between the daytime on Earth and the position of the sun. Detailed Definition: The equation of time exists because the orbit of the Earth around the sun is elliptical (where the orbit is not centered around the sun) and not circular which results in a difference in speed around the elliptical orbit as a difference in the length of the Earth days. The equation is the following: EOT =GHA- GMHA where EOT is the equation of time, GHA is the Greenwich Hour Angle of the apparent sun and GMHA is the Universal Time-Off. As a result, the 21./22. December is the shortest day of a year, the real local time (WOZ) results in uneven long hours and the middle time (MOZ) results in a sun orbit, which is unsymmetrical to the time. Etymology: Equation - latin aequationem (" an equal distribution, a sharing in common") Time - Proto-Germanic Timon-/timi ("Time, proper time") Sample Sentence(s): " The equation of time is the reason a Analemma( a diagramm which shows the position of the sun from one point at a specific time over a year) can be seen" Translation: French: équation du temps German: Zeitgleichung Polish:
Równanie czasu
Swedish:
tidsekvation
Links to Videos/Articles:
https://youtu.be/Mx9AJJSKIL4
https://astro.dur.ac.uk/~ams/users/equation_of_time.html
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hn0js5EzmEc
| ||
Euclid mission | ||
|---|---|---|
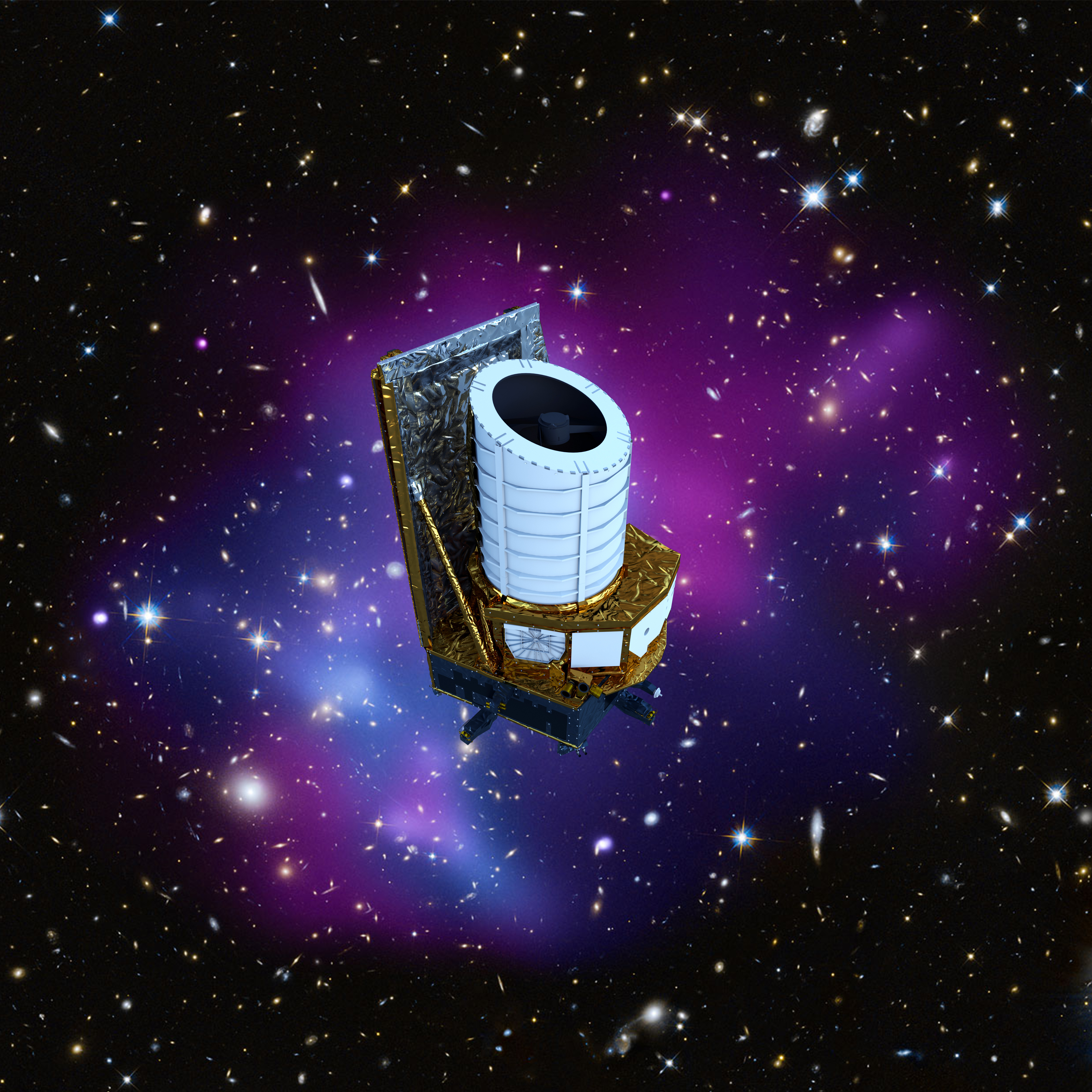 Image source: https://www.esa.int/var/esa/storage/images/esa_multimedia/images/2019/09/euclid_spacecraft/19709645-1-eng-GB/Euclid_spacecraft.jpg Short Definition: The euclid mission is project, being prepared by ESA to investigate dark matter as well as dark energy. At this moment, it is planned to launch the mission in the year 2023 (no specific date is set yet). The planned time the mission will take is set for six years and can be extended, but is limited by the amount of cold gas propulsion. Detailed definition: ESA has started the euclid mission is a project to try to investigate dark matter as well as dark energy. The spacecraft consists of a camera in the visible wavelength and a camera /spectrometer which works in the near-infrared area. It will launch from the Europe'sSpaceport in Kourou, which is located in French Guiana, and will move in an orbit which is halo shaped around the Sun-Earth Lagrange point. Another aspect which will be inspected by the mission is the reason why the expansion of the universe in accelerating and how the evolution of the universe took place, to gain more information about fundamental physics and cosmology. Etymology: Euclid - Greek euclid ("renowned, glorious") mission -Latin missionem ("act of sending a dispatching; a release, a setting at liberty") Sample Sentence: The Euclid mission is expected to bring new knowledge about the history of the universe and dark matter. Translations: French: Mission Euclide German:Euklid-Mission Polish: Misja Euclid Swedish: UppdragEuclid Links to Articles: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/missions/euclid https://sci.esa.int/web/euclid https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/euclid/main/index.html | ||
European Space Agency | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: https://about.gitlab.com/customers/european-space-agency/ Definition:European Space Agency is an intergovernmental organisation, whose mission is to develop space capabilities through exploration for the benefit of citizens of Europe and the whole world. European Space Agency was established in 1975 and is dedicated to the peaceful exploration of space. It comprises of 22 Member States, who work together to find out more about the Earth and space, but it also cooperates closely with other organisations outside of Europe, for example with NASA. The aim is to develop research, coordinate space programmes and to promote mutual agreements between the members. It is funded by membership donations calculated based on each country’s gross national product. Sample Sentence(s):"The European Space Agency is using a launching facility situated in French Guiana in Latin America." "The Eurobot Ground Prototype is a mobile reconnaissance robot from the European Space Agency (ESA)." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.esa.int/ | |||
EVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
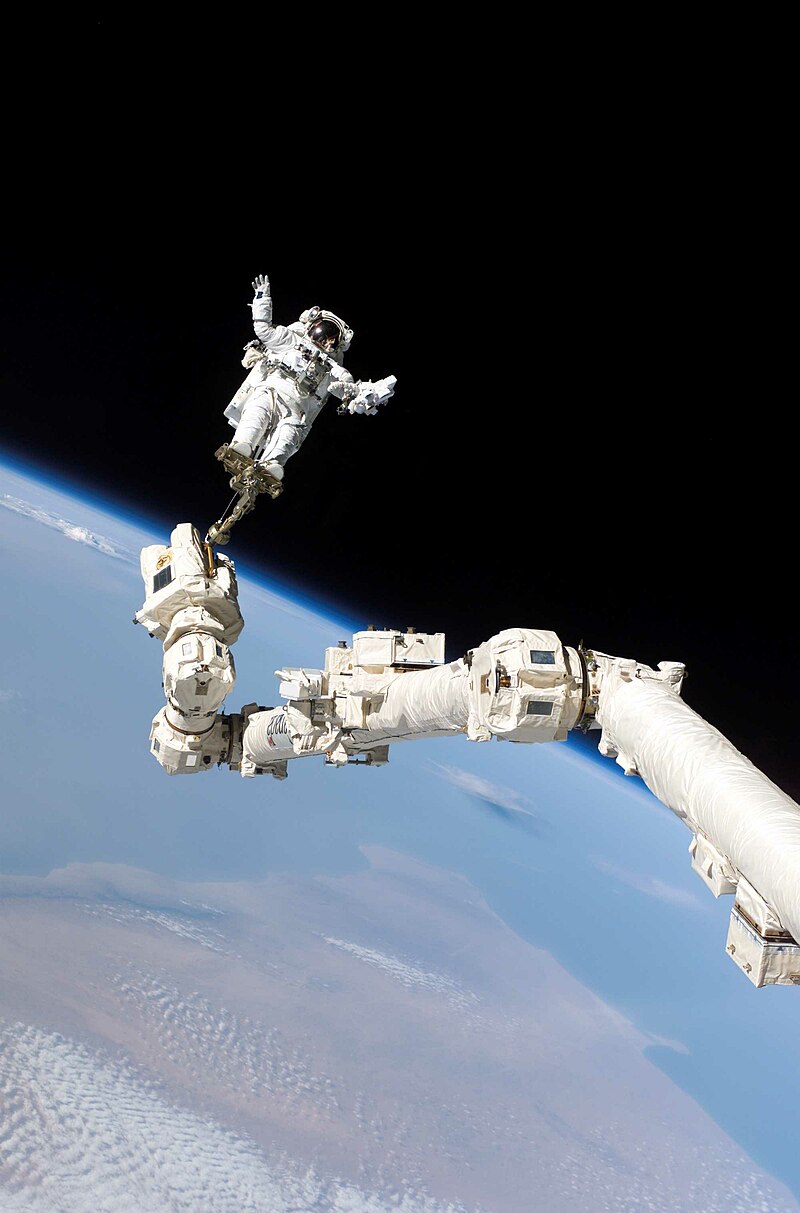 Astronaut Steve Robinson performing an EVA during STS-114 mission. Source: Wikipedia/NASA Short Definition: EVA is an act of performing different activities outside your spaceship while in orbit. This could include repairing, attaching or other experiments. Detailed Definition: Performing an EVA can refer to activities such as spacewalks, where astronauts leave the spacecraft to work in the vacuum of space, as well as other tasks such as inspections or repairs on the exterior of the spacecraft. EVAs are a common part of space exploration and are conducted by astronauts in a variety of different settings, including the International Space Station and during lunar, or in the future, planetary missions. Etymology: EVA stands for Extravehicular Activity Sample Sentence(s): Astronauts on the ISS are preparing to perform an EVA. Yesterday's EVA was completed successfully. Translations: French: Sortie extravéhiculaire German: Außenbordeinsatz Polish: Spacer kosmiczny Swedish: Rymdpromenad Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nasa.gov/content/extravehicular-activities/ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extravehicular_activity | |||
Event Horizon | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source(s): Short Definition: The event horizon of a black hole is a threshold around the black hole where the escape velocity surpasses the speed of light. It is also referred to as a boundary beyond which events cannot affect an observer. Detailed Definition: The term event horizon is used to describe the phenomena of a very strong gravitational pull in the vicinity of a massive and compact object, which is able to prevent even light from escaping. The escape velocity is a threshold value for which the event horizon occurs. It is the velocity needed for an object to overcome the forces acting due to the presence of an enormous mass. If it is greater than the speed of light, it is impossible to witness any event taking place past the event horizon. Etymology: The term was first used by Wolfgang Rindler in the 1950s. Sample Sentence(s): "The event horizon is the ultimate prison wall - one can get in but never get out." - Avi Loeb, chair of astronomy at Harvard University. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Horizon des événements German: der Ereignishorizont Polish: Horyzont zdarzeń Swedish: Händelsehorisont Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.space.com/black-holes-event-horizon-explained.html https://astronomy.com/news/2019/04/the-event-horizon-telescope-may-soon-release-first-ever-black-hole-image | |||
ExoMars Programme | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 DefinitionA programme created in cooperation between ESA and Roscosmos, which is trying to find signs of biological processes on Mars indicating whether life has ever existed on that planet. The programme includes two missions:
The Trace Gas Orbiter’s task is to look for trace atmospheric gases, including methane, which would indicate the presence of biological processes, whereas the Rosalind Franklin rover is supposed to look for evidence of life on the surface and underground. Etymology:“Exo” in ExoMars refers to “exobiology”, a branch of sciences investigating life beyond Earth. A rover involved in this mission is named after Rosalind Franklin, who was an English chemist known in particular for her contribution to DNA research. The platform Kazachok is named after a Russian folk dance. Sources:https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Exploration/ExoMars More about the mission:https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Exploration/ExoMars/ExoMars_Factsheet | |||
Expansion of the universe | |||
|---|---|---|---|
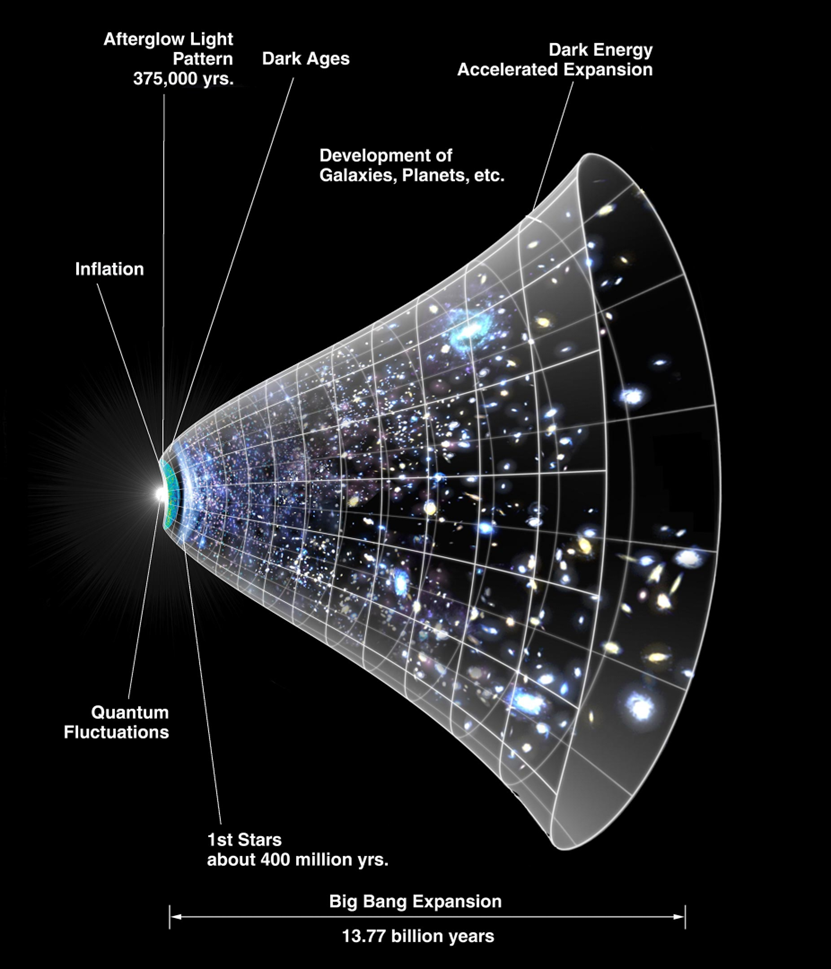 Image/Video/Audio Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Expansion_of_the_universe#/media/File:CMB_Timeline300_no_WMAP.jpg
Short Definition: The expansion of the universe is a phenomenon, which describes the
inherent property of the universe, where two galaxies that are gravitationally unbound
tend to increase the distance to each other and the rate of expansion is even accelerating.
Far away parts of the observable universe will not be observable in the near
future, because the velocity of expansion is higher than light speed from an
outside perspective.
Detailed Definition: The expansion of the universe is a phenomenon, which explains an inherent property of the universe to expand. The fact that the universe seems to expand, was first doubted because of the gravitational force and the fact that releases of energy like the big bang should normally lose power and should slow over time, but the opposite was observed. The elusive culprit was found quite fast. Dark matter is to be responsible for this phenomenon, but since we know even less about dark matter than about the expansion of the universe, details of how and why it expands are still unknown. This expansion occurs at
every location of the universe and only gravitationally bound galaxies will be
able to observe each other, because unbound galaxies will escape our observable
universe at some point. The expansion can in some way be compared to an elastic
rubber band, where the distances also increase when you stretch it, but not
literally and not on a human scale. It is more that at a scale so far zoomed
out, that the universe looks like a cosmic fluid and at this scale it is apparent
that the density is decreasing over time. There are three viable methods to
measure this expansion. One is based on redshifts, while another on the cosmic
distance ladder. Those measurements gave non-matching results, and so 2018 information
from gravitational waves made it possible to determine the rate of expansion
even more precisely.
Etymology:
Expansion à from Latin expandere à spread out Universeà from Old French univers à from Latin universumSample Sentence(s):
In a thought experiment of an ascending civilization in a faraway galaxy in the far future, they would only be able to observe their neighbouring galaxies and will think that this is all there is to the universe and all this due to an expansion of the universe. The rate of expansion of the universe is thought to be accelerating. French: Expansion de l'universGerman: Ausdehnung des Universums
Polish: Ekspansja Wszechświata Swedish: Utvidgning av universum
Links to Videos/Articles:
Expansion of the universe - Wikipedia | |||
F |
|---|
Falcon 9 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source : SpaceX (2016, January 16). Falcon 9 vertical at Vandenberg Air Force Base. wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=64851825 Definition:Falcon 9 is the world's first orbital class reusable rocket, created and manufactured by SpaceX. It is a reusable, two-stage rocket capable of transporting both people and payloads into Earth's orbit and beyond. Reusability allows to reuse the most expensive parts of the rocket, which diminishes the cost of space access. The standard parameters of the rocket are: Height - 70 m / 229.6 ft Diameter - 3.7 m / 12 ft Mass - 549,054 kg / 1,207,920 lb The engine used in production of Falcon 9 is the Merlin, which uses grade kerosene (RP-1) and liquid oxygen as rocket propellants in a gas-generator power cycle. The Merlin engine was originally designed for recovery and reuse. Falcon 9 has already been used in numerous missions or tests (Crew-1 Mission, Crew-2 Mission, Crew-3 Mission, DART Mission) and is planned to be launched in the next ones (for example Polaris Dawn in the last quarter of 2022). Sample Sentence(s):"This rocket is the Falcon 9 that successfully reached orbit after 9 minutes and 38 seconds on its maiden test flight." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.spacex.com/updates/ | |||
Fluid shift in the human body | ||
|---|---|---|
 Image Source: S, M. (2023, June 01). Illustration of fluid distribution. self. self-made The fluid shift in the body is an adaption to the reduced gravitation force in space. This results in a shift of the body fluids from the lower body to the upper body. Detailed Definition: When a human body is placed on the earth surface, it has a hydrostatic (gravitational) blood pressure gradient and every body region has a different arterial pressure. In the reduced gravity of space, the hydrostatic pressure in the arteries and veins is altered to a homogeneous arterial pressure in all regions (which is the original arterial pressure of the hearth), which results in the shifted fluid distribution through the body. The human body reduces the volume of the total fluid and after the space resident, the fluid is shifted because of the returned gravity force. This phenomenon can cause several issues like cardiac arrhytmia, muscular athropy and visual problems (because the globe is flattened, the blood flow is changed slightly and the diamteter of the optical nerve can increase). Etymology: fluid - Latin fluidus ("fluid, flowing, moist") shift - Proto-Germanic skiftan (" to divide, change, seperate") Sample sentence(s): A medical
effect of a space flight may be a fluid shift. Nasa is studying
the effect of the fluid shift and how it affects changes in vision. Translation: French: déplacement du fluide German: Flüssigkeitsverschiebung Polish: Przemieszczenie płynów w ludzkim organizmie Swedish: vätskeförskjutning Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nasa.gov/content/fluid-shifts-study-advances-journey-to-mars https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/20150001888 | ||
Frequency | ||
|---|---|---|
Image Source: Short Definition: A frequency (f) is a physical variable which measures how often a event is repeated in a defined period of time. The SI-unit is Hertz (hz) or s^-1. A common scenario in which the frequency is used, is in a wave, in which it can be calculated by measuring the Period T (the time it takes to complete one cycle) and using the equation: f = 1/T Detailed Definition: Another equation by which the frequency can be calculated, is the following with \( \lambda = \) wavelength and v= phase velocity (if the wave is detected in a vacuum, the following applies: v=c) \( f = v/ \lambda \). There exist two special types of frequency, the angular frequency and the spatial frequency, which will be explained in the following: The angular frequency (ω) describes how fast a vibration / wave is occurring by measuring the overstepped phase angle of the vibration / wave in a defined time period. This frequency can be calculated in the already introduced frequency f by using the following equation: \( \omega = 2 \pi f = 2 \pi /T \). The spatial frequency (ξ) measures how often sinusoidal components (components of a sinusoidal wave) of a structure repeat per unit of distance, which can be calculated by using the following equation: \( \xi = 1/ \lambda = f/v \). Etymology: frequency - Latin frequentia (" an assembling in great numbers, a crowding; crowd, multitude, thong") Sample Sentence(s): The frequency can be identified by calculating the inverse of the period T. The frequency is a variable which can characterize a wave. Translations: French: Fréquence German: Frequenz Polish: Częstotliwość Swedish: Frekvens Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.britannica.com/science/frequency-physics https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6WIDhLeryWM https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/Lesson-2/Frequency-and-Period-of-a-Wave | ||
G |
|---|
Galactic disk | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short Definition: A galactic disc is a component of disc galaxies. An example are spiral galaxies and the Milky Way. The set-up of Galactic discs are a stellar component (these encompass the majority of the galaxy's stars) as well as a gaseous component (simply largely composed of cold gas and dust). Detailed Definition: The stellar disc of our Galaxy is divided into two components because the vertical density profile determined from star counts can be explained by a superposition of two exponentials, but not by a single exponential. (Gilmore & Reid, 1983). Further study found a thick-disc component with high-velocity dispersion, significant enrichment, and ancient age. Many writers believe that the thick disc was a relic of a turbulent period in Galactic history when the thick disc developed from accreted satellites or a thin disc heated the substance at high temperatures by one or more merger events (for a discussion, see Reddy Lambert, and Allende Prieto 2006). This structure was first observed in external edge-on galaxies and later proposed as a distinct part of the Milky Way in a 1983 article by Gilmore and Reid. It is separate from both the thin disk and the halo. The thick disk is a structural component of approximately two-thirds of all disk galaxies, including the Milky Way. It was initially detected in external edge-on galaxies. Soon later, in the 1983 article by Gilmore and Reid, it was proposed as a galactic structure in the Milky Way, distinct from the thin disk and the halo.Etymology The term galaxy was derived from the Greek word galaxas (kklos) (o), which means "milky (circle)," and was called by its appearance in the sky as a milky ring of light. Sample Sentence(s): 1. It would take two billion years for the changes caused by a Galactic Battle to be realized. 2. It glows on the galactic scale. 3. The galactic disk is the Milky Way's disk component. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages Polish: dysk galaktyczny French: disque galactique German: galaktische Scheibe Italian: disco galattico Swedish: galaktisk skiva | ||
Galaxy | ||
|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio Source: Short Definition: Detailed Definition: Etymology: Sample Sentence(s): Translations: German: Polish: Swedish: Spanish: Links to Videos/Articles: | ||
Galaxy cluster | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short Definition
Sample Sentence(s) Galaxy clusters can consist of thousands of galaxies. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: amas de galaxies German: Galaxienhaufen Italian: mmasso di galassie Polish: gromada galaktyk Swedish: galaxhop Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Galaxy Evolution | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Picture: Model of Evolution of Galaxy Image/Video/Audio Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/a3/Evolution_in_slow_motion.jpg Short Definition: Galaxy evolution or evolution of galaxy is a term that we have used for understanding the formation process and changes of galaxies since the beginning that made up the known universe. The term galaxy evolution also represents the models we form about the universe filled by the observed photons and the expansion since the big bang. At this point, the sizes, shapes and contents of all galaxies give us an idea about the formation and evolution of the universe. Detailed Definition: Galaxy evolution is a term used to understand the structure of the universe and the ongoing formation processes by comparing the morphology, brightness and content of galaxies with each other. The term galaxy evolution here studies galaxies in four main groups. These are Elliptical Galaxies, Lenticular Galaxies, Spiral Galaxies, and Irregular galaxies. The evolution process of galaxies in these four groups is examined under three main headings. These are Passive evolution (The state where the galaxy does not interact with any other galaxy [interactions or mergers] and thus does not produce star formations.), Interactions and Mergers (The state in which galaxies are affected by interacting with other galaxies), Secular Evolution (Situation in which processes by internal changes of galaxies affect their colour, luminosity and shape.) Etymology: From Latin ‘Galaxias’ and From Latin ‘ēvolūtiōnis’ (Unrolling/Unfolding) Sample Sentence(s): ‘’Radio telescopes have played a pivotal role in the understanding of galactic evolution.’’ (Galaxy Evolution, Cosmology and Dark Energy. (2018, May 30). Public Website. https://www.skatelescope.org/galaxyevolution/) ‘’Understanding how black holes shape their host galaxies is part of the study of galactic structure and evolution.’’ (Galaxy Formation and Evolution | Center for Astrophysics. (n.d.). https://www.cfa.harvard.edu/research/topic/galaxy-formation-and-evolution) Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French: Évolution de la galaxie German: Galaxienentwicklung Polish: Ewolucja galaktyki Swedish: Utveckling av galaxer Turkish: Galaksi Evrimi Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.britannica.com/science/galaxy/Evolution-of-galaxies-and-quasars https://www.jwst.nasa.gov/content/science/galaxies.html https://www.skatelescope.org/galaxyevolution/ https://www.cfa.harvard.edu/research/topic/galaxy-formation-and-evolution https://sites.astro.caltech.edu/~george/ay20/eaa-galevol.pdf https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/E/evolution+of+galaxies https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rdd9KAUcvgQ&ab_channel=TakayukiSaitoh https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_WtvU4Xn2UE&ab_channel=CaltechAstro | |||
Galaxy Merger | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: https://www.eso.org/public/images/1016-galaxy_formation_merger/ Short Definition: A galaxy merger is the phenomenon of two or more galaxies colliding with each other, resulting in the formation of a new, enlarged galaxy. Detailed Definition: A galaxy merger occurs when two or more galaxies collide with each other, leading to the creation of a larger galaxy. Galaxy mergers are the most violent type of galaxy interaction. When a collision of several galaxies occurs, the stars and dark matter in each of them become affected, which has influence on both the orbits of the stars and the shape of the newly formed galaxy. During a merger, an increase in star formation can be observed, as the friction interaction of gas and dust contributes to the raise of energy in the resulting system. Galaxy mergers provide astronomers with the merger rate, which is a fundamental measurement of galaxy evolution and sheds some light on how galaxies have increased in size over time. Etymology: merge - Latin mergere"to dip, dip in, immerse, plunge" galaxy - Late Latin galaxias - Greek galaxías Sample Sentence(s): Galaxy mergers can be simulated in computers, to learn more about galaxy formation. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Fusion de galaxies German: Galaxienfusion Polish: Fuzja galaktyk, połączenie się galaktyk Swedish: Galaxsammanslagning Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.eso.org/public/images/1016-galaxy_formation_merger/ https://www.thoughtco.com/interacting-galaxies-have-interesting-results-3072045 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4disyKG7XtU | |||
Gamma ray | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Illustration of an emission of a gamma ray ( γ ) from an atomic nucleus Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_ray#/media/File:Gamma_Decay.svg Short Definition: Gamma rays are very high frequency electromagnetic radiation emitted as an outcome of radioactivity. Due to high frequency, gamma rays have very high energy. Natural sources of gamma emission originating on Earth are mainly an effect of radioactive decay and secondary radiation from atmospheric interactions among cosmic ray particles. Detailed Definition: A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation, is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation originating from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. Gamma rays from radioactive decay are within the energy range starting at few kiloelectronvolts (keV) to roughly 8 megaelectronvolts (MeV), matching to the usual energy levels in nuclei among reasonably long lifetimes. The energy spectrum of gamma emission can be utilized to recognize the decaying radionuclides with a technique called gamma spectroscopy. Very-high-energy gamma rays in the 100–1000 teraelectronvolt (TeV) range have been observed from sources such as the Cygnus X-3 microquasar. Etymology: gamma - The third letter of the Greek alphabet (Γ, γ), Sample Sentence(s): "Solar flares emit across the entire electromagnetic spectrum, including gamma rays." Translations: French: Rayon gamma German: Gammastrahlung Polish: Promieniowanie gamma, promienie gamma Swedish: Gammastrålning Links to Videos/Articles: | |||
Geosynchronous orbit | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Projection of the path traced by geosynchronous satellites of different inclinations. Source: Wikipedia Short Definition: | |||
Gravity | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| |||||||||||
Gravity Assist | ||
|---|---|---|
Source: http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/multimedia/display.cfm?IM_ID=2143, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=18049439 Short Definition:Gravity assistance describes the intentional use of the gravitational attraction of a celestial body, in order to modify the trajectory of a space vehicle. This maneuver allows the spacecraft to save rocket fuel. Detailed Definition:Etymology:1. Gravity (Noun.), originating from the Latin word gravitatem, with the meaning of “weight, heaviness, pressure” 2. Assist (Verb.), originating from Latin word assistere, which means “standing by, help” Sample Sentence(s): “The global minimum velocity increments of direct transfer trajectory and gravity-assist trajectories are obtained for each candidate target.” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Great Red Spot | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Sources: Stewart, P. (2018, June 8). Jupiter. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/106648653@N05/42658035711 Definition:A persistent large anticyclonic storm in the atmosphere of Jupiter, 22° south from its equator, which has been continuously observed since the 19th century.As of 2021, the Great Red Spot is reported to be about 10,000 miles across and 300 miles deep into the atmosphere of Jupiter. However, according to NASA observations, it is shrinking and becoming taller, and it is not yet clear whether the Great Red Spot will stabilize or disappear completely. Translation:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JDi4IdtvDVE | |||
H |
|---|
Heavy Element | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Image/Video/Audio: Image: Periodical Table Image/Video/Audio Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ionization_energy_periodic_table.svg
Short Definition:
Heavy elements are the general name for elements containing atomic numbers greater than 92. Above these, elements with atomic numbers 112 and above are called superheavy elements. The state that creates the atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of the element. Detailed Definition:
Heavy elements, which are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of the element (this called atomic number) are elements with atomic number greater than 92. One row above them there is superheavy elements with atomic numbers greater than 112. The first artificially produced heavy and superheavy elements were first produced during the Cyclotron experiments. One of the most important issues about heavy elements is the concept of 'island of stability'. This concept refers to the region in the table of nucleides where elements with half-lives longer than some other super heavy elements are found. However, it should be noted that we are ona narrow time scale, from minutes to micro/nano seconds at most. The term was first coined in 1998 with the discovery of the super heavy element 114 (Flerovium).
Etymology:
Heavy – From Proto Germanic (hafiga) Element – From Latin (elementum) (origin and meaning of heavy. (n.d.). Etymonline. https://www.etymonline.com/word/heavy) (element - Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/element)
Sample Sentence(s):
‘’The heaviest element known at the end of the 19th century was uranium, with an atomic mass of approximately 240 (now known to be 238) amu.’’ (Wikipedia contributors. (2022, December 31). Superheavy element. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Superheavy_element) ‘’Although the scientific community has assigned these heaviest elements to their own spots on the periodic table, there is still a lot we don’t know about them.’’ (Exploring the superheavy elements at the end of the periodic table. (n.d.). cen.acs.org.)
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French:
Élément lourd German:
Schweres element Polish:
Ciężki pierwiastek Swedish:
Tungt element Turkish: Ağır Element
Links to Videos/Articles:
Cookie Absent. (n.d.). https://physicstoday.scitation.org/action/cookieAbsent Discovery of Elements 113 and 115. (n.d.). https://pls.llnl.gov/research-and-development/nuclear-science/project-highlights/livermorium/elements-113-and-115 Seeker. (2019, November 10). This Superheavy Atom Factory Is Pushing the Limits of the Periodic Table [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kg0AN8bZ4us Wikipedia contributors. (2022, December 31). Superheavy element. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Superheavy_element | |||
Heliosphere | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Term/Concept: Heliosphere Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| |||||||||||
Hubble Space Telescope | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short Definition
Sample Sentence(s):
Hubble
Space Telescope helped researchers make new discoveries.
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French: Hubble German: Hubble-Weltraumteleskop Italian: telescopio spaziale Hubble Polish: Kosmiczny Teleskop Hubble’a Swedish: Hubbleteleskopet Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Hubble's Law | ||
|---|---|---|
Wikipedia contributors. (n.d.). File:Hubble constant.JPG - Wikipedia. https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/2c/Hubble_constant.JPG Short Definition: Hubble's Law is a concept formed by Edwin Hubble, defining a positive relation between the distance and the speed of galaxies moving away from earth. The further they are, the faster they move away. This theory was a base to observe the expansion of universe. Detailed Definition: Hubble's law defines a relation between distance of galaxies and their speed of moving away from each other. The concept was observed through detection of redshift emitted by these galaxies, visible from earth. In simpler terms, the galaxies emit light on a spectrum further towards the red extreme, which can be observed by comparing measurements from different times, to calculate that the light has changed its wavelength and frequency, thus shifting on the visible light spectrum. The theory proves that the universe is constantly expanding, and thus it contributes to the Big Bang Theory. The constant movement of galaxies away from earth and each other, points to the increase of space in the universe. The theory also derives a so called, Hubble's constant which is a measure of how fast a given galaxy moves away at a given distance, and it comes out to around 70 (km/s)/Mpc which translates to expansion of 70 kilometres per second for every megaParsec of distance from the galaxy. Thus, for a galaxy 1 megaParsec away from earth, the structure moves away at a speed of 70 km/s. Etymology: Hubble's Law comes from the last name of the physicist Edwin Hubble. Sample Sentence(s): 1. Hubble's Law contributed largely to the theory of relativity. Translations: French - Loi de Hubble German - Hubbles Gesetz Italian - Legge di Hubble Polish - Prawo Hubble'a Swedish - Hubbles lag | ||
I |
|---|
Ilmenite | ||
|---|---|---|
Short Definition:A usually massive iron-black mineral that consists of an oxide of iron and titanium and that is a major titanium ore. Detailed Definition:Ilmenite is named after the Ilmenski mountains in Russia, where the mineral was first discovered. It is slightly magnetic, which means that magnets can be used to separate it from other minerals in sand deposits. Ilmenite is also a common accessory mineral in igneous rocks, sediments, and sedimentary rocks in many parts of the world. Also, it is a black iron-titanium oxide with a chemical composition of FeTiO3. Etymology:
Named after Ilmen Mountains in Russia + -ite in 1827. The suffix –ite is used to form nouns denoting rocks or minerals, from Latin -ītēs, and from Ancient Greek -ῑ́της. Sample Sentences:
"Ilmenite is an economically important and interesting mineral." "Ilmenite is the most important ore of titanium and the main source of titanium dioxide, which is used in paints, printing inks, fabrics, plastics, paper, sunscreen, food and cosmetics." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Inflation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Sources: https://wmap.gsfc.nasa.gov/universe/bb_cosmo_infl.html https://www.space.com/42261-how-did-inflation-happen-anyway.html Definition:Rapid expansion of the universe at its early stages of development (at around 10-36 seconds after the Big Bang). The Inflation Theory was developed in 1980 by Alan Guth, Andrei Linde, Paul Steinhardt, and Andy Albrecht and attempted to account for phenomena that could not be explained by the Big Bang Theory (the Horizon Problem, the Flatness Problem and the Monopole Problem). Nowadays, the Inflation Theory is considered to be an extension of the Big Bang Theory. Translation
| |||
Infrared | ||
|---|---|---|
Image:
Source: Short Definition: Light with wavelength from 800 nanometers to 1 millimiter. Detailed Definition: Electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from 800 nanometers to one millimeter. It is next to the red end of the visible spectrum, hereby the name. Also called IR, it is a kind of electromagnetic radiation that has qualities like both a wave and a particle, the photon, and propagates energy and momentum as well as exerting radiation pressure. Etymology: Infrared comes from Latin: infra, which means below. Sample Sentence(s): To keep an eye on workplace activities, they used infrared cameras. Without disturbing the bats, an infrared camera records them. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: infrarouge German: Infrarot Polish: podczerwień Swedish: infraröd Links to Videos/Articles: https://science.nasa.gov/ems/07_infraredwaves https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/infrared-vision | ||
Initial mass function (IMF) | ||
|---|---|---|
 Image source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d5/Plot_of_various_initial_mass_functions.svg/800px-Plot_of_various_initial_mass_functions.svg.png Short Definition: The initial mass function (IMF) describes the distribution of stellar masses as a large cluster of stars is newly formed and is based on an average from stars in our Milky Way. This function is useful for understanding the formation of stellar systems and their evolution. In most cases, the initial mass function is shown with a logarithmic scale. Derailed Definition: The initial mass function shows few massive stars which are more massive than the sun, while sun-sized stars are more abundant and stars that are smaller than the sun are quite common (this trend does not continue linear the smaller they get): The function can be described by using the following law: IMF = constant x m^(-α) where m = initial star mass and α = slope of the logarithmic plot. Until this point in time, it is not certain if the IMF varies in extreme situations and if the calculation based on our Milky Way can be unconditionally applied to other galaxies. Etymology: initial - Latin initialis ("initial, incipent, of the beginning") mass - old French masse (" lump, heap, pile; crowd, large amount") function - Latin functionem (" a performance, an execution") Sample sentences: There are different curve forms of the initial mass function based on the way the alpha and the constant are calculated. Translation: French: fonction de masse initiale German: Anfangsmassenfunktion Polish: początkowa funkcja masy Swedish: funktion för dem ursprungliga massan Links to Videos/Articles: http://astro1.physics.utoledo.edu/~megeath/ph6820/lecture12_eqn.pdf http://www.astro.yale.edu/larson/papers/Nagoya99.pdf https://www.cfa.harvard.edu/news/initial-mass-function https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V5WlgcBh9T8 | ||
International Asteroid Warning Network | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short
Definition
Sample Sentence(s): IAWN includes members from all over the world that are creating a response in case of meteorite impact. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French: International Asteroid Warning Network
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
International Space Station | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:A research facility that was launched in 1998, is orbiting around the Earth and is operated by multinational groups of astronauts sent regularly by five space agencies participating in the project – NASA (the USA), Roscosmos (Russia), ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan) and CSA (Canada). Translations:
| |||
Interstellar Medium | ||
|---|---|---|
 webteam@eso.org. (n.d.). ESO - The Planet, the Galaxy and the Laser. 1999- 2008 ESO. https://web.archive.org/web/20081121184421/http://www.eso.org/gallery/v/ES OPIA/Paranal/phot-33a-07.tif.html Short Definition: The interstellar medium (ISM) is a composition of radiation and matter which occurs between star systems, which are compositions of stars orbiting each other. The medium is usually created from various gasses, mostly hydrogen and helium. This matter is a filler between the stars. Detailed Definition: The interstellar medium (ISM) is a region filled with gas and dust in between stars. The medium is created when a star dies. As the star collapses into itself, it releases huge amounts of energy and matter at high velocity and high temperature. When this mix encounters patches of interstellar gas, the visible nebulas of interstellar medium are created. The gas is ionized, and space dust blocks certain light waves which. Contrary to common belief, space is not completely empty and is not a full vacuum but is filled with matter such as gas and space dust. The interstellar medium is impactful in formations it is in. Stars which are positioned in the denser areas of ISM supply it with matter and energy through stellar winds or supernovae (the explosion of a star). The inter-influence of stars and ISM formations helps scientists determine the lifespan of given star formations. Etymology: This phrase is a conjunction between the words 'interstellar' and 'medium'. The word 'interstellar' comes from combining the prefix 'inter' from Latin for "between" and the word 'stellar' from Latin 'stellaris' meaning "pertaining to a star". The word 'medium' from Latin medium "the middle, midst, center; interval" Sample Sentence(s): 1. The interstellar medium can be visible with long exposure astrological
photography. Translations: French: milieu interstellaire German: interstellares Medium Italian: mezzo interstellare Polish: ośrodek międzygwiazdowy Swedish: interstellärt medium | ||
J |
|---|
James Webb Space Telescope | ||
|---|---|---|
Source: Short Definition: The James Webb Space Telescope is a large telescope in space that conducts infrared
astronomy. The cutting edge telescope technology aims to shine light on stars or
galaxies, that were previously hidden in “plain” sight. Many people think this
is the successor to the Hubble telescope, but in reality, it is more of a
successor for the Spitzer space telescope, which also is an infrared telescope.
The property of light to shift to red makes this a helpful telescope to look at
the oldest galaxies. Detailed Definition: The James Webb Space Telescope is a visualizing device for away structures or phenomenons that work in the infrared range. The biggest telescope in space had to overcome many difficulties to even be transported to space. The telescope had to be folded to even fit in the rocket, and so they used Origami techniques to transport it safely to its place. JWST is not an all-rounder telescope like Hubble is. JWST aims to discover secrets from almost the beginning of time with the most sophisticated infrared sensors, cameras and lenses that were used till now, but looking at the oldest stars and galaxies is not its only job. JWST will also be used to identify fitting exoplanets by scanning the atmospheres of those planets for the right gas composition.Etymology: Latin- spatiumà Old French -espaceà Middle English – space Modern latin– tele and modern latin -scopiumà Modern latin – Telescopiumà English telescopeSample Sentence(s): Webb will be the largest telescope ever placed in space; 100 times more powerful than Hubble. So big it has to fold origami-style to fit in the rocket and will unfold like a "Transformer" in space (NASA) NGC 346, one of the most dynamic star-forming regions in nearby galaxies, is full of mystery. Now, it is less mysterious with new findings from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. (NASA)French: télescope
spatial james webb German: James Webb Weltraumteleskop Polish: Kosmiczny Teleskop Jamesa Webba Swedish: James Webb rymdteleskop Links to Videos/Articles: https://webb.nasa.gov/ https://webbtelescope.org/ | ||
Jet engine | ||
|---|---|---|
 U.S. Air Force. (2010, November). F100 F-15 engine. Retrieved from https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/69/F100_F-15_engine.JPG Photograph of a jet engine in operation, with a long converging plume of hot gas streaming out from the nozzle Short Definition: A jet engine is a reaction engine that produces a jet of heated gas to be discharged from the engine as a reaction mass. The Propelling gas is usually air, especially when the engine is used in the atmosphere on flying vehicles, but can be other gas or liquid. Detailed Definition: A jet engine is a reaction engine that discharges a fast-moving (often supersonic) jet of hot gas (usually air, if the engine is used in the atmosphere) and to generate thrust. Jet engines are usually internal combustion engines and used everywhere: on planes, boats and rockets. Etymology: Jet – from French jet– throw, cast, gush, spurtEngine – from Middle English engyn or Anglo-Norman engine or Old French engin– skill, cleverness, war machine Sample Sentences: The jet engine roared as the airplane accelerated down the runway. Translations French: Moteur à réactionGerman: Turbinen-Strahltriebwerk Italian: Esoreattore Polish: Silnik odrzutowy Swedish: Jetmotor Russian: Реаĸтивный двигатель Ukrainian: Реаĸтивний двигун References: SKYbrary Aviation Safety. (2019, December). Jet engine. Retrieved from https://www.skybrary.aero/articles/jet-engine Airbus. (2016, November). Flight operations briefing notes – Supplementary techniques : Handling engine malfunctions. Retrieved from https://web.archive.org/web/20161022181226/http://www.airbus.com/fileadmin/media_gallery/files/safety_library_items/AirbusSafetyLib_-FLT_OPS-SUPP_TECH-SEQ07.pdf | ||
Jupiter | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Stewart, P. (2018, June 8). Jupiter. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/106648653@N05/42658035711 Definition
Etymology:The planet is named after Jupiter, the highest ancient Roman deity, the god of sky and thunder. Translations:
| |||
K |
|---|
Kalpana Chawla | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: http://lk.astronautilus.pl/astros/366.htm Definition:Kalpana Chawla, born in Karnal, India, in 1962, is first astronaut with an Indian descent. In her early years, her father took her to local flying clubs, where she developed her passion for flying. She moved to the U.S. to pursue degrees in engineering (Ph.D. in aerospace engineering from the University of Colorado) and eventually after graduation, she did research, focusing on vertical take-off and landing concepts. Her area was the development and implementation of efficient techniques for performing aerodynamic optimization. In 1994, Chawla was chosen as an astronaut candidate and took part in 2 space flights. The second flight ended tragically in 16.01.2003, as Space Shuttle Columbia exploded while being on the way back to the Earth, after 15 days and 22 hours spent in space. The explosion while re-entrng into Earth's atmosphere killed all seven astronauts on board, including Kalpana Chawla. Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/atoms/files/chawla_kalpana.pdf https://www.space.com/17056-kalpana-chawla-biography.html | |||
Kepler’s laws | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Image/Video/Audio Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/98/Kepler_laws_diagram.svg Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles: | |||||||||
Kuiper Belt | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image:  Image: Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=38097918 Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||||||||||
L |
|---|
Lagrange Point | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: NOAA Images (2016, September 21). Lagrange Points. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/125201706@N06/29832072485 Short Definition: A Lagrange Point is a place where the gravitation force of two large masses (for example the earth and sun) addition together, so that a small object (for example a spacecraft or a telescope) can move with the two large masses on a path. There are 5 different Lagrange points in total for each constellation. Detailed Definition: In the spot of a Lagrange point, the gravitational force by two large masses equal the centripetal force (the force that makes a body follow a curved path), which is required for the small mass to move along the two large masses and can reduce the fuel usage. The Lagrange points L1,L2 and L3 are unstable, which can lead to an unwanted movement of the small mass away from the Lagrange point if a force is properly applied to the small mass. The Lagrange points L4 and L5 are stable. The calculation is done by solving the three-body problem, where the Lagrange points are the constant solution for. Etymology: The word point originated from the Latin word pungere("to prick, pierce"). Sample Sentence(s): "The Lagrange point L2 is the position of the James Webb Space Telescope." Translations: French: PointdeLagrange German: Lagrange-punkt
Polish: punkt Lagrange’a, punkt libracji
Swedish: Lagrangepunkt
Italian: punto di Lagrange
Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.chicagospace.org/the-five-lagrange-points-l1-l2-l3-l4-and-l5/ https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/resources/754/what-is-a-lagrange-point/ https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Operations/What_are_Lagrange_points | |||
Launch escape system | ||
|---|---|---|
 NASA. (1965, June). Apollo Pad Abort Test #2. Retrieved from https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/17/Apollo_Pad_Abort_Test_-2.jpg Short Definition: Launch escape system (LES) or launch abort system (LAS) is a system in rockets that will separate a capsule with crew and move it away from the rocket in case of emergency such as pending rocket explosion. This is a safety measure necessary to evacuate the crew when their presence in the rocket is life-threatening. Detailed Definition: LES is attached to the capsule and usually has thrusters and a little fuel. It is just enough to propel it for a short time and send the capsule away from the rocket. It can be placed above capsule as a tower (as in Apollo) or be a part of capsule (as in Crew Dragon). LES doesn't have to be detachable from the capsule with crew, but if it is (as towers), it will be separated as soon as it runs out of fuel or when it is no longer needed. When LES finished working, capsule can land or splash with its own parachutes. Nowadays all crewed missions are equipped with some kind of launch escape system. Etymology: Launch – from Old French lancier– to fling, hurl, throw, castEscape – Old French eschaper– free oneself from confinementSystem – from Late Latin or Greek systema– an arrangement, organized whole, a whole compounded of parts Sample Sentences: The launch escape system provided a critical safety measure for astronauts in case of a rocket malfunction. Translations: French: Tour de sauvetageGerman: Rettungsrakete Italian: Sistema di fuga di lancio Polish: Rakietowy System Ratunkowy Swedish: Starta utrymningssystem Russian: Система аварийного спасения Ukrainian: Система аварійного порятунĸу References: McHale, S. (2014, February). Soyuz launch escape system. Retrieved from https://web.archive.org/web/20140221212224/http://suzymchale.com/ruspace/soyescape.html Clark, S. (2010, February). Orbital sees bright future for Orion launch abort system. Retrieved from https://spaceflightnow.com/news/n1002/18orionlas/ | ||
Lenticular Galaxy | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: Short Definition: A lenticular galaxy is a type of galaxy which contains a large-scale disc but does not have large-scale spiral arms. Detailed Definition: Galaxies can be divided into various types - spiral, elliptical, lenticular and irregular. A lenticular galaxy exhibits characteristics of both an elliptical and a spiral galaxy. It is determined by a central bulge and disks (as in the case of an ellipcital galaxy) combined with the absence of arms, which can be found in spiral galaxies just as the Milky Way. The name refers to the shape of the galaxy, which is very similar to a lens. Etymology: lenticular (lĕn-tĭk′yə-lər) - Latin lenticularis - having the shape of a double-convex lens Sample Sentence(s): "Lenticular galaxies tend to be old galaxies that have used up most of their gas and dust and are just living the twilight years." Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Galaxie lenticulaire German: Linsenförmige Galaxie Polish: Galaktyka soczewkowata Swedish: Linsformad galax Links to Videos/Articles: https://scitechdaily.com/hubble-image-of-the-week-lenticular-galaxy-ngc-2655/ https://www.universeguide.com/fact/lenticulargalaxy https://www.thoughtco.com/lenticular-galaxies-structure-formation-3072047 | |||
Light Pollution | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Law, L. (2015, February 25). Night sky with light pollution from Coachella Valley. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/115357548@N08/16026201013 Short Definition: Light pollution is the effect of excessive or poor use of artificial outdoor light sources. There are several negative impacts from it: it disrupts both the human sleep and natural patterns of wildlife, it is a factor in the increase in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, and obscures the celestial bodies in the night sky. Detailed Definition: Light pollution, also referred to as luminous pollution, is the negative consequence of excess of artificial light and its misuse. There are several major repercussions to the increasing amounts of light in the night sky, such as sky glow, disruption of natural body rhythms in both human and animals, and the obscured ability of celestial object observation. The sky glow is the over presence of artificial light in densely populated areas after sunset, which results in disruptions of melatonin hormone in humans, causing sleep deprivation, fatigue, headaches, stress, and anxiety. Studies indicate a connection between the low melatonin levels and cancer. Light pollution also impacts the behaviour of animals, such as migration patterns, wake-sleep habits and habitat formation. Sky glow impairs the research of the night sky, obscuring stars and other celestial bodies. Etymology: "light" - Old English leht, West Saxon leoht, German Licht - brightness, radiant energy, that which makes things visible "pollution" - Late Latin pollutionem, Latin polluere - defilement, to soil, defile, contaminate Sample Sentence(s): "Light pollution disrupts astronomers in their study of space." "It is increasingly difficult to appreciate the beauty of the evening sky, as the light pollution obscures the visibility of stars." Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Pollution lumineuse German: Lichtverschmutzung Polish: Zanieczyszczenie światłem Swedish: Ljusförorening Links to Videos/Articles: https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/light-pollution https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/mapmaker-light-pollution https://planetfacts.org/light-pollution/ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UdIGJNVUwmE | |||
Liu Yang | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short
Definition
Soon
after, on June 16, 2012, Liu Yang launched into space, accompanied by commander
Jing Haipeng and operator Liu Wang.
This milestone
mission marked China's first successful crewed space docking with the Tiangong
1 space module. During the mission, Liu Yang took charge of conducting medical
experiments. Etymology Sample Sentence(s) "[…] having Liu Yang on board will not only help the country's aspiring space program test equipment designed for women in preparation for the building of an orbiting space station, but it will also expand the social impact of human space missions." Wolchover, N. (2012, June 15). Who Is China’s First Female Astronaut? livescience.com. https://www.livescience.com/34002-china-female-astronaut.html
Links to Videos/Articles:
● Wolchover, N. (2012, June 15). Who Is China’s First Female Astronaut? livescience.com. https://www.livescience.com/34002-china-female-astronaut.html ● China’s first female astronaut ready for new space mission. (2022, June 4). CGTN. https://news.cgtn.com/news/2022-06-04/China-s-first-female-astronaut-ready-for-new-space-mission-1aAKaX706GI/index.html ● Gregersen, E. (Invalid Date). Liu Yang. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/biography/Liu-Yang ●
CGTN. (2022, September 6). Liu Yang: No preferential treatment for being
a woman in space [Video]. YouTube.
| ||
Low Earth orbit | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Orbitalaltitudes.svg Short Definition: The Low Earth Orbit (in short, LEO) is an orbit that is relatively low compared to typical space orbits. An object orbiting Earth above 100 km and below 2000 km can be described as orbiting on Low Earth Orbit. In terms of orbiting time, a low Earth orbit have an orbiting period of 128 minutes or less. Low Earth Orbit is often used as temporary orbit for spacecrafts travelling further into space. Detailed Definition: The Low Earth Orbit (LEO in short) is a zone around Earth from a 100 km (Kármán line) to about 2000 km above Earth's surface. Due to orbits shape varying from circles to ellipses, better description is done using time. A body orbiting at the Low Earth Orbit has an orbiting time around 128 minutes or less. The pull of gravity in the LEO is only slightly less than on the Earth's surface, and the orbiting body still encounters atmospheric drag from present gas particles. Due to this, the LEO is often used as a transitive stage for spaceships traveling further into space, as the mean orbital velocity needed to maintain a stable low Earth orbit is about 7.8 km/s, rather than being used as a stable orbit due to constant need of course correction. The most famous spacecraft orbiting in the LEO is the International Space Station, orbiting at around 400 km above Earth’s surface. Etymology: Low - From Middle English lowe, lohe, lāh, from Old Norse lágr (“low”) Sample Sentence(s): "The International Space Station is the largest modular space station currently in the Low Earth Orbit." Translations: French: Orbite terrestre basse German: Niedrige Erdumlaufbahn Polish: Niska orbita okołoziemska Swedish: Låg omloppsbana Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2020/03/Low_Earth_orbit | |||
Lunar regolith | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/89/Apollo_11_bootprint.jpg Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles: | |||||||||
Lunar Theory | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: Newton, I. (1687, January 1). Isaac Newton's diagram from the 'Principia' of 1687 (Book 3, Proposition 25, at p.434). wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:096-newt1687-figp434.jpg
Short Definition:
Lunar Theory is the measurement and prediction of the movements of the moon as a method of a priori deduction with the principles of the laws of gravity. For the first time in the modern era, Isaac Newton mentioned in his book Principia in 1687 that the motion of the moon could be calculated mathematically by the law of gravity.
Detailed Definition:
Lunar theory, the theory that the movements of the moon can be calculated by gravitational laws, put forward by Isaac Newton in 1687, is a cumulative result of moon observations that found their roots in ancient Babylonian, Greek and Arabian geography. In his book, Newton's Principia, he made the first inferences about how the gravitational motion of the Earth and Moon towards the sun could be measured mathematically. With the development of technology, especially after the 1960s, lunar theory has been retested with the help of automatic digital computation and modern observational data-types. With computer-assisted algebra, new analytical developments have been experienced, and new analytical theories have been created.
Etymology:
Lunar – Latin (lūnāris) Theory – Ancient Greek (theōréō ) (lunar - Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/lunar) (theory - Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/theory)
Sample Sentence(s):
‘’These views, however, are due to a lack of understanding of the close relation that exists between the kinematical model of Horrocks, and the dynamical lunar theory of Newton.’’ (Newton’s lunar theory. (n.d.). http://physics.ucsc.edu/. http://physics.ucsc.edu/~michael/koll.html) ‘’Newton's dynamics, and his lunar theory especially, were difficult for his contemporaries and they are perhaps even more difficult now.’’ (Success and failure in newton’s lunar theory. (n.d.). Oxford Academic. https://academic.oup.com/astrogeo/article/41/6/6.21/225623)
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French:
Théorie lunaire German: Mondtheorie Polish:
Teoria Księżyca, teoria ruchu Księżyca Swedish:
Månteori Turkish: Ay Teorisi
Links to Videos/Articles:
Newton’s lunar theory. (n.d.). http://physics.ucsc.edu/. http://physics.ucsc.edu/~michael/koll.html ScienceClic English. (2019, January 5). Newton’s Gravity [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OE5LBi7hZkU Success and failure in newton’s lunar theory. (n.d.). Oxford Academic. https://academic.oup.com/astrogeo/article/41/6/6.21/225623 | |||
M |
|---|
Manipulator | |||
|---|---|---|---|
source of image: Short definition: A robot manipulator is a multi-segmented electronically controlled mechanism that performs tasks by interacting with its surroundings. They are also commonly known as robotic arms. They are widely used in the industry to assist workers to deal with radioactive or biological hazard materials, moving or lifting objects that are too heavy. Detailed Definition: A manipulator is a tool used in robotics to move objects around without the operator having to touch them directly. They have been used in a variety of applications, including robotic surgery, welding automation, and space travel. It is an arm-like device made up of several sliding or jointed segments known as cross-slides that can grip and move items with a variety of degrees of freedom. A manipulator is a lift-assist device used in industrial ergonomics to assist workers in lifting, moving, and placing objects that are too heavy, too hot, too big, or otherwise too challenging for one worker to handle manually. A column boom manipulator is utilized in welding to improve deposition rates, decrease human error, and lower costs in a manufacturing environment. Furthermore, manipulator tooling allows the lift assist to pitch, roll, or spin the part for proper placement. For example, removing a part from a horizontal press and pitching it up for vertical placement in a rack, or rolling a part over to expose the back of the part. Sample sentence: 6-axis robotic manipulators are the most commonly seen in industry because their range of motion is similar to the human arm.Chinese: French: Manipulatrice (feminine)Manipulateur (masculine) German: Manipulator Polish: Manipulator Swedish: Manipulator Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figure-1-1-Standard-robot-manipulators-1_fig1_330599518 | |||
Mars | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 24). Artistic AI Illustration of a martian landscape. midjourney. midjourney.com Definition:The second smallest planet in the Solar System (6792,4 km in diameter), the fourth planet from the Sun, also referred to as the Red Planet. Etymology:The planet is named after Mars,the ancient Roman god of war. Translations:
| |||
Mars Habitat | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio Source: Short Definition: A Mars habitat is a proposed idea to colonize Mars and establish an autonomous
colony. The horrid conditions of Mars will pose an almost insurmountable problem, where concrete solutions still elude us. In theory, Elon Musk said that a crewed
landing would occur in 2029, which Is still 6 years away, but this seems to be
an unachievable goal in the near future. Detailed Definition: A Mars habitat would be a habitat on Mars where humans’ strife to be self-sufficient. In some ways, Mars is even similar to the Earth, but it just differs in too many life essential conditions. The mean temperature on Mars only reaches -63°C and the average natural radiation levels are 40-50 times higher than on Earth due to the missing Ozone layer on Mars. These conditions would be enough to classify it as horrid, but the list goes on. Breathing normally is impossible due to the wrong gas composition, and even the ground you would walk on is cancerous. Another negative is the different gravitational pull, because Mars’ gravity only reaches 38% of the gravity on Earth, which will lead to muscle atrophy and the necessity of intensive sport programs. These conditions would make an underground base under frozen CO2 that could be harvested from Mars and another layer of Mars soil a necessity to decrease the chance of getting cancer. At the start of the colony, only nuclear could be used as an energy option, because the varying conditions make others not effective and Mars as a whole is relatively energy poor. To achieve self-sufficiency proves to be an insurmountable problem, because even food will be hard to produce, because the soil does not have the needed nitrogen compounds and the soil would have to be decontaminated. To make a Mars habitat is certainly possible, but the feasibility and the ethicality have to be called into question.Etymology: Mars come from older Latin (older than 75 BCE) Māvors which was used as god of war from Middle English Habitat comes from Latin habitareà meaning habitat (it dwells) Sample Sentence(s): Mars habitats would have to contend with surface conditions that include almost no oxygen in the air, extreme cold, low pressure, and high radiation. (Wikipedia) French: Habitat mars German: Mars-Habitat Polish: habitat marsjański Swedish: Mars livsmiljö Links to Videos/Articles: | |||
Mercury | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| |||||||||||
Meridian | ||
|---|---|---|
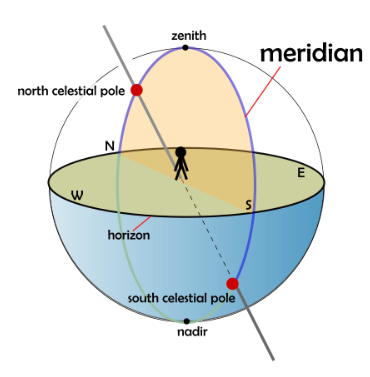 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Meridian_(astronomy) Short definition: An imaginary line in the sky running from due north to due south through the observer's location and the zenith.Detailed Definition:
In astronomy, a meridian is an imaginary line in the sky that runs from due north to due south, passing through the observer's location and the zenith. The zenith is the point in the sky that is directly overhead. The meridian is used to measure the altitude of objects in the sky, as well as their right ascension and declination. The meridian also marks the boundary between the eastern and western halves of the sky, with objects east of the meridian being in the morning sky and those west of the meridian being in the evening sky. Etymology: Latin - medius ‘middle’ + dies ‘day’. Sample Sentence(s):
"The planet Venus will cross the meridian at 8:00 pm tonight." "The altitude of the North Star above the horizon can be measured relative to the observer's meridian." "The meridian passage of a celestial object is the time it crosses the observer's meridian." Translations: French: Le Meridien German: Höhepunkt Polish: Południk Links to videos/articles: https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/m/meridian https://www.britannica.com/science/celestial-meridian | ||
Meteor Crater (Barringer Crater) | ||
|---|---|---|
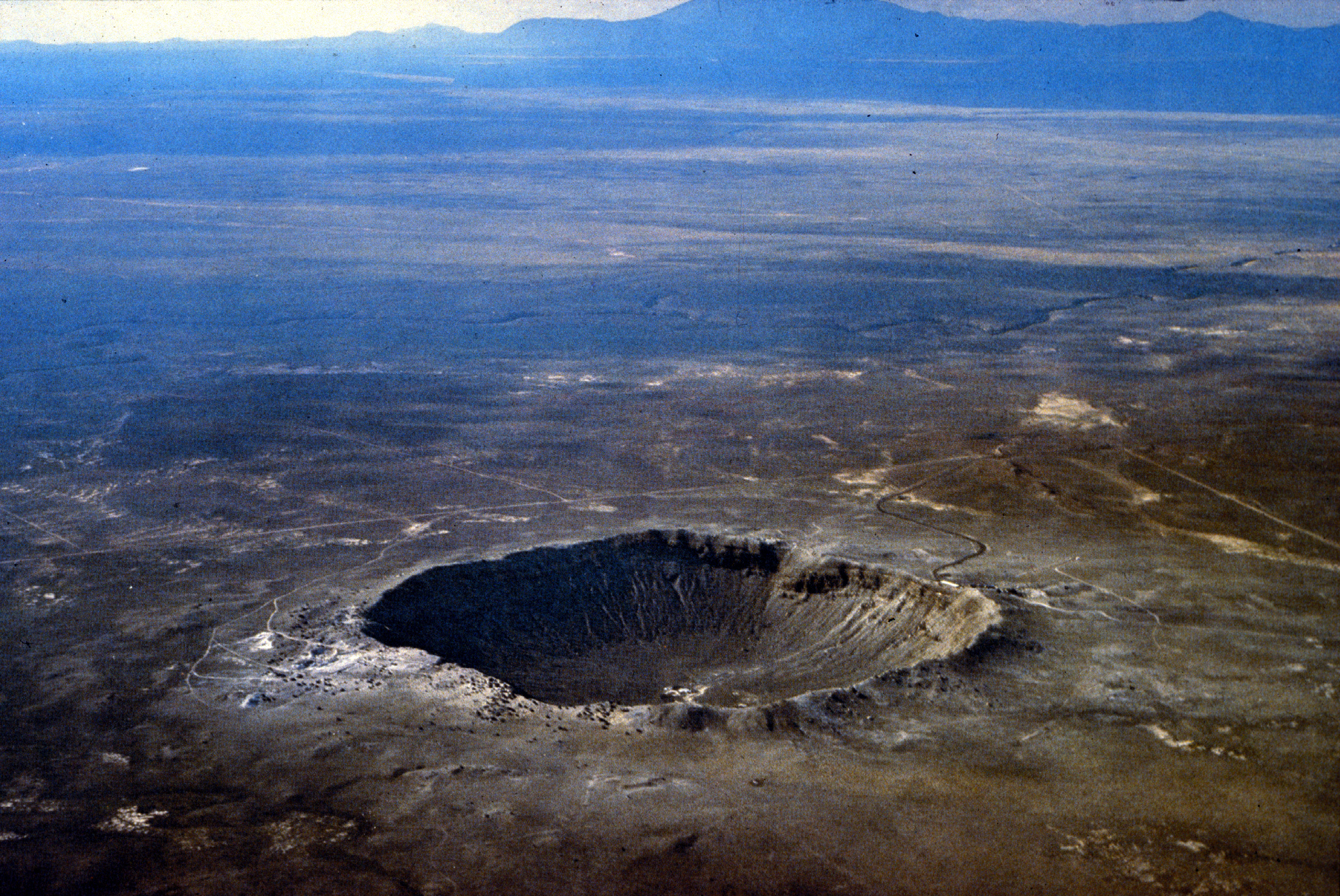 Short Definition Meteor Crater, also known under the name Barringer Meteor Crater, is the first crater known to be caused by the impact of a meteorite. The crater caused 50,000 years ago was long thought to be volcanic until it was proven in 1961 that it was caused by the impact of an asteroid hitting earth.
Found pieces of the asteroid are known under the Canyon Diablo Meteorite and can be seen among other things at the museum nearby. To this day, it is the best-preserved crater caused by impact to be found. Because of that, scientist have done much research inside and astronauts have been trained there. Today it is part of a museum and can be visited. Etymology Sample Sentence(s): Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
Other sources/links: ● Meteor Crater Natural Landmark. (2023a, May 23). Meteor Crater | Barringer Space Museum | Winslow, AZ. Meteor Crater | Barringer Space Museum. https://meteorcrater.com/ ●
AZFamily, Arizona News. (2019, July 22). How Arizona’s meteor crater was
created [Video]. YouTube. ● Meteor Crater, Arizona, USA | NASA Solar System Exploration. (n.d.). NASA Solar System Exploration. https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/resources/2257/meteor-crater-arizona-usa/
| ||
Meteorite | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short definition: A meteorite is a piece of rock or metal originating from space that has landed on the Earth’s surface. Before a meteorite enters the Earth’s atmosphere, it’s called a meteoroid. The phenomenon of a meteoroid burning up and leaving a glowing trail behind is called a meteor. Detailed definition: A meteorite is a piece of debris, usually of a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that has survived its passage through the Earth’s atmosphere and reached the surface. Meteorites vary greatly in size: some, that are called micrometeorites, are less than 1mm in size, and very few are large enough to leave an impact crater. The biggest meteorite ever found - the Hoba meteorite in Namibia - weighs about 60 tons. Most meteorites are stony, and only about 6% of meteorites are iron meteorites or a mix of stone and metal. Etymology: meteor (from Greek ta meteōra"the celestial phenomena, things in heaven above") + -ite Sample sentence(s): Commonly, chondrules can make up 75% of the volume of the meteorites in which they occur. (Source: Cambridge English Corpus | Cambridge University Press | ELT. (n.d.). Cambridge.es. https://www.cambridge.es/en/) Translations: French: météorite German: Meteorit Italian: meteorite Polish: Meteoryt Swedish: Meteorit Links to Videos/Articles: Alexander, C. M., & Wetherill, G. W. (2023, May 11). Meteorite | Definition, Types, Identification, & Facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/meteorite meteorite. (n.d.). https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/meteorite/ Science with Thomas Stevenson. (2022, August 9). What is a Meteorite? [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/Cv82yiksbl8 | ||
Meteoroid | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short definition: A meteoroid is a small rocky or metallic body in space that has not yet entered the Earth's atmosphere. When a meteoroid enters the Earth’s atmosphere at a high speed and burns up, it leaves a glowing trail, which is called a meteor. Detailed definition: Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than meteoroids are called micrometeoroids or space dust. Most meteoroids are fragments from comets or asteroids, containing extraterrestrial nickel and iron. Etymology: Meteoroid comes from meteor + -oid. -oid is a suffix coming from Ancient Greek εἶδος (eîdos, “form, likeness”), which means “resembling; having the likeness of”. Sample sentence(s): It was found that meteoroids from cometary sources were typically of porous, aggregate compositions with relatively low densities. (Source: Cambridge English Corpus | Cambridge University Press | ELT. (n.d.). https://www.cambridge.es/en/) Translations: French: Météoroïde German: Meteoroid Italian: Meteoroide Polish: Meteoroid Swedish: Meteoroid Links to Videos/Articles:Atkinson, N. (2018, April 8). What Is The Difference Between Asteroids and Meteorites? - Universe Today. Universe Today. https://www.universetoday.com/36398/what-is-the-difference-between-asteroids-and-meteorites/ Meteors & Meteorites. (n.d.). NASA Solar System Exploration. https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/asteroids-comets-and-meteors/meteors-and-meteorites/overview/?page=0&per_page=40&order=id+asc&search=&condition_1=meteor_shower%3Abody_type Encyclopaedia Britannica. (2019, January 2). DEMYSTIFIED: What’s the difference — meteoroids, meteors, & meteorites | Encyclopaedia Britannica [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/tXfjUxdzqBY | ||
Microgravity | ||
|---|---|---|
Short definition: Microgravity, also known as micro-g environment, is when a person or object appear to be weightless but the g-forces are never exactly zero. A clear example of microgravity can be seen when astronauts or objects float in space. Detailed definition: Microgravity, also known as micro-g environment, is a condition in which an object or a person appear to be weightless, though the g-forces are never exactly zero. "Micro" means “very small”, so microgravity refers to the phenomenon in which gravity appears to be very small. The effects of this condition can be seen when objects and astronauts float inside a spacecraft or outside, while on a spacewalk. Microgravity has a variety of effects on the human body. Muscles and bones, for example, can become weaker without having to work as hard. Furthermore, many things appear to behave differently in microgravity. Fire burns in different ways. Flames are more round when the pull of gravity is absent. There is a better growth of crystals. Their shapes are more perfect without gravity. Etymology: “Micro” from ancient greek mikrós/“small” + “gravity” from Latin gravitās/“weight” Sample sentences:
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages:
Sources: https://www.nasa.gov/audience/forstudents/5-8/features/nasa-knows/what-is-microgravity-58.htmlhttps://www.snexplores.org/article/explainer-gravity-and-microgravity https://www.britannica.com/video/163292/aspects-life-microgravity-Earth | ||
Milky Way | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Milchstraße#/media/Datei: Artist's_impression_of_the_Milky_Way_(updated_-_annotated).jpg 5th November 2021 Definition:A large spiral galaxy consisting of several hundred billion stars, dust and gas.The galaxy that includes our solar system, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. Etymology:The term Milky Way is a translation of the Latin via lactea, from the Greek γαλακτικός κύκλος (galaktikos kýklos), meaning "milky circle”. Translations:
| |||
Moon | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Full moon Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:FullMoon2010.jpg 25 Nov. 2021 Natural satellites Source : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural_satellite#/media/File:Moons_of_solar_system_v7.jpg 25 Nov. 2021 DefinitionThe Moon (Luna, Selene, Cynthia) as Earth’s only natural satellite; moons as natural satellites Etymology:From Proto-Indo-European “mēnsis” meaning “month" -> Proto-Germanic “mēnōn” -> Old English “mōna” Translations:
Links to videos/articles: | |||
Moon Base | |||
|---|---|---|---|
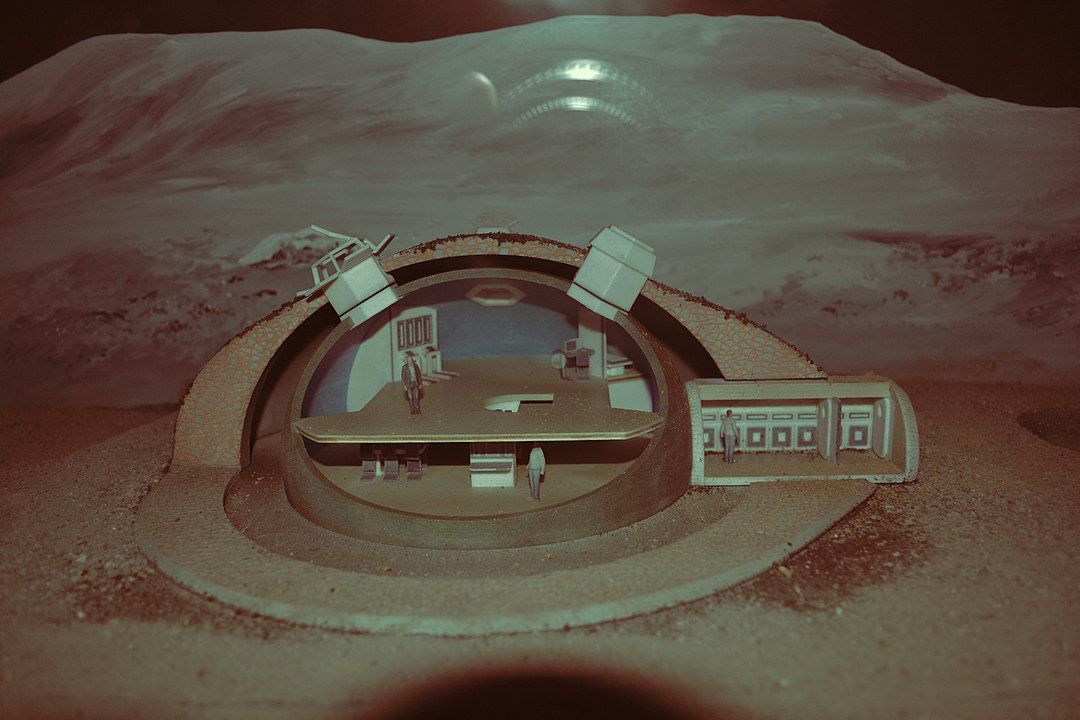 By SpaceMusk - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=76817044 Short Definition: A Moon Base is a type of facility on the surface of the moon, that could help us building up a colony on the moon.It could be the next frontier on our endeavour to become intergalactic and it could be a steppingstone to regions, that are not feasibly reached by spacecraft from earth, or it could become a centre for industry. In this way we could outsource industry or practices, that are not likely to become CO2-neutral soon. Detailed Definition:
A Moon Base is a type of facility on the surface of the moon, which enables human activity on the moon. As China and USA chose the same locations for their proposed moon bases, it could lead to the next smaller space race to the moon, only this time the mission would be to stay on it and to leave a small team to colonize the moon. Ice from the poles could be melted to get Water and this in turn could be split by electrolysis to hydrogen and oxygen, which are the main ingredients for liquid rocket fuel. The moon base could be used as a steppingstone to far distances because the rocket fuel needed to transport cargo from the moon is much lower than the earth due to the decreased escape velocity. So, a moon base could be used as a stopover to other proposed ideas like asteroid mining or it could help the Mars base. To justify the high investment costs, the moon base needs to be economically viable sooner rather than later. The mining of important resources like aluminium, titanium, and helium -3, which is used to fuel fusion reactors, could be helpful, if it proves to be economically and ecologically viable. A few suggestions could make this project much more autonomous by producing living soil from lunar regolith and mixing the moons soil, regolith and a plant-based glue to produce a 3D-printing material, which will prove to be absolutely essential for this kind of project. Etymology:
Moon from Old English mōna Base from Latin basis and from Ancient Greek βάσις (básis) Sample Sentence(s):A Moon base could help with making fusion reactors more efficient, by having a higher abundance percentage of Helium-3, which is used as a fuel in those reactors. If a Moon base can prove to become autonomous, we could outsource some of our CO2- intensive industries to the moon, if it also proves to be economically viable French:base lunaire German: Mondbasis Polish: baza księżycowa Swedish: månbas Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=moon+base https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moonbase https://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2021/nasa-s-artemis-base-camp-on-the-moon-will-need-light-water-elevation/ | |||
Moon Treaty | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short Definition
Sample Sentence(s) Moon Treaty is an important Agreement, and its topics are still important discussion today. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Traité sur la Lune German: Mondvertrag Italian: Trattato sulla Luna Polish: Traktat Księżycowy, Układ Księżycowy Swedish: Månfördraget Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
N |
|---|
Nadir | ||
|---|---|---|
Media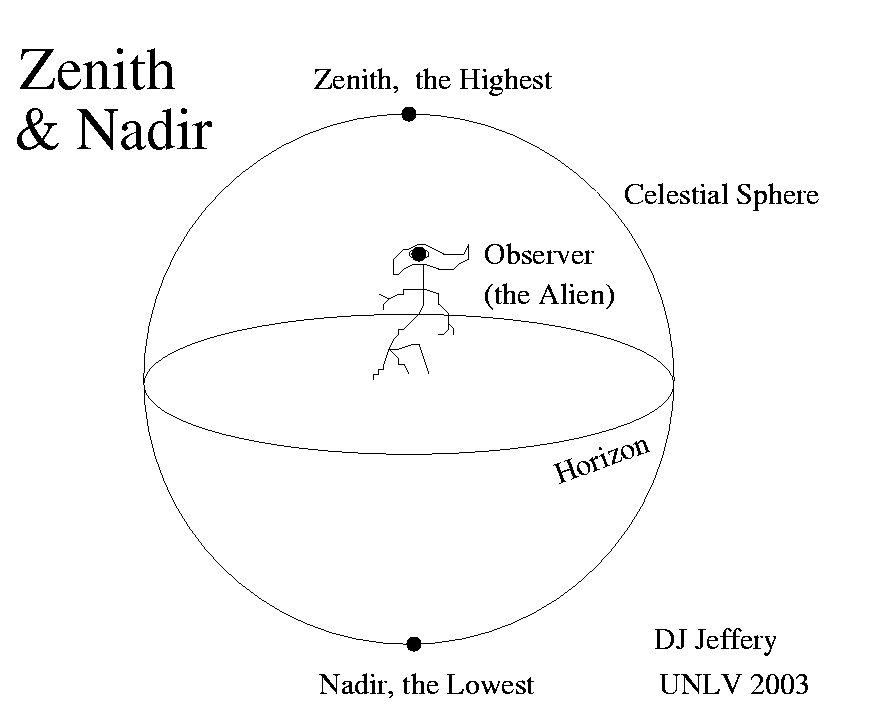 Media Zenith & Nadir, DJ Jeffery, University of Nevada, Las Vegas, 2003 DefinitionsShort Definition Detailed Definition In medicine, nadir is predominantly used to describe blood cell counts at their lowest during chemotherapy. Each chemotherapy treatment comes with the nadir period. Figuratively, nadir means the lowest point and may be used to emphasize the state of one’s feelings, quality of activity and affairs. Etymology Sample Sentences A nadir image is a satellite image or an areal photo of Earth taken vertically in the downward alignment. During chemotherapy, the nadir time usually comes in about 10 days after the start of treatment, although this is mostly dependent on drugs given. The relationship between the USA and USSR reached its nadir in the 1980s. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French German Italian Polish Swedish Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Languages Russian Ukrainian Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
National Aeronautics and Space Administration | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: https://www.nasa.gov/audience/forstudents/5-8/features/symbols-of-nasa.html Definition:National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency responsible for America’s civil space program, which aims to research areas of space for the benefit of humanity. National Aeronautics and Space Administration is a global leader in space exploration. It has 20 centres and facilities across the United States. Basic activities of the agency are studying the Earth, climate, Sun, Solar System and beyond. It conducts research (missions), testing and development to advance and develop space technologies. NASA's work also includes cooperation with U.S. industry, international partners, as well as with academia. Sample Sentence(s):National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) unveiled its newest supercomputer, the Columbia, which is powered by 10,240 Intel Itanium 2 processors." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.nasa.gov/ | |||
Nebula | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source : Kirk, A. (2015, April 25). The Mighty Orion Nebula from New Zealand. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/67481624@N05/17243621226 Short Definition: Any kind of giant cloud that includes miscellaneous gas and dust; especially hydrogen, cosmic dust, and helium located in outer space. Detailed Definition: As the basic components of galaxies, nebulae were stars before they formed. During the formation phase of these stars, the gases released into space initiate a fusion reaction with hydrogen atoms and form the foundations of a new star. Thus, the universe continues to expand. Etymology: Ancient Greek (νεφέλη - nephélē): Cloud Sample Sentences: 'Today the term nebula generally refers exclusively to the interstellar medium.' 'A nebula that is visible to the human eye from Earth would appear larger, but no brighter, from close by.' Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French: Nébuleuse Italian: Nebulosa German: Nebel Polish: Mgławica Turkish: Nebula Links to Videos/Articles: https://spacecenter.org/what-is-a-nebula/ https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/nebula/en/ https://www.space.com/nebula-definition-types https://www.britannica.com/science/nebula | |||
Neil Armstrong | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short
Definition
After earning a degree in aeronautical engineering from Purdue University in 1955, Armstrong began working as a civilian research pilot for the organization that would later evolve into the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). In 1962, Armstrong joined NASA's space program and 7 years later, on July 20, 1969, he made history by stepping onto the surface of the moon, saying his iconic words, "That's one small step for [a] man, one giant leap for mankind." Following this achievement, Armstrong resigned from NASA in 1971. He then dedicated himself to teaching in the Department of Aerospace Engineering at the University of Cincinnati until 1979. He passed away in 2012 at the age of 82.
Etymology Sample Sentence(s) "Neil and Buzz's footprints will be on the Moon for millions of years, because there is no wind to blow them away.” Who was Neil Armstrong? (2022). BBC Bitesize. https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/zhpchbk/articles/z4w3mfr
Links to Videos/Articles:
● Who was Neil Armstrong? (2022). BBC Bitesize. https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/zhpchbk/articles/z4w3mfr ● Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia (Invalid Date). Neil Armstrong. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/biography/Neil-Armstrong ●
NTD. (2012, August 25). Neil Armstrong - First Moon Landing 1969
[Video]. YouTube. ● Banijay History. (2018, October 10). First Man on the Moon: The Real Neil Armstrong | History Documentary | Reel Truth History [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fXTML_0DBDM | ||
NEO (Near-Earth Object) | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Video from NASA explaining NEO: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r-OCcFnp2RA Short Definition:NEO, or near-Earth object, is a celestial body which is in the size range of meters to tens of kilometres, that orbits the sun and approaches the earth within the distance of 1.3 AU (astronomical units). Detailed Definition:Among the 600,000 known asteroids, only 20,000 of them are NEOs. To be classified as such, the object must be natural and cannot be manmade. Some of them could potentially hit the earth and for this reason, some organisation keep track of them everyday. Historically speaking, NEOs have had an impact of the earths geological and biological history. Most of the NEOs are Apollo asteroids (55.4%), meaning that they come from the Apollo asteroid group. The second most common are Amor asteroids (36.4%), and third most common are Aten asteroids (7.7%). Etymology:Acronym of "near-Earth object." Sample Sentence:An astronomer would for example say during a lecture: “The Amor asteroid, 433 Eros, was the first NEO discovered in 1898, by D. Witt of Berlin, Germany, using a photographic plate to record its position.” Translations:
Links to Articles/Videos: | ||
Neptune | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short
Definition
Sample Sentence(s)
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
French
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Lang... Dutch Neptunus Turkish Neptün Spanish Neptuno Links to Videos/Articles: ● Miner, E. D. (Invalid Date). Neptune. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/place/Neptune-planet · Moses, J. A., Cavalié, T., Fletcher, L. N., & Roman, M. R. (2020). Atmospheric chemistry on Uranus and Neptune. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 378(2187), 20190477. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2019.0477 ● In Depth | Neptune – NASA Solar System Exploration. (n.d.). NASA Solar System Exploration. https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/neptune/in-depth/ ● National Geographic. (2019, March 28). Neptune 101 | National Geographic [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NStn7zZKXfE ●
Astrum. (2016, October 13). Our Solar System’s Planets: Neptune [Video].
YouTube.
| ||
Neutron star | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Short Definition: A Neutron star is a celestial body
and is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star that had a total mass of
about 10-25 solar masses. Compared to other stellar objects, they are much
smaller and much denser. Not counting black holes or hypothetical stellar
objects, they are the densest stellar object in the universe. Detailed Definition: A Neutron stars is a stellar object, which is only a few kilometres in
diameter, but has the mass of a star. So even compared to others stellar objects they have a mind-boggling density and are even so dense, that they are on the
cusp of becoming a black hole. Stars hold an equilibrium between the force of
gravity forcing plasma inwards, which in turn enables fusion of hydrogen to
helium, and this releases energy that pushes outwards. So the equilibrium is
directly linked to the amount of hydrogen available in stars. Breaking this equilibrium
in our sun would result in it transforming to a red giant and then to a white
dwarf. In those massive supergiant stars, gravity will prevail and will
compress the core to the density of an atomic nucleus, which in turn forces
heavier elements to fuse, and thus the outer layer will get bigger by a factor
of x100. After a time the heavier elements are fused to iron and can not be fused any more, so the fusion activity will cease, and the star will collapse to its
core. Electrons and Protons will be forced into each other and form Neutrons as
dense as in atomic nuclei, where nuclei are so densely packed, they form a
layer that is called nuclear pasta. Another interesting property is that they
are spinning really fast, which empowers their magnet fields and gives them the
strongest magnet field in our universe. Etymology: Neutron from Ne and uterà neutral +on ending from ion subatomic particle suffix Star from Proto-Indo-European rooth₂stḗrSample Sentence(s): The physics in the core of the Neutron stars are still largely unknown and are still subject of speculation. Scientists were able to detect gravitational
waves of two merging Neutron stars and confirmed the theory of Albert Einstein. French: Étoile à neutrons German: Neutronenstern Polish: Gwiazda neutronowa Swedish: Neutronstjärna Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=udFxKZRyQt4&list=PLFs4vir_WsTwEd-nJgVJCZPNL3HALHHpF&index=16 https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/science/neutron_stars.html | |||
Nicolaus Copernicus | ||
|---|---|---|
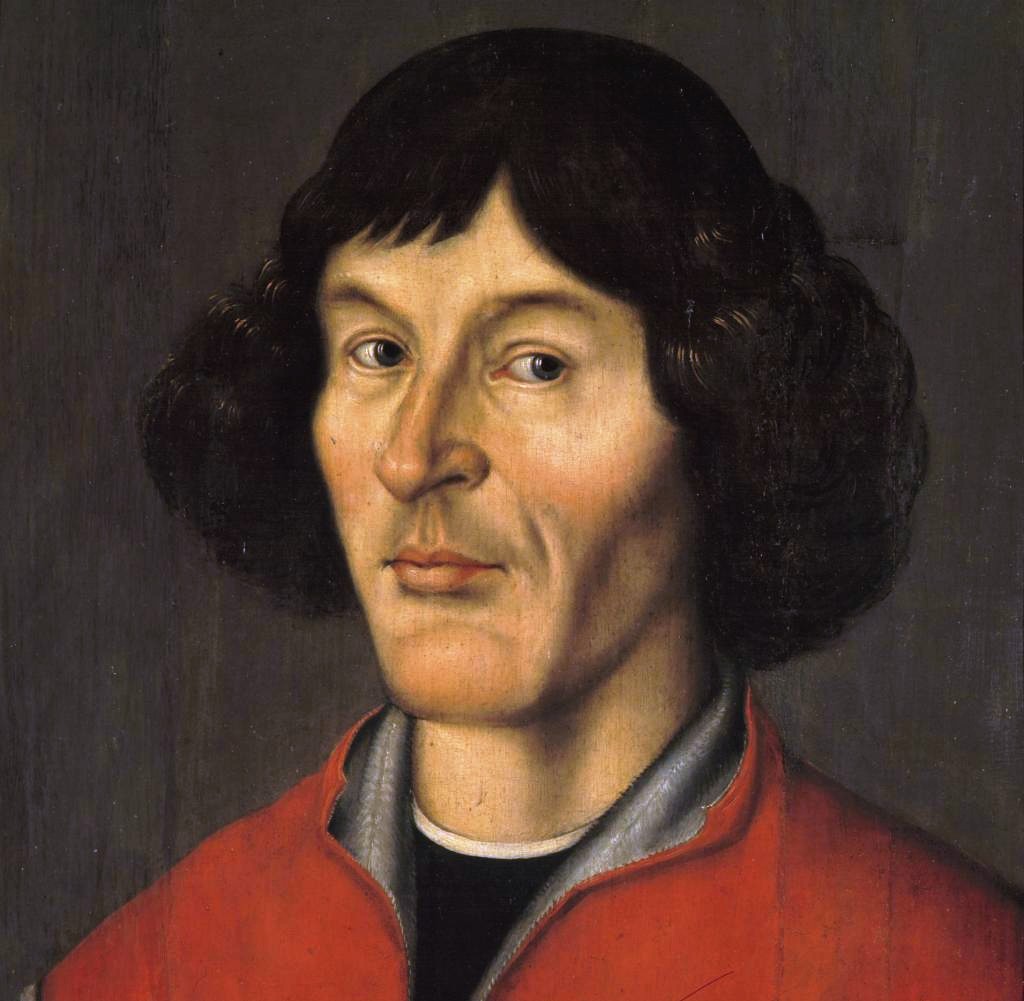 https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Nicolaus_Copernicus#/media/File:Nikolaus_Kopernikus.jpg Author : Unknown Year: (n.d.) Title: Nicolaus Copernicus Description: Portrait of Nicolaus Copernicus Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nikolaus_Kopernikus.jpg
Definitions
Etymology Sample Sentence(s) 1. Before Nicolaus Copernicus published his heliocentric theory, people generally agreed that the Moon and the Sun orbited the motionless Earth and that Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn were beyond the Sun in that order. Author : Britannica Year: (n.d.) Title: Nicolaus Copernicus Source: Encyclopedia Britannica Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from https://www.britannica.com/biography/Nicolaus-Copernicus
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French German Italian Polish Swedish Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Lang... Russian : Николай Коперник Links to Videos/Articles: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/7740908.stm Author : BBC News Year: 2008 Title: Poland honours Copernicus Source: BBC News Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/7740908.stm https://www.britannica.com/biography/Nicolaus-Copernicus
| ||
O |
|---|
Orbit | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Image Source: MS Paint (2023, May 25). MS Paint Illustration of orbits. ms paint. ms paint Short Definition: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6cUe4oMk69E&list=TLGG8tIphgpDAHkxMzA0MjAyMw&t=1s | |||
Orbit (entry exists but has poor description) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Image source: Short Definition: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6cUe4oMk69E&list=TLGG8tIphgpDAHkxMzA0MjAyMw&t=1s | |||
Orbital Manufacturing | ||
|---|---|---|
The concept of orbital manufacturing visualized by a primate building space mission components with blocks. Source: Short Definition:Orbital manufacturing refers to the production of various components required for space missions in orbit. Detailed Definition:
In orbital manufacturing, parts, materials, and tools needed for space missions are manufactured in orbit around planets. This manufacturing capability provides a solution for sustainable, flexible missions and enables on-demand repair, fabrication, and recycling on critical systems. These capabilities provide tangible cost savings by reducing launch mass, as well as significant risk mitigation by reducing dependence on spare parts and/or oversizing systems for reliability. There are several advantages of manufacturing in space: The effects of microgravity and vacuum in space enable the study and manufacturing of products that would otherwise be impossible to make on Earth. When compared to launching all essential resources from Earth, the harvest and processing of raw materials from other astronomical bodies, commonly known as In-Situ Resource Utilisation (ISRU), could enable more sustainable space research missions at a lower cost. Raw materials might be transferred to low Earth orbit and processed into products before being delivered back to Earth. This aims to preserve the Earth by replacing terrestrial production on the planet. Etymology:
Orbit - Latin - orbita “course, track, impression, mark” Manu - Latin - manus “Hand” Facture – Latin - factura “Making” Sample Sentence(s):
“Was this arm made using orbital manufacturing?” “Orbital manufacturing is particularly suitable for long space missions.” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles: | ||
P |
|---|
Parabolic flight | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: https://www.esa.int/Education/Fly_Your_Thesis/Parabolic_manoeuvres Definition:Flight manoeuvre in which the aircraft alternatingly ascends and descends to achieve weightlessness or to simulate reduced gravity. Parabolic flights are performed to train astronauts in zero-g manoeuvres, giving them about 25 seconds of weightlessness out of 65 seconds of flight in each parabola. During such training, the airplane typically flies about 40–60 parabolic manoeuvres. Initially, the aircraft climbs with a pitch angle of around 45 degrees, the sensation of weightlessness is achieved by reducing thrust and lowering the nose such that the aircraft follows a ballistic trajectory. Weightlessness begins while ascending and lasts all the way "up-and-over the hump", until the craft reaches a downward pitch angle of around 40 degrees. Etymology:from Ancient Greek παραβολικός /parabolikós/ “of or pertaining to a parable” Translations:
| |||
Parallax | ||
|---|---|---|
Media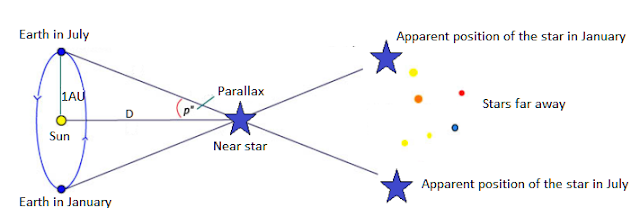 Insight Observatory (n.d.). Star Parallax. DefinitionsShort Definition Detailed Definition Etymology Sample Sentences Eyes of live creatures with binocular sight, humans included, exploit parallax to perceive depth and measure distances. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages Frenchla parallaxe
German
die Parallaxe
Italian la parallasse
Polish paralaksa
Swedish parallax
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other LanguagesRussian Ukrainian Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Parsec | |||
|---|---|---|---|
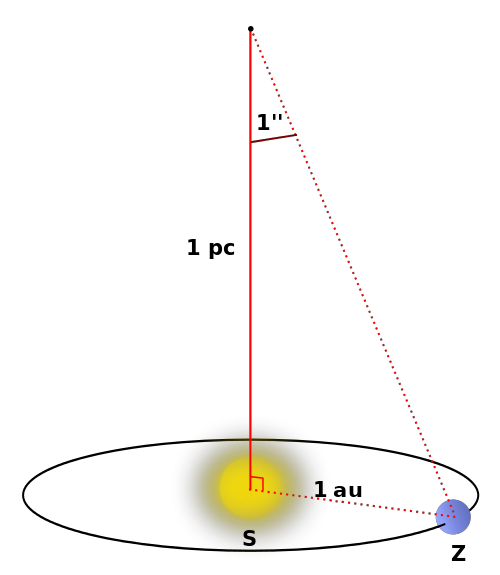 Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Parsek_pl.png Short Definition: The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System. Parsec is approximately equal to 3.26 light-years or 206,000 astronomical units (symbol: AU), or 30.9 trillion kilometers. As an example, the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is about 1.3 parsecs from the Sun. Most stars visible to the naked eye are within a few hundred parsecs of the Sun, with the most distant at a few thousand. Detailed Definition: A Parsec is the distance for which the annual parallax of the position of the Earth, viewed perpendicular to the plane of the orbit, is 1 arc second (arcsec). A parsec can equally be described as the distance from which half of the Earth's orbital major axis (equal to 1 AU) is visible as an arc of 1 arcsecond. Although distance equal to one parsec is tremendous still, multiples of parsecs are required for the larger scales in the universe, including kiloparsecs (kpc) for the more distant objects within and around the Milky Way, megaparsecs (Mpc) for mid-distance galaxies, and gigaparsecs (Gpc) for many quasars and the most distant galaxies. The term parsec is a combination of "parallax" and "arcsecond," which derives from the use of triangulation when measuring the distance between two stars. Etymology: Combination of words parallax and arcsecond Sample Sentence(s): "Distance to the nearest star is about 1.3 parsecs." Translations: French: Parsec German: Parsec Polish: Parsek Swedish: Parsec Links to Videos/Articles: https://earthsky.org/space/what-is-a-parsec/ | |||
Perihelion | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Diagram of a body's direct orbit around the Sun, with its nearest (perihelion) and farthest (aphelion) points. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apsis#/media/File:Perihelion-Aphelion.svg Short Definition: Perihelion is the farthest point in the orbit of a planetary body about the Sun. This point is present in every Solar System orbiting body orbit due to the fact all orbits are elliptical. Detailed Definition: Perihelion is the farthest point in the orbit of a planetary body about the Sun in the Solar System. In case of describing generic star orbiting system, such point is called an apsis as the farthest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For bodies moving around the Sun in a stable elliptical orbit, the perihelion is crossed at regular intervals, every orbital period. At perihelion, the Earth is 147.1 million km (0.9833 au) from the Sun. This usually takes place between 2nd and 4th January and occurs at a slightly different time each year due to interference from other celestial bodies. Etymology: From Proto-Indo-European *per- (“before, in front; first”) + ἥλιος (hḗlios, “sun”) + -on (suffix forming nouns) (from Ancient Greek -ον (-on)) Sample Sentence(s): "If the comet's perihelion (its closest point to the sun) coincides with the shower's peak, a rare meteor storm can occur, creating thousands of meteor showers per hour." - Skyler Caruso, Peoplemag, 4 Oct. 2022 "Earth makes its closest past on Jan. 4, which is called perihelion." - Dave Epstein, BostonGlobe.com, 4 July 2022 Translations: French: Périhélie German: Perihel Polish: Peryhelium Swedish: Perihelium Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.space.com/what-is-perihelion | |||
Perseids Meteor Shower | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Sutton, B. (2015, August 19). Perseid Meteor Shower over the Ocotillo Patch; 8/12/15. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/115357548@N08/20713070995 Definition:A meteor shower that recurs annually between the July 17th, and August 24th, with a peak of shooting stars in the days around August 12th. They have a high velocity (60 km/s) and, as so-called fireballs, can even reach the brightness of Venus. The radiant, apparent origin of this shower, lies in the eponymous constellation Perseus, near its border with Cassiopeia. Etymology:from Greek Περσείδαι “Perseidai”, the sons of Perseus in Greek mythology Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:Perseid meteor shower on NASA TV 2015 (4 hours)https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DIvVLyltJe8 | |||
Phobos | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:
Etymology:Named after Phobos, the ancient Greek god of fear, twin brother of Deimos, son of Ares (the equivalent of the Ancient Roman god of war Mars). Translations:
| |||
Photometer | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2018/04/Photometer Short Definition: A photometer is an instrument used to measure the strength of electromagnetic radiation. It is the primary tool used in the field of photometry, a field that focuses on the study of the emitted intensity of the electromagnetic radiation of an astronomical body. Detailed Definition: One of the devices used in the research electromagnetic radiation is the photometer. The most crucial component of the photometer is a photoresistor, photodiode, or photomultiplier, varying on the type of the photometer, which is responsible for the conversion of light into electric current. Among others, photometers most commonly measure illuminance, irradiance, light absorption, fluorescence, and luminescence. Most of the photometers measure light by the incoming flux, however, photon counting is also a viable technique. Light detection occurs after the light passes through a filter, which then distinguishes the respective wavelengths. Photometers are used in many medical, laboratory and industrial applications. Uses include the identification and quantification of chemical components, pharmaceutical quality control and astronomical calculations. Etymology: "photo-" - Greek, combining form of phōs (genitive phōtos) - word-forming element meaning "light" "-meter" - French -mètre, Greek metron - word-forming element meaning "a measure" Sample Sentence(s): "Photometers are used to gather data for improved lunar calibration of Earth-observing instruments." "A photometer is often used in conjunction with a telescope." Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Photomètre German: Fotometer Polish: Fotometr Swedish: Fotometer Links to Videos/Articles: https://planetfacts.org/photometer/ https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-photometry-definition-process-uses.html https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=95_yDQ9tAfs | |||
Pillars of Creation | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short Definition The Pillars of Creation are a part of the Eagle Nebula that is located in constellation Serpens. They became popular when Hubble Telescope took first picture of them in 1995. The Pillars of Creation since then were revisited by various telescopes on multiple occasions throughout the years.
In Pillars of Creation, we can see new stars being formed. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
French
German
Italian
Polish
Swedish Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Planet | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Starkiteckt (2016, June 30). Icy Planet. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/141051222@N04/27966261236 Definition:A large round celestial body orbiting around a star. EtymologyFrom the Greek word “πλανήτης” (“wanderer”). Translations:
| |||
Planet Mars | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Term/Concept: Planet Mars Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| |||||||||||
Planetary geology | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short definition: Planetary geology is a science discipline that focuses on the geology of solid-surface celestial bodies, such as planets and their moons, asteroids and meteorites. It is also known as space geology, astrogeology or exogeology. Detailed definition: Planetary geology is a relatively new discipline, having appeared in the 1960s. Some topics that planetary geology is concerned with are: studying and analysing the composition of celestial bodies to better understand their origins and history; determining the properties and processes in the internal structure of astronomical objects, such as their volcanism, impact craters and fluvial processes; classifying exoplanets based on their geology and composition. Planetary geology is closely linked with the Earth’s geology, and many planetary geology studies are conducted by comparing the geology of the celestial body with the Earth’s geology. One of the main aims of these studies is trying to figure out whether other planets are capable of supporting life. Etymology: Even though the prefix -geo comes from Ancient Greek γῆ (gê, “earth”) and is mostly associated with topics related to the Earth, planetary geology is named as such for historical and convenience reasons. Sample sentence(s): Planetary geology researchers at Harvard contribute to robotic space missions to other planets. Translations:
French: Géologie planétaire German: Astrogeologie Italian: Esogeologia Polish: Geologia planetarna Swedish: Astrogeologi Links to Videos/Articles:
Byrne, P. K. (2021). Planetary Geology. In Elsevier eBooks (pp. 37–51). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-102908-4.00125-9 TAWNIA VANDERWOOD. (2019, August 20). Meet a Planetary Geologist [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/POMlppgXgM4 | ||
Point Nemo | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 25). AI illustration of point nemo. Midjourney. midjourney Space junkyard... Tags: space junkyard Keyword(s): Space Junkyard Probe (Last edited: Monday, 24 July 2023, 3:44 PM) Source: Todd, G. (October 2013). Mariner Space Probe. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/101561334@N08/10437025414 Space junkyard... | |||
Probe | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Todd, G. (October 2013). Mariner Space Probe. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/101561334@N08/10437025414 Short Definition: A probe is a smaller spacecraft meant to explore the space, but will return to a space station upon return from the exploration. Detailed Definition: A probe's role is to study other planets and moons, perform scientific observations and gather data about the universe. It's an unmanned spacecraft that can be remotely controlled and monitored during its mission. Some famous probes include Voyager, Pioneer and Galileo probes. Etymology: From latin proba - meaning "proof" Sample Sentence(s): Voyager 2 probe was launched in 1977. Translations: French: sonde German: Sonde Polish: Sonda Swedish: sond Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/parker-solar-probe https://www.space.com/40437-parker-solar-probe.html | |||
Q |
|---|
Quasar | ||
|---|---|---|
 Creator(s): Unknown Year: (n.d.) Title of image: Artist's rendering of ULAS J1120+0641 Description of image: Artist's rendering depicting ULAS J1120+0641, a distant quasar discovered in 2011. Retrieved from URL: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Artist%27s_rendering_ULAS_J1120%2B0641.jpg on May 29, 2023
Definitions
Sample Sentence(s) 1. In 1963, the first measurement of the distance to a quasar — a radio source that looks like a star in visible light — showed it to be an enormously powerful beacon lying billions of light years away. Author : Rober Antonucci, Year: (2013) Title of the article: Astronomy: Quasars at record distance Title of the Journal: Nature Volume : 495(7439) Page range: 165-166, Retrieved from https://www.nature.com/articles/495165a on May 29, 2023
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French German Italian Polish Swedish Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Lang... Russian: Квазар Links to Videos/Articles:
https://www.britannica.com/science/quasar | ||
R |
|---|
Radiation | ||
|---|---|---|
Image:  Image: Source: https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Engineering_Technology/Proba_Missions/Detecting_radiation Short Definition: Generation of strong and hazardous energy that results from atoms being broken up. Detailed Definition: The full process through which energy is released by one body, transported across a space or other intermediary, and then absorbed by another body. The universe is full of radiation as it is a form of energy that is emitted in the form of rays, electromagnetic waves, and/or particles, which are found all over the cosmos. Radiation may be utilized cautiously to learn more about biological and mechanical systems, despite the fact that it can also be harmful to both of these systems. Etymology: Radiation comes from the Latin radiare, which means emit rays. Sample Sentence(s): High radiation doses are administered to patients during cancer therapy. Alpha particles are an illustration of ionizing radiation. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: radiation German: Strahlung Polish: promieniowanie Swedish: strålning Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nasa.gov/feature/how-nasa-prepares-spacecraft-for-the-harsh-radiation-of-space https://www.nasa.gov/analogs/nsrl/why-space-radiation-matters | ||
Reaction control system | ||
|---|---|---|
Image Image Shepard, A., NASA. (1972, December). Apollo 14 LM RCS quads. Retrieved form https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/2d/LM_RCS.jpg Short Definition Reaction control system (RCS) is a system of low-thrust engines that is used to control orientation of a spacecraft in space (attitude control) and for fine position and velocity adjustments. Detailed Definition The reaction control system of a spacecraft consists of multiple low-thrust engines that are placed symmetrically on the spacecraft equidistantly from its barycentre to ensure even force and torque distribution. Thrusters can provide thrust in any direction and combining thrusters in different positions allows acquiring force in any direction or torque in any plane, which enables the spacecraft to perform translational motion in any direction and any of roll, pitch and yaw rotations. RCS is used for attitude control (for example, to keep a telescope pointed at one object for a long time), precise manoeuvring (for example, while spacecraft docking), orbit correction and other purposes. Etymology Reaction – re- (back, again, anew) + action (from French réaction)Control – from Anglo-French contreroller– exert authoritySystem – from Late Latin or Greek systema– an arrangement, organized whole, a whole compounded of parts Sample Sentences The spacecraft's reaction control system precisely adjusts the orientation and stability of the vehicle during maneuvers in the microgravity environment of space. Translations in partner languages: German: Reaktionskontrollsystem (RCS) French: système de contrôle de la réaction (RCS) Swedish: seaktionskontrollsystem (RCS) Polish: system sterowania reakcyjnego (RCS) Italian: sistema di controllo della reazione (RCS) Translations in other languages: Russian: Реактивная система управления Ukrainian: Реактивна система керування References Colas, A. L., Valenzuela, J. G. (2020, August). Reaction Control System Performance Characterization using Vacuum Chamber Thrust Stand. Retrieved form https://arc.aiaa.org/doi/10.2514/6.2020-3526 Boeing. (2006, November). ISS Motion Motion Control System. Retrieved from http://forum.nasaspaceflight.com/index.php?action=dlattach;topic=34777.0;attach=586775 | ||
Reaction engine | ||
|---|---|---|
Image  Image U.S. Air Force. (2010, November). F100 F-15 engine. Retrieved from https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/69/F100_F-15_engine.JPG Short Definition A reaction engine is an engine that produces thrust by expelling reaction mass. It works in accordance with the third Newton's law of motion. Detailed Definition Reaction engines work in accordance with the third Newton's law of motion, stating that for every action force there is an equal by magnitude, but opposite in direction, reaction force. Thus, reaction engines apply force to the reaction mass, under which reaction mass accelerates and leaves the engine. As a result, the engine together with the vehicle are accelerated by the reaction force that makes the vehicle move. Jet engines and different types of rocket engines are reaction engines. In fact, this is the only engine capable of working in a vacuum, since there is nothing to propel a vehicle besides the fuel (reaction mass) carried by the vehicle itself, which makes those engines the only applicable to spacecrafts. Reaction engines have a broad application area that is not limited to space. For example, boats and ferries are often powered by reaction engines. But instead of a jet of heated gas, they expel water. Etymology Reaction – re- (back, again, anew) + action (from French réaction)Engine – from Middle English engyn or Anglo-Norman engine or Old French engin– skill, cleverness, war machine Sample Sentences The reaction engine utilized a combination of fuel and oxidizer to generate thrust for propulsion. Translations from alliance partner languages: French: Moteur de réactionGerman: Rückstoßantrieb Italian: Motore a reazione Polish: Silnik reakcyjny Swedish: Reaktionsmotor Translations from other languages: Belarusian: Рэактыўны рухавік References The European Space Agency. (2020, December). System study results for SABRE-powered reusable launcher. Retrieved from https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Transportation/Future_space_transportation/System_study_results_for_SABRE-powered_reusable_launcher Petrescu, R. V., Aversa, R., Apicella, A., Petrescu, F. I. T. (2018, January). Romanian Engineering, "On the Wings of the Wind". Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.3844/jastsp.2018.1.18 | ||
Redshift | ||
|---|---|---|
 Image Source: https://itu.physics.uiowa.edu/sites/itu.physics.uiowa.edu/files/2021-08/itu/redshift_galaxyspectra.png Short Definition:
Redshift is a physical concept which describes a shift in the light spectrum towards the red part of the spectrum which is emitted by distant galaxies. Based on this phenomenon the Hubble Law was concluded which states that the velocity at which the galaxies receded were proportional to the distance and that the redshift increased with the distance. Detailed Definition:
This phenomenon was described as an effect of the Doppler shift when it was first discovered by Hubble. The Doppler shift is a effect where an observer which moves away from a light source can see light with a longer wavelength than the emitted light (redshift). If the observer moves towards the light source the light appears to have a shorter wavelength (blueshift). A characteristic of the universe which was concluded by Edwin Hubble by the redshift is that the Universe is expanding. The previously mentioned Hubble Law is the following cosmological velocity-distance law in a equation: velocity = Ho x distance. The variable Ho is the Hubble constant, which describes how fast the universe is expanding and isn´t yet measured. Etymology:
Red – German röthe (“redness, red”) Shift – Proto- Germanic skiftan (“to divide, change, seperate”) Sample Sentence(s):
“Red shift” is a key concept for astronomers. Relativistic, gravitational and cosmological redshifts can be understood under the frame transformation laws. Translations:
French: Déplacement vers le rouge
German: Rotverschiebung
Polish: Przesunięcie ku czerwieni
Swedish: Rödförskjutning
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
RemoveDEBRIS Mission | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:A mission under the supervision of the Surrey Space Centre of the University of Surrey (supported by Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd., Airbus Defense and Space, Innovative Solutions in Space, CSEM, Inria and Stellenbosch University) that aimed to find the best method of capturing and removing space debris. The project was based on a satellite containing several pieces of equipment (a net, a harpoon, a drag sail and vision-based navigation equipment, as well as a set of targets simulating space debris), which remained in orbit between 2018 and 2021. The satellite platform for the project RemoveDEBRIS was launched using SpaceX Falcon 9, was delivered to the International Space Station and later deployed into orbit, where a series of experiments on debris removal were conducted, using several pieces of equipment:
Translations:
Links to Videos:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XLuHk5gWx3k https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_QUhCLTfXf0 Articles:https://www.surrey.ac.uk/surrey-space-centre/missions/removedebris https://www.airbus.com/en/products-services/space/in-space-infrastructure/removedebris https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/r/removedebris | |||
Rocket engine | ||
|---|---|---|
Image  Image NASA. (2000, January). RS-68 being tested at NASA's Stennis Space Center. Retrieved from https://www.nasa.gov/images/content/148709main_d4_testing_08.jpg Photograph of a rocket engine in operation, with a converging plume of hot gas streaming out from the nozzle Short Definition A rocket engine is a jet engine that discharges a jet of high-temperature gas as reaction mass, which was acquired from the propellant stored internally in a vehicle. Rocket engines, unlike general jet engines, can only use internally stored propellant to create a jet, because they have to operate in space, where there is no medium like air or water which can be used as a reaction mass in jet engines on Earth. Detailed Definition A rocket engine is an internal combustion jet engine that discharges a jet of high-temperature gas as reaction mass, which was acquired from the propellant stored internally in a vehicle. Rocket engines, unlike general jet engines, can only use internally stored propellant to create a jet of gas as a result of chemical reactions, because they have to operate in space, where there is no medium like air or water which can be used as a reaction mass in jet engines on Earth. The nozzle is always an integral part of a rocket engine because it makes the jet accelerate as gas moves through the nozzle, and the higher the speed of a discharged jet, the more efficient the engine. The de Laval nozzle is the most common type of nozzles used in rocket engines, as it accelerates the gas passing through it most efficiently. Gas, when burnt, moves at a low subsonic speed and accelerates as it moves through the nozzle, reaching supersonic speed by the moment it leaves the nozzle. Etymology Rocket – from Old Italian rochetto– a bobbinEngine – from Middle English engyn or Anglo-Norman engine or Old French engin– skill, cleverness, war machine Sample Sentences The rocket engine ignited with a powerful roar, propelling the spacecraft into space. Translations from our alliance partners' languages: French: Moteur-fuséeGerman: Raketentriebwerk Italian: Motore a razzo Polish: Silnik rakietowy Swedish: Raketmotor Other language translations: Russian: Ракетный двигатель Ukrainian: Раĸетний двигун Belarusian: Ракетны рухавік References Braeunig, R. A. (2012). Rocket propulsion. Retrieved from http://www.braeunig.us/space/propuls.htm Oberth, H. (1972, January). Ways to spaceflight. Retrieved from https://archive.org/details/nasa_techdoc_19720008133/page/n35/mode/2up | ||
Roscosmos | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:Russian state corporation formed in 2015 and responsible for various aspects of the country’s space exploration activities (space equipment, infrastructure, international cooperation, etc.). The corporation is a legal successor of the Soviet space program which existed from 1955 to 1991 and Russian Space Agency founded in 1992. EtymologyThe name of the corporation “Роскосмос” consists of two elements: “Рос” (abbreviation for “Russian”) and “космос” (“space”). Translations:
| |||
Rover | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Image/Video/Audio Source: Author: Kamila Kopacz Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Other sources: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GMMQUXrcOGY https://www.britannica.com/topic/Mars-Exploration-Rover | |||||||||
S |
|---|
Satellite data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: NOAA Images (2015, August 18). Hurricane Katrina as seen by NOAA satellite. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/77790740@N08/20676559362 Definition:Satellite data, also referred to as satellite imagery, provides information about Earth and other planets in space, which are collected by man-made satellites in their orbits. Satellite data allow us to observe the Earth, as satellites deliver information about the surface and weather changes on the planet Earth. Satellite data is generated via remote sensing technologies. In fact, it is very useful for providing authentic information about the atmospheres, oceans and land masses by constantly collecting data from joined satellites. Etymology:The english word satellite derives from Latin satelles which means "accomplice, follower, attendant, or guard." There are natural satellites, e.g. the planet Moon which is following the Earth on a fix route, but also several artificial satellites which fulfill certain task, e.g. scientific or commercial. Data is the classical plural of Latin datum which means (thing) given. In classical use originally ". From 1897 the term is referred to as "numerical facts collected for future reference." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles: | |||
Solar Eclipse | ||
|---|---|---|
Short Definition
Sample Sentence(s) A solar eclipse cannot be visible from all the places on Earth all at once. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
French
German
Italian
Polish
Swedish Links to Videos/Articles: Hocken, V. (n.d.), What Are Solar Eclipses?, Retrieved from https://www.timeanddate.com/eclipse/solar-eclipse.htmlNASA Science SpacePlace Explore Earth and Space (n.d.), What Is Solar Eclpise?, Retrieved from https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/eclipse-snap/en/ Dobrijevic, D. (n.d.), What is a solar eclipse?, Retrieved from https://www.space.com/15584-solar-eclipses.html Online Etymology Dictionary (n.d.), eclipse (n.), Retrieved from https://www.etymonline.com/word/eclipse Online Etymology Dictionary (n.d.), solar (adj.), Retrieved from https://www.etymonline.com/word/solar#etymonline_v_23841 ESA (2015), Europe’s solar eclipse seen from Proba-2, Retrieved from https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Videos/2015/03/Europe_s_solar_eclipse_seen_from_Proba-2 | ||
Solar sail | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 31). . midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition: Solar sails (also known as light sail or photon sail) are a method of spacecraft propulsion using radiation pressure exerted by starlight on large mirrors. Solar sails can be used instead of traditional fuel consumption. First proposed in the 1980s as alternative propulsion method for low-weight long-distance spacecrafts, the first real usage of the solar sail system was in JAXA’s IKAROS mission, launched in 2010. Detailed Definition: The Solar sails use a phenomenon called solar pressure, which is the force produced by the impact of sunlight photons on the surface of the spacecraft. Normally, solar pressure is affecting all spacecrafts during flights and must be accounted for in trajectory planning, but in that specific case it is used as thrust. Vessels using solar sails must be lightweight as the total force exerted on an eight hundred by eight hundred meters solar sail is about 5 Newtons at Earth's distance from the Sun, so this propulsion method requires specially constructed spacecraft. If solar sails are implemented in space vessel it can produce propulsion without need of fuel usage and thus can be great for small satellites to travel to distant objects without great amount of storage for fuel and engines. The negative side of this technology is significantly small force compared to traditional liquid fuel engines and fragile sail build. Also, this system cannot be used far away from “propulsion” star, as thrust generated by the solar sail is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. Etymology: Solar
- From Latin sōlāris, from sōl (“sun”), Sample Sentence(s): “The IKAROS probe is the world's first spacecraft to use solar sailing as the main propulsion system.” Translations: French: Voile solaire German: Sonnensegel Polish: Żagiel słoneczny Swedish: Sol segel Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305884757_Solar_sail_technology-A_state_of_the_art_review | |||
Solar Storm | ||
|---|---|---|
Media: 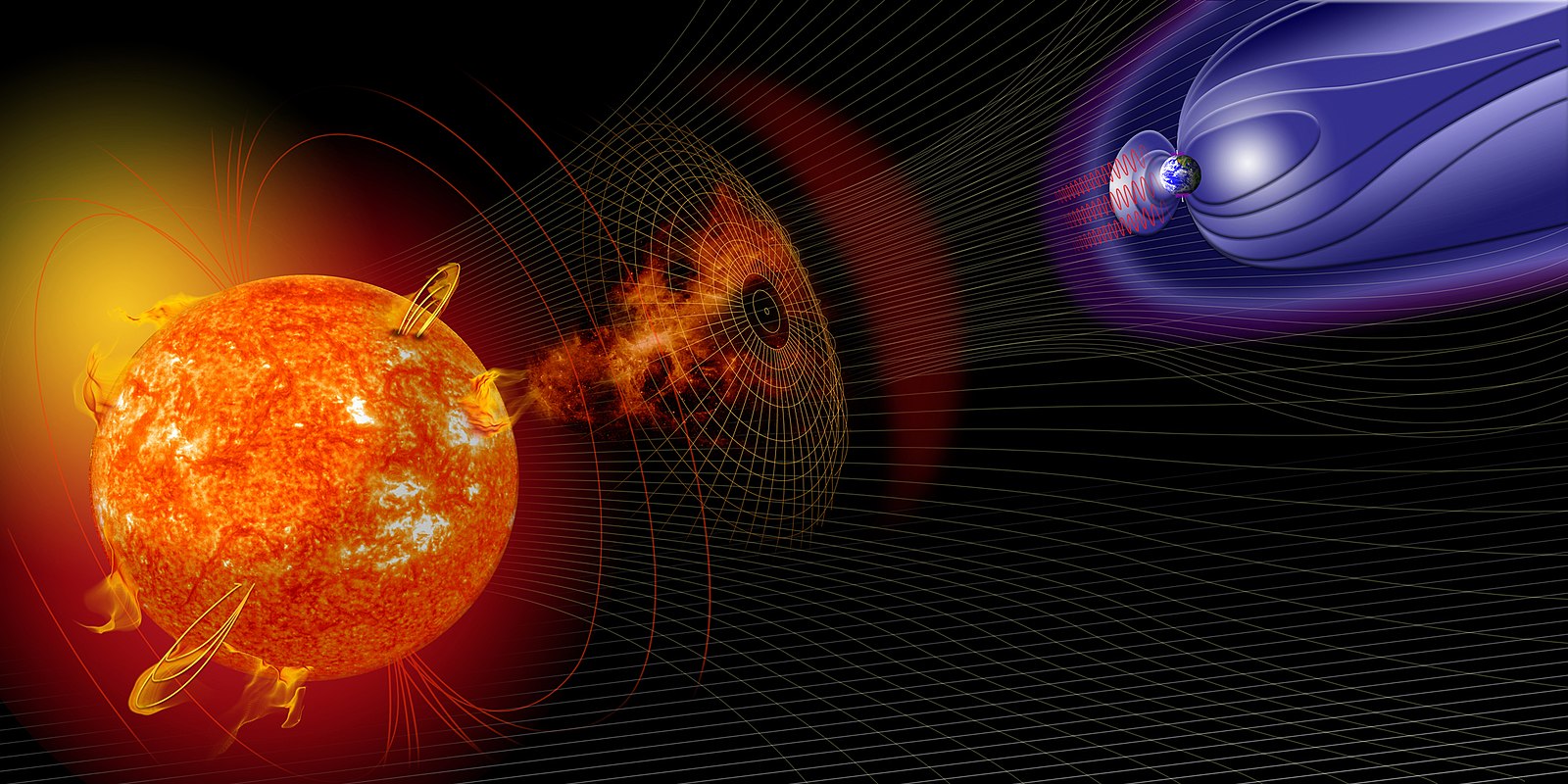 Media: File:Storms From the Sun (6819077978).jpg - Wikimedia Commons . (2005, April 24). https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Storms_From_the_Sun_%286819077978%29.jpg Short Definition: A solar storm is a magnetic eruption happening on a star, causing a large burst of particles at very high speeds. This event is usually associated with visible arches on the sun. Detailed Definition: A solar storm is a phenomenon which is caused by a magnetic eruption on the Sun, which in hand happens due to increasing velocity of charged particles in the Sun's magnetic field. Such eruption, called a solar flare, shoots out mostly protons, which achieve speeds close to the speed of light. Such protons, while reaching the Earth's magnetosphere, they get guided towards both poles and lose their speeds. The occurrence of solar storm, has some negative effects on the earth, but most of the bursts, are light enough to be neutralized by the magnetosphere. The protons that manage to reach earth, usually disturb radio communications or other services and technologies which utilize waves. Etymology solar from Latin "solaris" or "sol" meaning "the sun". Storm from Middle/Old English "storm" meaning "a disturbed state of the atmosphere, especially as affecting the earth's surface". Sample Sentence(s) - The Solar storm is depending on the solar cycle, which lasts around 11 years. - The solar storm disturbed the TV, I couldn't finish watching the game!
Translations: French - tempête solaire German - Sonnensturm Italian - tempesta solare Polish - Burza słoneczna Swedish - solstorm | ||
Sounding rocket | ||
|---|---|---|
 AGH Space Systems' Skylark rocket launch in Drawsko Pomorskie Source : Autor's photo Short Definition: Sounding rocket is a small, unmanned rocket that is meant to take measurements and perform scientific experiments on suborbital flights. Detailed Definition: A sounding rocket is a type of rocket that is used to carry scientific instruments to high altitudes for the purpose of collecting data. These rockets are typically smaller and less powerful than other types of rockets, and are launched vertically from a launchpad. The main advantage of sounding rockets is that they can reach altitudes of up to several hundred kilometers, allowing researchers to study the upper atmosphere and the effects of space on various materials and phenomena. Sounding rockets are often used for experiments in fields such as atmospheric science, astrophysics, and meteorology. Etymology: Sounding rockets take their name from the
nautical term “to sound,” which means to take measurements. The term doesn't come from any latin or greek words. Sample Sentence(s): Next week, several sounding rockets will be launched from this site. Translations: French: Fusée-sonde German: Höhenforschungsrakete Polish: Rakieta suborbitalna, rakieta sądująca Swedish: Klingande raket Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=weeEGY4SR38 https://www.nasa.gov/missions/research/f_sounding.html | ||
Space debris | ||
|---|---|---|
 Image source: Midjourney (2023, June 01). AI illustration of space debris in earths orbit. midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition:
Detailed Definition: space -> spatium from Latin - meaning: space debris -> débriser from French - meaning: break down Sample Sentence(s): French: Débris spatiaux German: Weltraummüll / Weltraumschrott Polish: kosmiczne śmieci Swedish: Rymdskepp Spanish: Desechos espaciales Links to Videos/Articles: https://youtu.be/f513HPs24VM [Space Debris by the European Space Agency, ESA] https://www.nasa.gov/news/debris_faq.html https://www.nasa.gov/centers/hq/library/find/bibliographies/space_debris | ||
Space graveyard | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:S4-space-junk-045.jpg Definition:An area on Earth's surface or orbit in which decommissioned spacecrafts or satellites are discarded. Etymology:Translations:
| |||
Space rendezvous | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:RENDEZVOUS_-_ARTIST_CONCEPT_-_GEMINI-TITAN_GT-VI_and_GT-VII.jpg Short Definition: A space rendezvous is a series of orbital maneuvers focused on bringing together two orbiting spacecrafts. In most cases, a space rendezvous occurs between a space station and a spaceship trying to dock to it. Rendezvous requires a precise match of the orbital velocities and position vectors of spacecrafts, allowing them to remain at a constant distance during final maneuvers or docking. Detailed Definition: A space rendezvous is an approach in space to a very close distance (e.g. within visual contact) between spacecrafts or between a spacecraft and a celestial object at zero or very low relative speed. The space rendezvous requires carrying out complex orbital maneuvers, which must be completed in a minimum time without excessive consumption of the propellant. Rendezvous may or may not be followed by docking or berthing, procedures which bring the spacecraft into physical contact and usually create a link between them. NASA's first attempt at rendezvous was made on June 3, 1965, when astronaut Jim McDivitt tried to maneuver his Gemini 4 spacecraft to meet the Titan II launch vehicle's upper stage. Rendezvous was first successfully accomplished by NASA on December 15, 1965, and then lead to success of Apollo's program and moon landing. Etymology: Space - From Middle English space, from Anglo-Norman space, variant of espace, espas et al., and spaze, variant of espace, from Latin spatium(“to stretch, to pull”). Sample Sentence(s): The first space rendezvous was in 1965 during Gemini program Translations: French: Rendez-vous spatial German: der Raumfahrt Rendezvous Polish: dokowanie, połączenie się statków w przestrzeni kosmicznej Swedish: Rymdmöte Links to Videos/Articles: https://airandspace.si.edu/stories/editorial/worlds-first-space-rendezvous https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oNXPtZDS-cg | |||
Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: https://www.nasa.gov/image-feature/the-canadarm2-robotic-arm-is-poised-to-capture-cygnus Short Definition: Ssrms is a manipulator system equipped with two long arms, seven attachment points, and various precision robotic equipment is also known as 'Canadarm2', it is a second-generation robotic arm system in the Mobile Servicing System of the International Space Station, whose main purpose is to take part in high-tonnage/cosmic catching missions. It is the most efficient heavy-duty robotic system (Up to 116 tons) left on the ISS after the Canadarm1 was retired in July 2011. Detailed Definition: It is a space manipulator attached to the international space station.As an improved version of the Canadarm 1, the Canadarm 2 is aimed at enhancing; size, load-carrying capacity, arm reach, durability, and increased mobility. It is a robotic system that assists astronauts with payload handling, approach and docking of space shuttles, making Cosmic catches, and maintenance of the station. The robotic arm, which can be managed by the astronauts on the ISS and the NASA and CSA centers on the world, is also adorned with advanced imaging-light systems. It is also used as an anchor point by attaching it to other robotic equipment itself. Sample Sentence(s): ''Canadarm2 is made up of parts that can be replaced while in space.'' ''Canadarm 2 will also help to berth the Axiom Space Station modules to the ISS.'' Translations: French Système de manipulateur à distance de la station spatiale Italian Sistema di manipolazione remota della stazione spaziale Polish System zdalnie sterowanego manipulatora stacji kosmicznej Turkish Uzay İstasyonu Uzaktan Manipülatör Sistemi
German Fernmanipulatorsystem der Raumstation Links to Videos/articles: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2020/04/Canadarm2_robotic_arm https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/iss/canadarm2/about.asp https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/elements/remote-manipulator-system-canadarm2/ | |||
Space tether | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: https://www.colorado.edu/faculty/kantha/sites/default/files/attached-files/sandoval_space_tethers.pdf proposed catch and release cycle of a spinning space tether Short Definition: Space tethers are long cables attached to a counterweight. It has many applications in space such as propulsion and momentum exchange etc. This idea could help lowering the amount of money needed to transport payload into low earth orbit by hooking onto specialized spacecrafts in the future and either increasing the speed for space travel or decrease it to prepare for landing.
Detailed Definition:
Despite recent achievements in making spacecrafts fully reusable, space travel and space infrastructure continues to be quite expensive and only reserved for a few institutions and companies. The aim is to commercialize space, but to achieve that goal we still need to vastly decrease the amount of money to get payload into low earth orbit. Skyhooks, a special type of space tethers, could help lowering the cost of transportation into space. The idea is to attach cable hundreds or thousands of kilometres to a counterweight and the weight spins in a circle. The tether will be lowered to be 80-150 kilometres above the earth, where it can hook onto spacecrafts and let them go at the best point to maximize speed adjustment. This idea could make reusable rockets much lighter and cheaper by lowering the amount of rocket fuel needed. This idea acts as a “orbital battery”, where decreasing the spacecrafts speed will increase the amount of energy in the tether and increasing the spacecrafts speed will decrease the amount of energy in the tether.Etymology:
Space from Latinspatium Tether from proto-Germanic teudrą(“rope;cord;shaft”)Sample Sentence(s): Space tethers could revolutionize the space industry by lowering the money needed to get payload into low earth orbit. French: Links to Videos/Articles: https://science.nasa.gov/tether-space | |||
Space Weathering | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: https://planetfacts.org/space-weathering/ Short Definition: Space weathering is a general term used for different surface processes which happen to objects and celestial bodies in the harsh environment of outer space. Detailed Definition: Bodies in the outer space, which do not have atmospheres, are exposed to a number of devastating weathering processes, such as collisions of galactic or solar cosmic rays, the irradiation, implantation and spluttering from solar wind particles; the bombardment by different sizes of meteorites and micrometeorites. These phenomena are encompassed in the blanket term space weathering. The toll that space weathering takes on both the physical and optical properties of the surfaces of many celestial bodies is an important issue, as remotely sensed data needs to be processed appropriately. Etymology: "space" - Old French espace, Latin spatium - room, area, distance, stretch of time "weather" - Old English weder, Old Saxon wedar, Old Norse veðr, German wetar - wind, weather "we-" - Proto-Germanic wedra - to blow Sample Sentence(s): "Space weathering has to be accounted for during the design of space equipment." Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Altération de l'espace German: Weltraumverwitterung Polish: Wietrzenie kosmiczne Swedish: Rymdvittring Links to Videos/Articles: https://spaceweather.com https://sservi.nasa.gov/articles/space-weathering-on-airless-bodies/ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fdzZdFZrGHA | |||
Spacecraft | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: SpaceX (2016, September 25). SpaceX's proposed Interplanetary Spaceship, at Saturn.. wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=51812109 Definition:Vehicle, machine or other apparatus designed to fly or orbit outside the Earth’s atmosphere, i.e. above the Kármán line of 100 km.Etymology:Closed compound noun, consisting of ‘space’ and ‘craft’ Translations:
Note: the Russian translation has a slightly different meaning as it includes devices operating in atmospheres and on surfaces of other celestial bodies. | |||
Spacecraft Propulsion | ||
|---|---|---|
Short Definition: Spacecraft Propulsion is a method utilised to accelerate a spacecraft and artificial satellites. Different methods exist for this purpose, with each method having its advantages and drawbacks. Most spacecrafts nowadays are propelled by what is called a rocket engine, which propels the space probe by heating the reaction mass and allowing it to eject out from the rear of the vehicle. Detailed Definition: A spacecraft propulsion system has the purpose of changing the velocity (acceleration) of a spacecraft and artificial satellites. It is utilised to both leave earth and for orbit insertion. To launch a spacecraft from earth, the propulsion method must overcome a higher gravitational pull to provide a positive net acceleration. The difficulty of achieving this change is directly proportional to the size of the vehicle, which is why spacecraft performance is generally discussed in amount of change in momentum per unit of propellant consumed, known as “specific impulse”. The higher the specific impulse, the better the efficiency. Once launched, satellites and spacecrafts may need to be moved between orbits, thus requiring propulsion. When a satellite has exhausted its ability to adjust its orbit, its useful life is over. The methods areas are divided into four groups: (1.) chemical propulsion (reaction and rocket engines), (2.) electric propulsion (ion, electrothermal and electromagnetic thrusters), (3.) advanced propulsion technologies and (4) supporting technologies. Etymology:
Sample sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages:
Links to Videos/Articles: Space Propulsion: a Survey Study About Current and Future Technologies. DOI: 10.5028/jatm.v10.829 | ||
Spaceship | ||
|---|---|---|
cf. Spacecraft | ||
Special Purpose Dextrous Manipulator (SPDM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: Short Definition: A Special Purpose Dextrous Manipulator (SPDM), also called 'Dextre', is a system that is part of the Mobile Servicing System (MSS) mounted on the International Space Station (ISS). This robotic system is designed to assist astronauts in spaces where human reach and endurance are limited. Detailed Definition: It is a multi-talented robot added to Canadarm2 on March 16, 2008, by Nasa astronauts Mike Foreman and Richard Linnehan. Designed to withstand the harsh conditions of space, this robot supports astronauts for small tasks around the ISS. These tasks include installing and maintaining the various parts of the ISS's exterior, maintaining the Station's electrical system, and pre-testing new equipment to be added. This robot, which has two hands as sensitive as human hands, has a retractable motorized wrench, camera, light, and connection module in both hands. Sample Sentence(s):' 'This multi-talented robot can ride on the end of Canadarm2 to move from worksite to worksite, or be ferried on the Mobile Base System.'' ''Dextre is the most sophisticated space robot ever built.'' Translations: French: Manipulateur agile à usage spécial German: Geschickter Manipulator für besondere Zwecke Italian: Manipolatore abile per scopi speciali Polish: Zręczny manipulator do zadań specjalnych (SPDM) Turkish: Özel Amaçlı Hünerli Manipülatör Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/elements/special-purpose-dextrous-manipulator/ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_Servicing_System https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/iss/dextre/about.asp https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/iss/dextre/ https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/iss/dextre/data-sheet.asp https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nNcRDBK8zxY&ab_channel=CanadianSpaceAgency | |||
Star | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Kutsaev, R. (no data). Stars Galaxy Free Stock Image. stocksnap. https://stocksnap.io/photo/stars-galaxy-IJ5DPL13HR Definition:1) A natural luminous body that is visible in the night sky and can be used for navigation. 2) A large celestial body producing light and energy by means of nuclear reactions inside of it. EtymologyGreek “αστέρι”, Latin “stella” Translations:
| |||
Stellar wind | ||
|---|---|---|
Media Media ESO/Callingham et al. DefinitionsShort Definition Detailed Definition Etymology Stellar: from Latin stella"star" Sample Sentences Bright bow shocks form around stars when their stellar winds interact with the Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages Frenchle vent stellaire German
der Sternwind
Italian
il vento stellare
Polish
wiatr gwiazdowy
Swedish stjärnvind
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Languages Russian Ukrainian Links to Videos/Articles: Stellar Wind. ESA/Hubble. Retrieved [ 06.14.2023 ], from https://esahubble.org/wordbank/stellar-wind/
Holzer, T. E., & Axford, W. I. (1970). The theory of stellar winds and related flows. Annual review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 8(1), 31-60. Retrieved [ 06.17.2023 ], from https://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu//full/1982ApJ...259..282A/0000282.000.html | ||
Supernova | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 25). AI illustration of a supernova. Midjourney. midjourney Definition:Brief, bright illumination of a supermassive star at the end of its lifetime by an explosion in which the original star itself is destroyed. As it dies, a supermassive star goes through various stages of fusing different elements, forming a red supergiant. During this process, more and more heavy material is deposited onto the stellar core. Once the core’s mass tips past a certain threshold it collapses under its own gravity (meaning it cannot withstand its own gravitational force). The outer layers are blasted outwards in a supernova, the biggest explosion known to occur in the Universe. At its peak, a supernova can be brighter than an entire galaxy. Supernovae reach their peak luminosity in a matter of days, so their appearance and early decline can be observed in real time. Etymology:from Latin super “beyond”, “over and above” and stella nova “new star” Translations:English: supernova (neutr.) – [ˌsuːpərˈnoʊvə] French: supernova (f)– [] German: Supernova (f) – [ˈzuːpɐˌnoːva] Polish: supernowa () – [] Russian: сверхновая звезда () - [ˌsvʲerxˈnovəjə zvʲɪzˈda] Swedish: supernova () – [] | |||
Supernova Remnant | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short
Definition
Detailed Definition First, the ejecta expands freely, gradually shedding their mass into the circumstellar or interstellar medium. Subsequently, the remnant begins to gather and compress surrounding gas, forming a prominent shell. In the ensuing phase, the shell undergoes cooling, resulting in the formation of a thinner, more delicate outer layer enveloping the still-hot interior. As the interior continues to cool, the shell expands further under its own momentum. Finally, the remnant merges with the surrounding interstellar medium, culminating in the formation of a fully-fledged supernova remnant. Notable examples of supernova remnants include the Crab Nebula, the remnants of SN 1572, and Kepler, the remnants of SN 1604, named after Johannes Kepler. G1.9+0.3, discovered in the galactic centre, stands as the most recent known remnant within our galaxy.
Sample Sentence(s) “Supernova remnants are very important to the structure of galaxies.” Mathis, J. S. (Invalid Date). supernova remnant. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/supernova-remnant
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
French
German
Italian
Polish
Swedish
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Lang... Turkish Dutch Supernovarest Spanish resto de supernova Portuguese Remanescente de supernova
Links to Videos/Articles: Astrum. (2016a, January 29). Supernova Remnants | Hubble Images
4K | Episode 2 [Video]. YouTube. | ||
Surface | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 25). AI illustration of a planets surface. Midjourney. midjourney Definition:The exterior of an astronomical body that is in contact with outer space or an atmosphere.Etymology:From Latin superficies. Translations:
Links to videos/articles: | |||
T |
|---|
Taikonaute | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source : https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/dd/%E8%88%AA%E5%A4%A9%E5%91%98%E9%99%88%E5%86%AC_Chen_Dong.jpg/800px-%E8%88%AA%E5%A4%A9%E5%91%98%E9%99%88%E5%86%AC_Chen_Dong.jpg
Detailed Definition
The term "taikonaut" is a term that refers to Chinese astronauts who are trained to participate in China's space missions. Taikonauts are selected from People's Liberation Army Air Force and undergo intensive physical and psychological training to prepare for the challenges of spaceflight. China plans to select and train more taikonauts for its future missions.
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: un taïkonaute German: der Taikonaut Italian: taikonauta Polish: tajkonauta Swedish: taikonaut
Translations of Terms/Concepts into other languages Japanese 宇宙飛行士 (uchū hikōshi) or taikonaut (タイコノート) Korean 태종 (taejong) Russian тайконавт (taikonavt) Spanish Taikonauta Portuguese taikonauta
Links to Videos/Article : Example sentence: A dozen of handpicked Chinese astronauts, or taikonauts as they are called, are set to explore new horizons in space in four manned flight missions within two years. In the first of these missions, three taikonauts aboard the Shenzhou-12 spacecraft have already successfully made it to space. CGTN. 2021. What does it take to be a taikonaut? Retrieved May 29, 2023, from https://news.cgtn.com/news/2021-06-22/What-does-it-take-to-be-a-taikonaut--11hwXVttCww/index.html Articles: VOA News Year: (n.d.) Title: Why China, African Nations Are Cooperating in Space Source: VOA News. Retrieved May 29, 2023, from https://www.voanews.com/a/why-china-african-nations-are-cooperating-in-space/6745595.html Unknown. Year: 2022. China Launches New Crew to Space Station Source: The Washington Post. Retrieved May 29, 2023 from https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2022/11/29/china-space-station-crew-launch/ Video: CGNT Chinese Global Television Network. 10. July 2021. Why are Chinese Astronauts called Taikonauts? Retrieved 18. June 2023 from | ||
Tektite | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tektite#/media/File:Two_tektites.JPG Short definition: Tektites are small pieces of natural glass that are typically black, green, brown, or grey in color. They are created when meteorites impact the Earth and cause terrestrial debris to be ejected and melted into a glass-like material. Detailed Definition: A tektite is a type of glass that is formed from the impact of a meteorite on the Earth's surface. The extreme heat and pressure of the impact melts and vaporizes the rocks at the impact site, which then cools and solidifies into a glass-like material. Tektites are typically black or green in color and have a smooth, rounded shape. They can vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Tektites are found in the areas around meteorite impact craters, and are used by scientists to study the effects of meteorite impacts on the Earth's surface. Etymology: tēktós - molten Sample Sentence(s):
"Sir Thomas Mitchell found a tektite and gave it to Charles Darwin." "Some human built objects, such as black buttons, can be mistaken for tektites." Translations: French: Tectite German: Tektit Polish: Tektyt Swedish: Tektit Links to videos/articles: https://australian.museum/learn/minerals/shaping-earth/tektites/ https://www.britannica.com/science/tektite | ||
Telecommunication | ||
|---|---|---|
 Image Source: Kratochvil, P. (n.d.). Telecommunication antennas free stock photo - public domain pictures. Public Domain Pictures. Retrieved April 25, 2023, from https://www.publicdomainpictures.net/en/view-image.php?image=501498&picture=telecommunication-antennas Short Definition: Telecommunication is a method of transmitting various data and information over long distances. It is a faster alternative to other methods, which might be more limited in speed and complexity limitations. Detailed Definition: Telecommunication is a broad spectrum of means of exchanging certain data types like audio or video over long distances using wide range technologies such as radio, electromagnetic systems and optical or wired connections. Telecommunication technologies are based on a simple system of transmitters and receiver located in various locations to ensure global reach of the network. Telecommunications have been popularised through rise of the internet which is based on the concept of network between telecommunication stations. Telecommunication networks might also be connected in a smaller scale on a more localised areas like Telephone networks (country-wide), academic wide area networks (WANs) or police dispatch networks (city-wide). Telecommunication technologies were changing with the flow of inventions. From wired connections to wireless. Etymology: Telecommunication is a compound of Greek and Latin. 𝑡𝑒𝑙𝑒 meaning distant,
faraway. 𝑐𝜊𝑚𝑚𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑟𝑒 meaning "to share" Translations: French - Télécommunication German - Telekommunikation Italian - Telecomunicazione Polish - Telekomunikacja Swedish - Telekommunikation Sample Sentences: 1. Telecommunication is essential for our everyday lives, from radio to phone calls. 2. Without telecommunication, our world wouldn't be so interconnected. | ||
Telescope | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: http://catalog.archives.gov/OpaAPI/media/23486741/content/stillpix/255-sts/STS125/STS125_ESC_JPG/255-STS-s125e011848.jpg Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles: | |||||||||
Terrestrial Planets | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short
Definition
The word "planet" has its roots in ancient Greek. It comes from the
Greek term "planētēs," which means "wanderer" or
"wandering star." Sample Sentence(s) "It's unclear what the dividing line is between a rocky planet and a terrestrial planet."
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
French
German
Italian
Polish
Swedish
Additional Translations Spanish Planeta terrestre Turkish Karasal gezegen Dutch Aardse planeten
Links to Videos/Articles
Dutfield, S., & Gammon, K. (2022). Terrestrial planets: Definition & facts about the inner planets and beyond. Space.com. https://www.space.com/17028-terrestrial-planets.html Morbidelli, A., Lunine, J. I., O’Brien, D. P., Raymond, S. N., & Walsh, K. J. (2012). Building Terrestrial Planets. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 40(1), 251–275. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-earth-042711-105319 Terrestrial | Planet Types – Exoplanet Exploration: Planets Beyond our Solar System. (n.d.). Exoplanet Exploration: Planets Beyond Our Solar System. https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/what-is-an-exoplanet/planet-types/terrestrial/ Cornerstone Television Network. (2015, October 8). Origins: The
Terrestrial Planets [Video]. YouTube.
MooMooMath and Science. (2019, August 22). Terrestrial Planets in Order
[Video]. YouTube. | ||
The Kuiper belt | ||
|---|---|---|
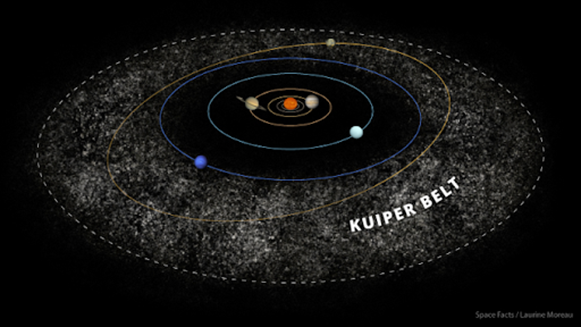 Image Source: https://theplanets.org/kuiper-belt/
Short Definition:
Detailed Definition: Etymology: Kuiper – Dutch
– Kuiper - cooper – from the name of the scientist Gerard Kuiper
Sample Sentence(s): French: German: Polish: Swedish: Spanish
Links to Videos/Articles: https://theplanets.org/kuiper-belt/ | ||
The Solar System | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Image Source: Short Definition: Detailed Definition: Etymology: Sample Sentence(s): French: Système solaire German: Układ Słoneczny Swedish: Solsystem Spanish:El sistema solar Links to Videos/Articles: | |||
Time Dilation | ||
|---|---|---|
Media:  Media: File:Nonsymmetric velocity time dilation.gif - Wikimedia Commons . (2006, January 28). https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nonsymmetric_velocity_time_dilation.gif Short Definition: Time Dilation is a phenomenon observable through the change of measuring of elapsed time by two clocks. The change usually occurs due to the difference in velocity or gravitational potential. The faster you move relative to some object, the slower time seems to flow. Detailed Definition: Time Dilation is an occurrence which takes place due to the difference in velocity or gravitational potential of a given object. It occurs when one of the objects has higher velocity than the other (commonly called a reference frame). The reference frame is a coordinate system defined by certain characteristic points, this frame is stable while the other object travels with a certain velocity, different from the frame. What can be then observed is that the travelling object experiences time slower, than the reference frame (observer). This phenomenon is strictly connected to Einstein's theory of relativity, as the time passes differently, relative to the state (either gravitational or velocity) of the object. Time dilation has been observed and calculated on the International Space Station. The differences in time perception are virtually insignificant (in milliseconds) at small distances, but might increase to even years in difference. Etymology: Time, from Old English "tima" defined as limited space of time. Dilation from Late Latin "dilatationem" meaning widening of something. Sample Sentence(s) 1. The astronauts on the ISS experienced time dilation of around 20 milliseconds, compared to earth. 2. The time on ISS is lagging by about 0.01 seconds for every 12 months on earth, due to time dilation. Translation: French - dilatation du temps German- Zeitdilatation Italian - dilatazione del tempo Polish - dylatacja czasu Swedish - Tidsdilatation | ||
Twilight | ||
|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio Source: Short definition: Twilight is the period after sunset when the Earth is illuminated by sunlight diffused in the atmosphere. The following twilight phases are distinguished: civil twilight, nautical twilight and astronomical twilight. The only difference between twilight phases is where the Sun is located, which makes the sky gets darker. When the Sun is up to 6° below the horizon, it is considered a civil twilight. When the Sun is between 6° and 12° below the horizon, it is said to be a nautical twilight. An astronomical twilight is when the Sun is located from 12° to 18° below the horizon. When Sun position is over 18° below the horizon line, it is considered as night. Etymology: late Middle
English: from Old English twi- ‘two’ (used in an obscure sense in this
compound) Sample Sentence(s): French: Le crépuscule German: Zmierzch Swedish: Skymning Spanish: El crepúsculo Links to Videos/Articles: | ||
Twins Study | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:A study aiming to investigate the effects of spaceflight on the human organism. The study was organized by NASA with the support of 8 universities across the USA. It was conducted in 2015-2016 and involved two identical twin brothers: Scott and Mark Kelly. Scott Kelly served on a year-long mission aboard the International Space Station, while his brother Mark Kelly, a former NASA employee, remained on Earth. The twins study included an array of biochemical, neurological and other types of medical tests conducted before, during and after the spaceflight, i.e. over the span of 27 months. The results confirmed the robustness and resilience of human health, since 91,3% of Scott Kelly’s medical parameters returned to baseline six months after the spaceflight. The remaining changes were to be used for development of personalized measures to predict and overcome possible adverse consequences of spaceflight. Translations:French: German: Polish: Eksperyment z bliżniakami Swedish: Article:https://www.science.org/doi/pdf/10.1126/science.aau8650 Other sources:https://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasa-s-twins-study-results-published-in-science https://www.nasa.gov/twins-study/about
| |||
U |
|---|
Umbra | ||
|---|---|---|
Source: Short definition: The umbra is the innermost and darkest part of a shadow, where light is completely blocked by an object. In the context of astronomy, the umbra is often observed during a solar eclipse, when the Moon's shadow is cast on the Earth. Detailed Definition: The Umbra is the innermost and darkest part of a shadow. It is the area where light is completely blocked by an object, such as a planet or moon. When a celestial body, passes between a star and another celestial body, it can cast a shadow on that body. The umbra is the part of the shadow that is directly behind the blocking body. The lighter part of the shadow - penumbra, is the area where only part of the light is blocked. The umbra and penumbra can be observed during a solar eclipse, when the Moon's shadow is cast on the Earth. Etymology: Umbra (Latin) - shadow Sample Sentence(s): "Terms "umbra" and "penumbra" are not limited to celestial bodies, they occur in shadows of everyday objects." "During solar eclipse, when an observer stands in umbra, dusk seems to set from all directions on the horizon at once." Translations: German: Umbra Polish: Cień całkowity Links to videos/articles: https://www.universetoday.com/155274/astronomy-jargon-101-umbra/ | ||
Universe | |||
|---|---|---|---|

Source:Cajina, I. (2017, September 17). Milky Way from Max Patch. unsplash. https://unsplash.com/photos/asuyh-_ZX54 DefinitionThe totality of all existing matter, energy, space and time. The universe is approximately 13,8 years old and has emerged as a result of the Big Bang, in which it emerged from a single point and continues to expand. Translation
Links to Videos/Articles:https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/what-is-an-exoplanet/what-is-the-universe/ | |||
V |
|---|
Vacuum | ||
|---|---|---|
Image:
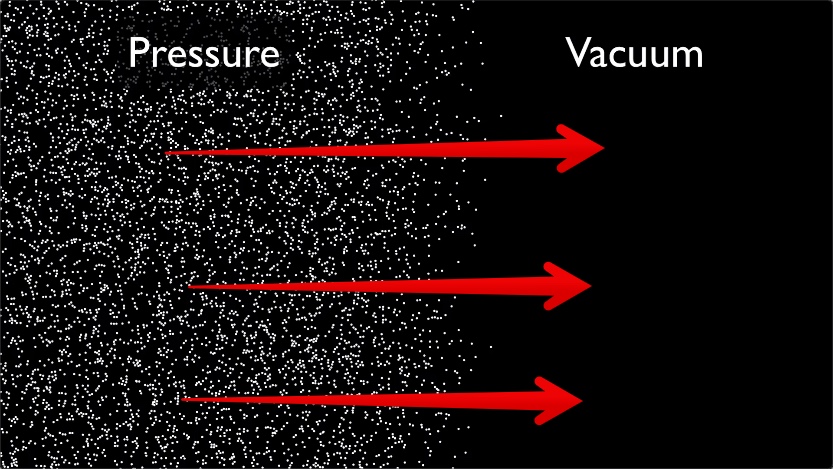 Image: Source: https://www.metabunk.org/attachments/metabunk-2018-10-31-08-37-23-jpg.34929/ Short Definition: A vacuum is a space in which there is no matter such as gas or particles. It is found in space or can be generated by machines. Detailed Definition: Space that does not contain any gas inside its boundaries. However, it is also required that there is not any matter in general in either state such as gas, liquid, or solid, among other complex definition states. Even though the vacuum is found naturally in space, it is used on earth for different machines such as vacuum pumps, and vacuum chambers, among others. Etymology: Vacum comes from the latin Vacuus, which means empty. Sample Sentence(s): Life cannot be found or developed in the vacuum of space. The dead body astronaut rambled in the vacuum of space. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: vide German: Vakuum Polish: próżnia Swedish: svenska Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/365382138_A_Review_of_Research_on_the_Vacuum_Plume DOI: 10.3390/aerospace9110706 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E43-CfukEgs&ab_channel=BBC | ||
Valentina Tereshkova | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Illustration: http://www.astronaut.ru/as_rusia/lady62/foto/tereshkova02.jpg Definition:The first female cosmonaut, the 10th person in the world to be sent into space. Valentina Tereshkova flew into space alone aboard Vostok-6 on June 16, 1963. The duration of the flight amounted to 2 days, 22 hours and 50 minutes, during which the spacecraft orbited the Earth 48 times. Valentina Tereshkova was born in 1937 in the village of Bolshoye Maslennikovo in Yaroslavl Oblast, USSR. In 1960, she graduated from Yaroslavl Light Industry Training School as a cotton spinning technician, and in 1969 received a qualification from Zhukovsky Air Force Engineering Academy as a pilot, cosmonaut and engineer. She enjoyed parachuting, which later turned out to be one of the criteria for cosmonaut selection. Following the spaceflight, she worked as a cosmonaut instructor until reaching mandatory retirement age in 1997. Later she continued working as a politician, which she had already been doing since 1966. Her daughter Elena is said to be the first child in the world whose parents are both cosmonauts. Translation:
Links to Videos/Articles:http://www.astronaut.ru/crossroad/010.htm https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Терешкова,_Валентина_Владимировна
| |||
Venus | |||
|---|---|---|---|
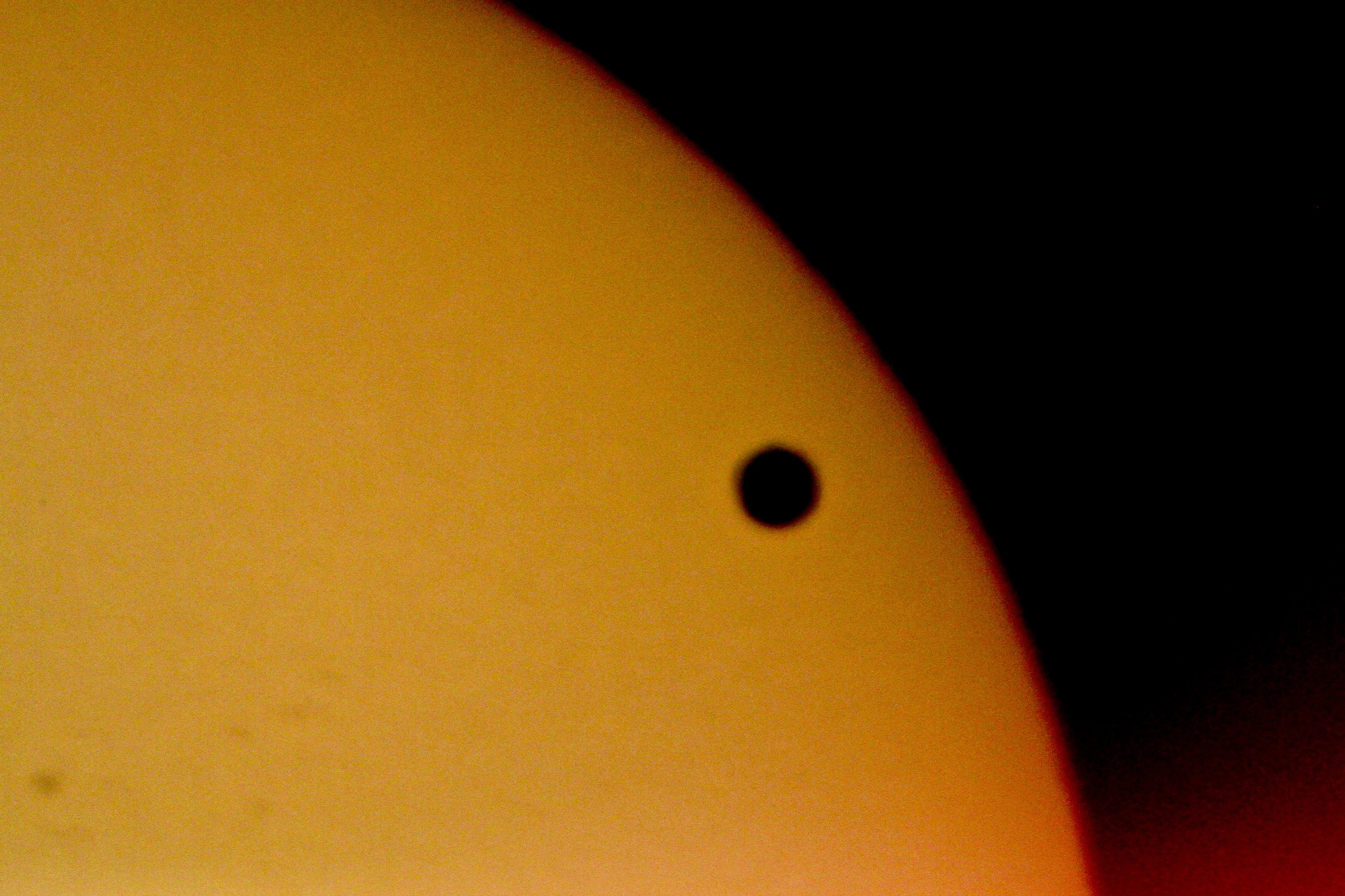 Source: Hecht, M. (2012, June 5). Venus Transit. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/76858203@N04/23105554654 Definition:Venus is the planet with the second closest orbit to the Sun. Venus is our inner neighbor in space in the Solar System. It is a celestial body located just 40 million kilometers far from the Earth. Venus resembles the earth in the main parameters: size, mass, density and internal structure almost match. Etymology:In Roman mythology (= ancient stories), the goddess (= female god) of beauty and love. Translations:
| |||
Volcano | ||
|---|---|---|
Image:  Image: Source: https://www.dw.com/en/volcanic-eruptions-can-cool-the-planet/a-40727123 Short Definition: A volcano is a hill or mountain with a hole where lava, rocks, or gas may be seen erupting from a planet or moon's interior. Detailed Definition: A crack in the earth's crust through which substances such as lava, steam, ashes, etc. are released continually or sporadically. Volcanoes are known to exist on the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, the Moon, Mars, and the moon Io of Jupiter. Only two of these bodies currently have active volcanoes: Earth and Io. However, Venus or Europa, the moon of Jupiter, may have volcanoes erupting. Etymology: Volcano comes from the Latin Vulcanus, which is the name of the fire god. Sample Sentence(s): The volcano's lava was pouring down the mountainside. On the seabed of Jupiter's moon Europa, there has been volcanic activity. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: volcan German: Vulkan Polish: wulkan Swedish: vulkan Links to Videos/Articles: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/topic/volcanoes https://chandra.harvard.edu/press/10_releases/press_081810.html | ||
W |
|---|
White Dwarf | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio: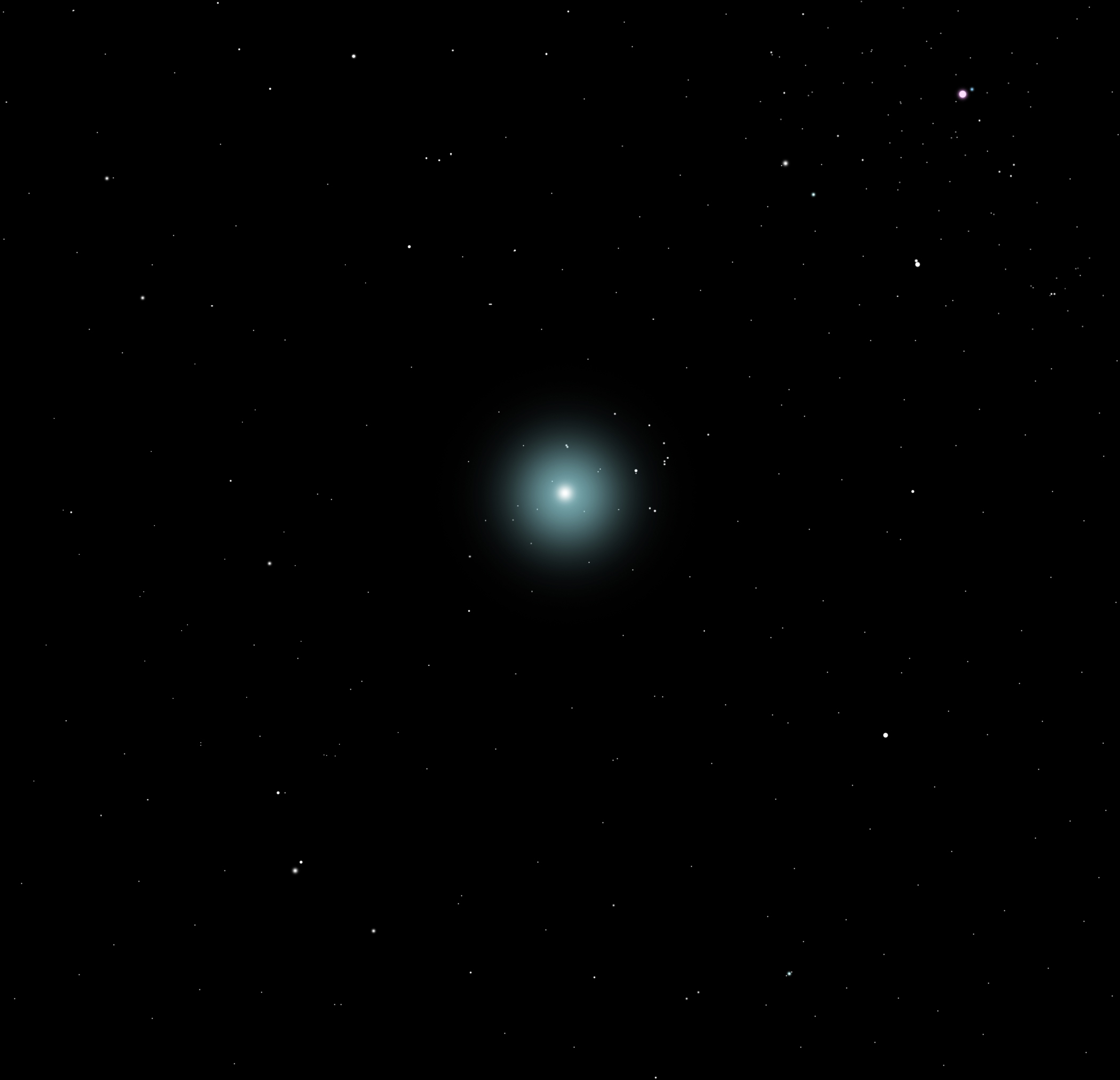  Image/Video/Audio: Picture: A white dwarf Image/Video/Audio Source: File:White dwarf.jpg - Wikimedia Commons. (2011, April 5). https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:White_dwarf.jpg Short Definition:
White dwarfs, or cold stars, is a term often used to describe stars in the final stages of their evolution. These stars, which lose their energy sources and cannot perform fusion reactions, are the stars that tend to squeeze into themselves due to the gravitational law. This phenomenon was firstly discovered by the British astronomer 'William Herschel' in 1783.
Detailed Definition:
As one of the densest stellar remnants in space, white dwarfs are stars that have run out of most of their nuclear fuel and tend to collapse inwards. These stars, which are relatively Earth-sized and composed entirely of carbon and oxygen mass, are less than 1.4 solar masses when their cores are stable, but they tend to suffer constant heat and radiation loss because they do not undergo any fusion process. According to NASA's calculations, the core temperatures of white dwarfs can reach up to 100,000 Kelvin. Apart from the carbon and oxygen mass that make up their core, their envelope are surrounded by thin helium and in some cases hydrogen atoms.
Etymology:
White - from Proto-Indo-European (ḱweydós) Dwarf - from Proto-Germanic (dwergaz) (white - Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/white) (dwarf - Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/dwarf)
Sample Sentence(s):
‘’White dwarfs evolve from stars with an initial mass of up to three or four solar masses or even possibly higher.’’ (The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (1998, July 20). White dwarf star | Definition, Size, Mass, Life Cycles, & Facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/white-dwarf-star) ‘’White
dwarfs reach this incredible density because they are collapsed so
tightly that their electrons are smashed together, forming what is
called "degenerate matter.’’ (Dobrijevic, D., & Tillman, N. T. (2022, March 4). White dwarfs: Facts about the dense stellar remnants. Space.com. https://www.space.com/23756-white-dwarf-stars.html)
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French:
Naine blanche German:
Weißer Zwerg Polish:
Biały karzeł Swedish:
Vit dvärg Turkish:
Beyaz Cüce Links to Videos/Articles:
Dobrijevic, D., & Tillman, N. T. (2022, March 4). White dwarfs: Facts about the dense stellar remnants. Space.com. https://www.space.com/23756-white-dwarf-stars.html Kurzgesagt
– In a Nutshell. (2017, May 4). The Last Light Before Eternal
Darkness – White Dwarfs & Black Dwarfs [Video]. YouTube.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qsN1LglrX9s The
Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (1998, July 20). White dwarf
star | Definition, Size, Mass, Life Cycles, & Facts. Encyclopedia
Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/white-dwarf-star White Dwarfs. (2021, May 4). Science. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/white-dwarfs | |||
Y |
|---|
Yuri Gagarin | ||
|---|---|---|
 Wikipedia Year: (n.d.) Yuri Gagarin - 1961-04-12. Wikimedia Commons. Retrieved May 29, 2023, from https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/vi/7/7f/Yurigagarin-1961-04-12.jpg
Definitions
Yuri Gagarin was a Soviet cosmonaut and the first human to travel into space. On April 12, 1961, aboard the Vostok 1 spacecraft, Gagarin completed a single orbit around the Earth, marking a significant milestone in human space exploration. His flight lasted 108 minutes and made him an international symbol of space exploration and achievement. Detailed Definition
Sample Sentence(s) 1. Gagarin's flight came at a time when the United States and the Soviet Union were competing for technological supremacy in space. David, L. Year: 2012 First Man in Space: Yuri Gagarin's Historic Vostok 1 Flight. Space.com Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from https://www.space.com/16159-first-man-in-space.html 2. The Gagarin crater on the Moon is named after Yuri Gagarin, in recognition of his achievement as the first human to journey into space. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French German Italian Polish Swedish Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Languages Russian: Юрий Гагарин Links to Videos/Articles: Britannica Year: (n.d.). Yuri Gagarin. Encyclopedia Britannica Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from https://www.britannica.com/biography/Yuri-Gagarin BBC News. 2021. Yuri Gagarin: The first man in space - BBC News. Retrieved Jun 12. 2024 from https://youtu.be/KANuFlelQ5k. | ||
Z |
|---|
Zenith | ||
|---|---|---|
Media Media Zenith & Nadir, DJ Jeffery, University of Nevada, Las Vegas, 2003. DefinitionsShort Definition Detailed Definition Etymology Sample Sentences Glowing with astral turquoise, the comet dashingly passed zenith and started decelerating as it was approaching the horizon.
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages Frenchle zénith
German
der Zenit
Italian lo zenit
Polish zenit
Swedish zenit
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Languages Russian Ukrainian Links to Videos/Articles: The Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica. (1998, July 20). Zenith | astronomy. Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved [ 06.14.2023 ], from https://www.britannica.com/science/zenith-astronomy
Zenith | COSMOS. (n.d.). Retrieved [ 06.20.2023 ], from https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/z/Zenith | ||

