Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
S |
|---|
Solar Eclipse | ||
|---|---|---|
Short Definition
Sample Sentence(s) A solar eclipse cannot be visible from all the places on Earth all at once. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
French
German
Italian
Polish
Swedish Links to Videos/Articles: Hocken, V. (n.d.), What Are Solar Eclipses?, Retrieved from https://www.timeanddate.com/eclipse/solar-eclipse.htmlNASA Science SpacePlace Explore Earth and Space (n.d.), What Is Solar Eclpise?, Retrieved from https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/eclipse-snap/en/ Dobrijevic, D. (n.d.), What is a solar eclipse?, Retrieved from https://www.space.com/15584-solar-eclipses.html Online Etymology Dictionary (n.d.), eclipse (n.), Retrieved from https://www.etymonline.com/word/eclipse Online Etymology Dictionary (n.d.), solar (adj.), Retrieved from https://www.etymonline.com/word/solar#etymonline_v_23841 ESA (2015), Europe’s solar eclipse seen from Proba-2, Retrieved from https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Videos/2015/03/Europe_s_solar_eclipse_seen_from_Proba-2 | ||
Solar sail | |||
|---|---|---|---|
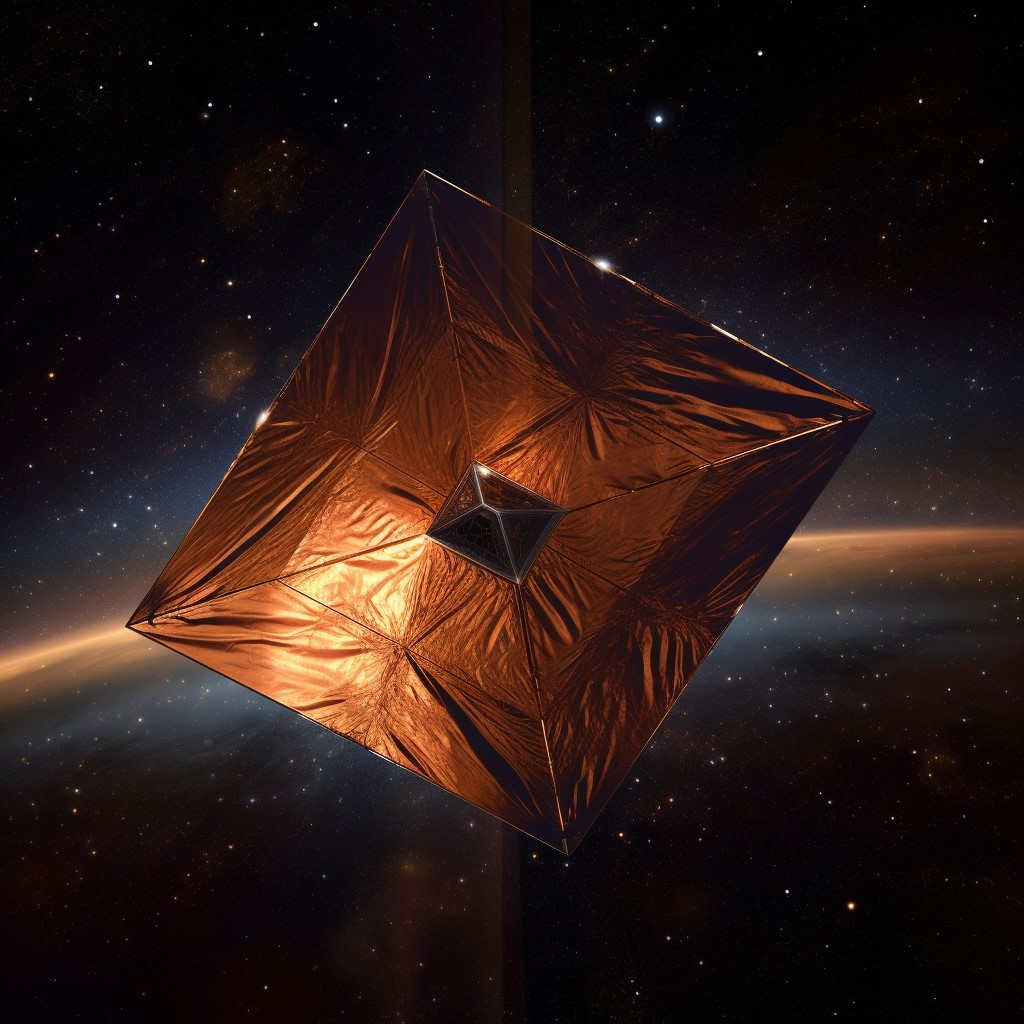 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 31). . midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition: Solar sails (also known as light sail or photon sail) are a method of spacecraft propulsion using radiation pressure exerted by starlight on large mirrors. Solar sails can be used instead of traditional fuel consumption. First proposed in the 1980s as alternative propulsion method for low-weight long-distance spacecrafts, the first real usage of the solar sail system was in JAXA’s IKAROS mission, launched in 2010. Detailed Definition: The Solar sails use a phenomenon called solar pressure, which is the force produced by the impact of sunlight photons on the surface of the spacecraft. Normally, solar pressure is affecting all spacecrafts during flights and must be accounted for in trajectory planning, but in that specific case it is used as thrust. Vessels using solar sails must be lightweight as the total force exerted on an eight hundred by eight hundred meters solar sail is about 5 Newtons at Earth's distance from the Sun, so this propulsion method requires specially constructed spacecraft. If solar sails are implemented in space vessel it can produce propulsion without need of fuel usage and thus can be great for small satellites to travel to distant objects without great amount of storage for fuel and engines. The negative side of this technology is significantly small force compared to traditional liquid fuel engines and fragile sail build. Also, this system cannot be used far away from “propulsion” star, as thrust generated by the solar sail is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. Etymology: Solar
- From Latin sōlāris, from sōl (“sun”), Sample Sentence(s): “The IKAROS probe is the world's first spacecraft to use solar sailing as the main propulsion system.” Translations: French: Voile solaire German: Sonnensegel Polish: Żagiel słoneczny Swedish: Sol segel Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305884757_Solar_sail_technology-A_state_of_the_art_review | |||
Solar Storm | ||
|---|---|---|
Media: 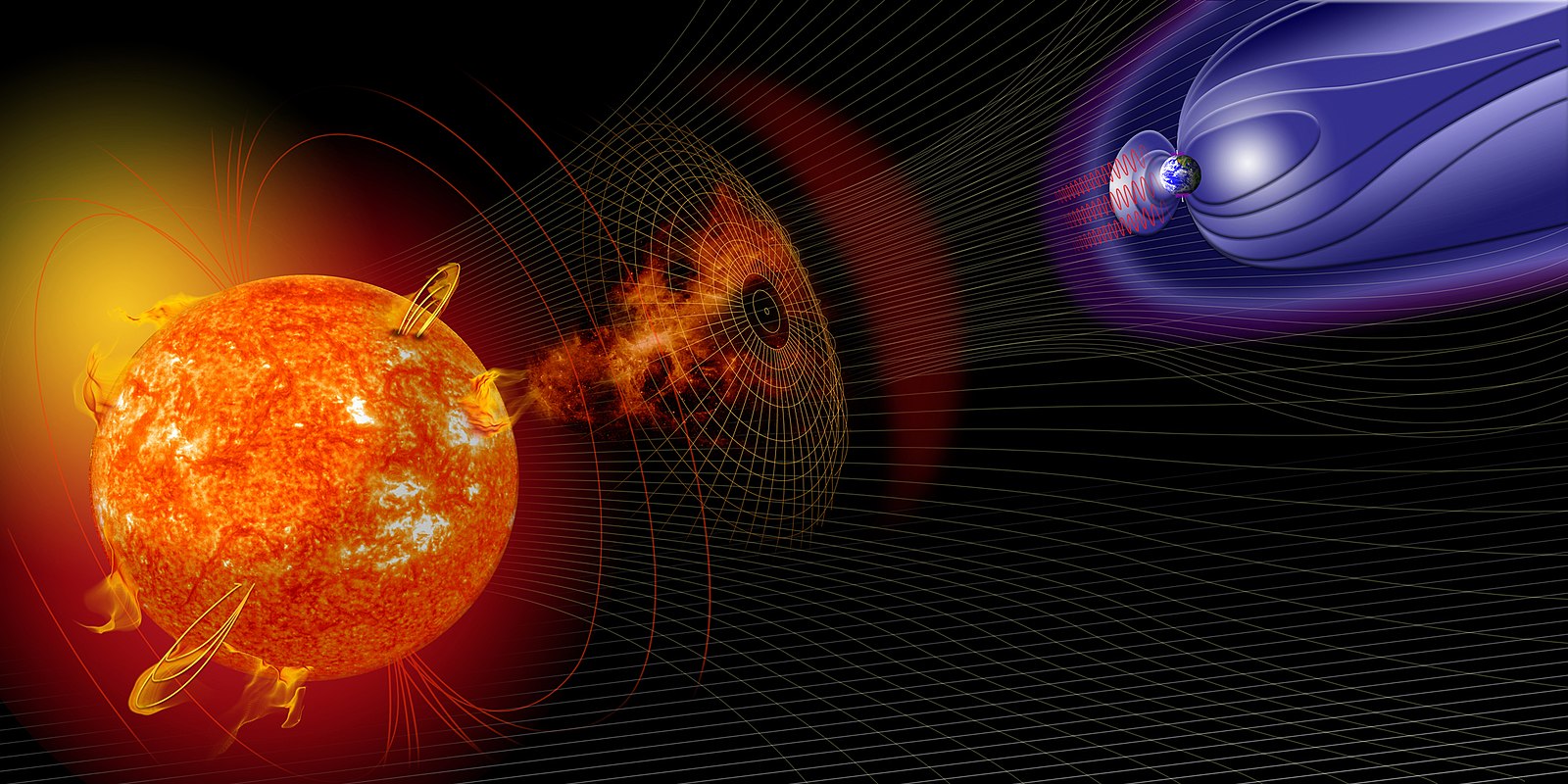 Media: File:Storms From the Sun (6819077978).jpg - Wikimedia Commons . (2005, April 24). https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Storms_From_the_Sun_%286819077978%29.jpg Short Definition: A solar storm is a magnetic eruption happening on a star, causing a large burst of particles at very high speeds. This event is usually associated with visible arches on the sun. Detailed Definition: A solar storm is a phenomenon which is caused by a magnetic eruption on the Sun, which in hand happens due to increasing velocity of charged particles in the Sun's magnetic field. Such eruption, called a solar flare, shoots out mostly protons, which achieve speeds close to the speed of light. Such protons, while reaching the Earth's magnetosphere, they get guided towards both poles and lose their speeds. The occurrence of solar storm, has some negative effects on the earth, but most of the bursts, are light enough to be neutralized by the magnetosphere. The protons that manage to reach earth, usually disturb radio communications or other services and technologies which utilize waves. Etymology solar from Latin "solaris" or "sol" meaning "the sun". Storm from Middle/Old English "storm" meaning "a disturbed state of the atmosphere, especially as affecting the earth's surface". Sample Sentence(s) - The Solar storm is depending on the solar cycle, which lasts around 11 years. - The solar storm disturbed the TV, I couldn't finish watching the game!
Translations: French - tempête solaire German - Sonnensturm Italian - tempesta solare Polish - Burza słoneczna Swedish - solstorm | ||
Sounding rocket | ||
|---|---|---|
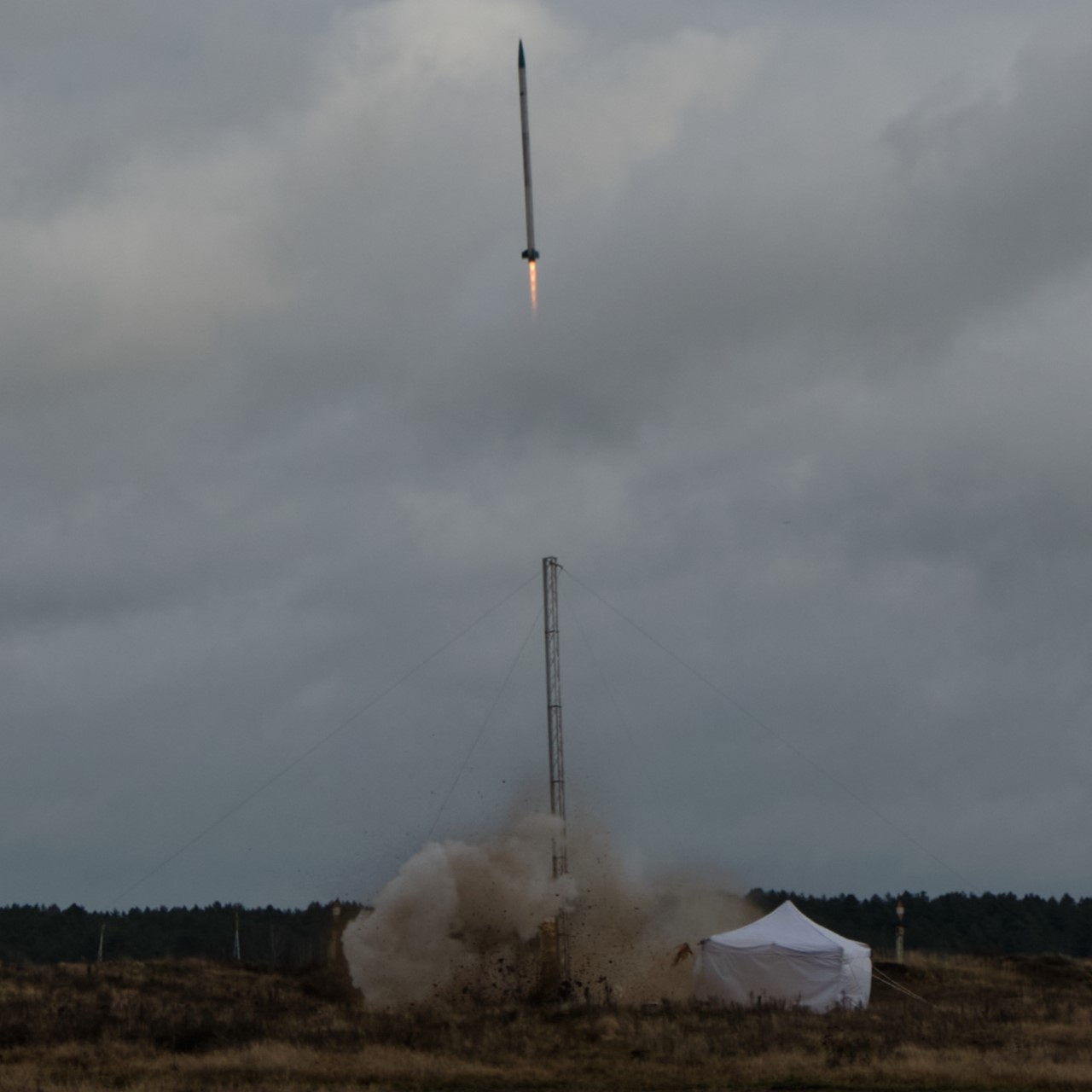 AGH Space Systems' Skylark rocket launch in Drawsko Pomorskie Source : Autor's photo Short Definition: Sounding rocket is a small, unmanned rocket that is meant to take measurements and perform scientific experiments on suborbital flights. Detailed Definition: A sounding rocket is a type of rocket that is used to carry scientific instruments to high altitudes for the purpose of collecting data. These rockets are typically smaller and less powerful than other types of rockets, and are launched vertically from a launchpad. The main advantage of sounding rockets is that they can reach altitudes of up to several hundred kilometers, allowing researchers to study the upper atmosphere and the effects of space on various materials and phenomena. Sounding rockets are often used for experiments in fields such as atmospheric science, astrophysics, and meteorology. Etymology: Sounding rockets take their name from the
nautical term “to sound,” which means to take measurements. The term doesn't come from any latin or greek words. Sample Sentence(s): Next week, several sounding rockets will be launched from this site. Translations: French: Fusée-sonde German: Höhenforschungsrakete Polish: Rakieta suborbitalna, rakieta sądująca Swedish: Klingande raket Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=weeEGY4SR38 https://www.nasa.gov/missions/research/f_sounding.html | ||
Space debris | ||
|---|---|---|
 Image source: Midjourney (2023, June 01). AI illustration of space debris in earths orbit. midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition:
Detailed Definition: space -> spatium from Latin - meaning: space debris -> débriser from French - meaning: break down Sample Sentence(s): French: Débris spatiaux German: Weltraummüll / Weltraumschrott Polish: kosmiczne śmieci Swedish: Rymdskepp Spanish: Desechos espaciales Links to Videos/Articles: https://youtu.be/f513HPs24VM [Space Debris by the European Space Agency, ESA] https://www.nasa.gov/news/debris_faq.html https://www.nasa.gov/centers/hq/library/find/bibliographies/space_debris | ||
Space graveyard | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:S4-space-junk-045.jpg Definition:An area on Earth's surface or orbit in which decommissioned spacecrafts or satellites are discarded. Etymology:Translations:
| |||
Space rendezvous | |||
|---|---|---|---|
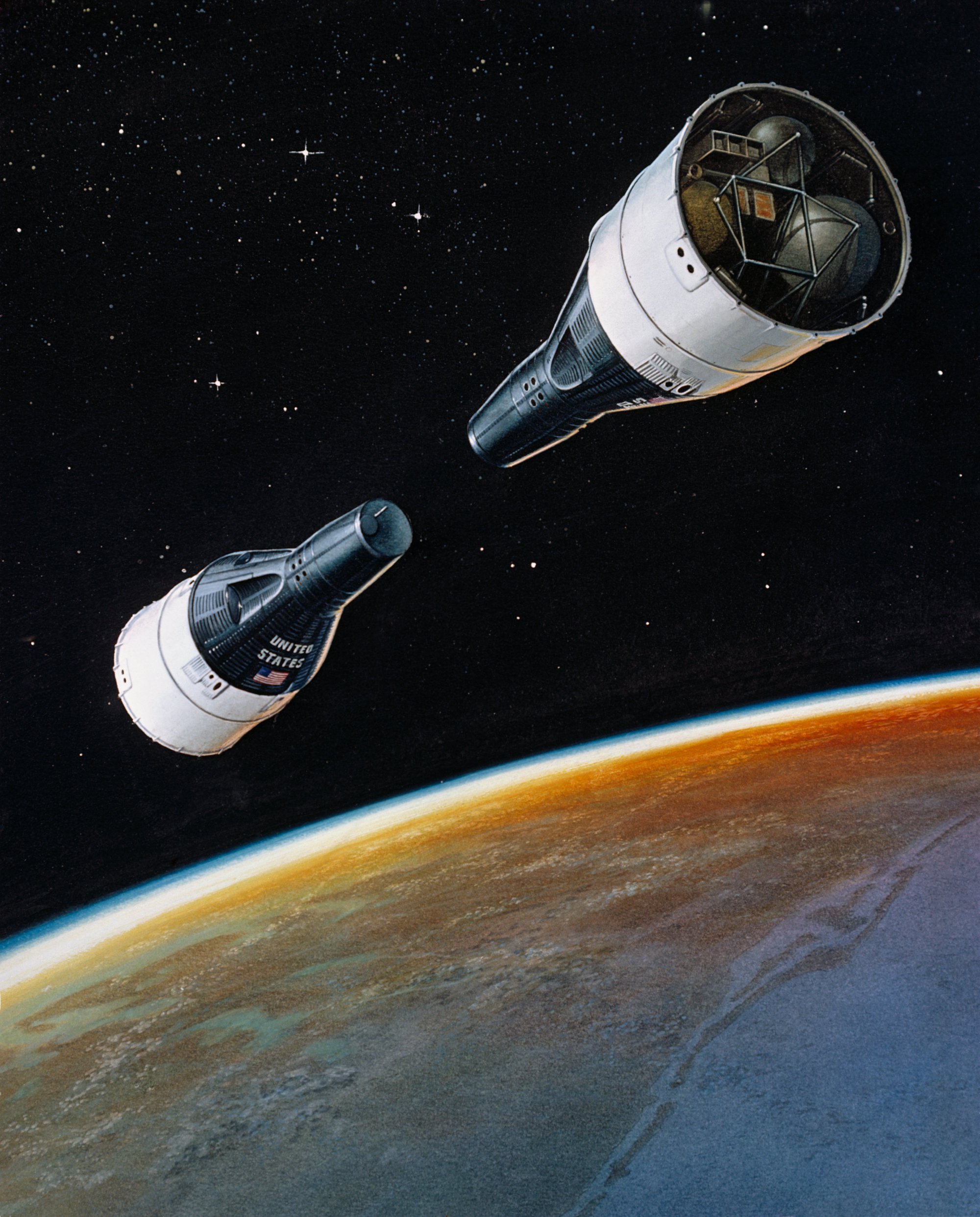 Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:RENDEZVOUS_-_ARTIST_CONCEPT_-_GEMINI-TITAN_GT-VI_and_GT-VII.jpg Short Definition: A space rendezvous is a series of orbital maneuvers focused on bringing together two orbiting spacecrafts. In most cases, a space rendezvous occurs between a space station and a spaceship trying to dock to it. Rendezvous requires a precise match of the orbital velocities and position vectors of spacecrafts, allowing them to remain at a constant distance during final maneuvers or docking. Detailed Definition: A space rendezvous is an approach in space to a very close distance (e.g. within visual contact) between spacecrafts or between a spacecraft and a celestial object at zero or very low relative speed. The space rendezvous requires carrying out complex orbital maneuvers, which must be completed in a minimum time without excessive consumption of the propellant. Rendezvous may or may not be followed by docking or berthing, procedures which bring the spacecraft into physical contact and usually create a link between them. NASA's first attempt at rendezvous was made on June 3, 1965, when astronaut Jim McDivitt tried to maneuver his Gemini 4 spacecraft to meet the Titan II launch vehicle's upper stage. Rendezvous was first successfully accomplished by NASA on December 15, 1965, and then lead to success of Apollo's program and moon landing. Etymology: Space - From Middle English space, from Anglo-Norman space, variant of espace, espas et al., and spaze, variant of espace, from Latin spatium(“to stretch, to pull”). Sample Sentence(s): The first space rendezvous was in 1965 during Gemini program Translations: French: Rendez-vous spatial German: der Raumfahrt Rendezvous Polish: dokowanie, połączenie się statków w przestrzeni kosmicznej Swedish: Rymdmöte Links to Videos/Articles: https://airandspace.si.edu/stories/editorial/worlds-first-space-rendezvous https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oNXPtZDS-cg | |||
Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
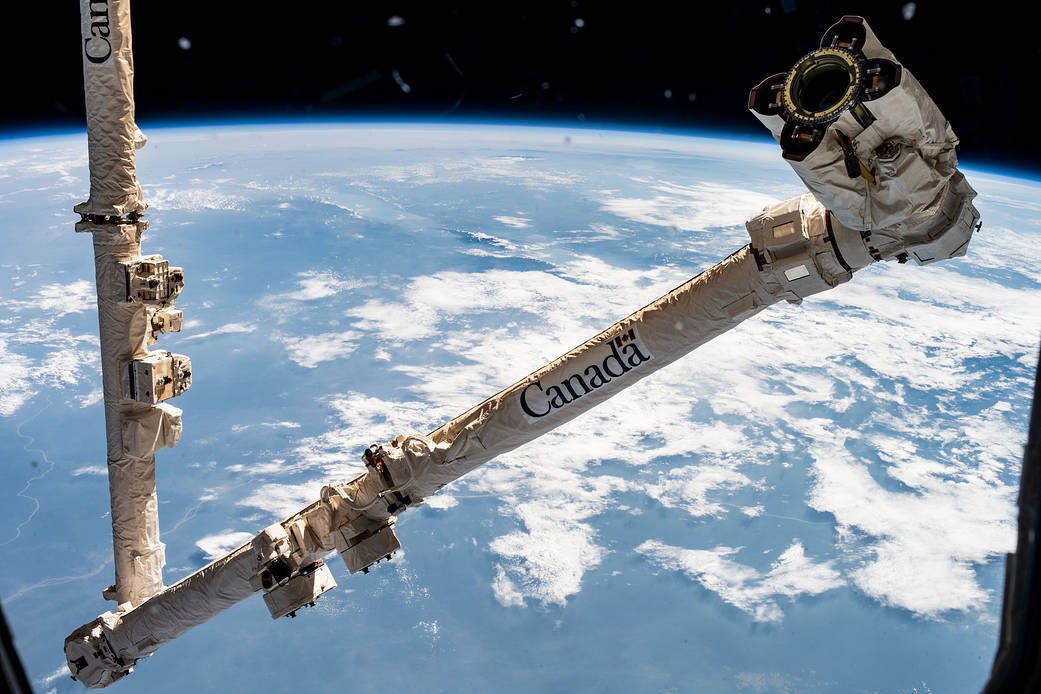 Source: https://www.nasa.gov/image-feature/the-canadarm2-robotic-arm-is-poised-to-capture-cygnus Short Definition: Ssrms is a manipulator system equipped with two long arms, seven attachment points, and various precision robotic equipment is also known as 'Canadarm2', it is a second-generation robotic arm system in the Mobile Servicing System of the International Space Station, whose main purpose is to take part in high-tonnage/cosmic catching missions. It is the most efficient heavy-duty robotic system (Up to 116 tons) left on the ISS after the Canadarm1 was retired in July 2011. Detailed Definition: It is a space manipulator attached to the international space station.As an improved version of the Canadarm 1, the Canadarm 2 is aimed at enhancing; size, load-carrying capacity, arm reach, durability, and increased mobility. It is a robotic system that assists astronauts with payload handling, approach and docking of space shuttles, making Cosmic catches, and maintenance of the station. The robotic arm, which can be managed by the astronauts on the ISS and the NASA and CSA centers on the world, is also adorned with advanced imaging-light systems. It is also used as an anchor point by attaching it to other robotic equipment itself. Sample Sentence(s): ''Canadarm2 is made up of parts that can be replaced while in space.'' ''Canadarm 2 will also help to berth the Axiom Space Station modules to the ISS.'' Translations: French Système de manipulateur à distance de la station spatiale Italian Sistema di manipolazione remota della stazione spaziale Polish System zdalnie sterowanego manipulatora stacji kosmicznej Turkish Uzay İstasyonu Uzaktan Manipülatör Sistemi
German Fernmanipulatorsystem der Raumstation Links to Videos/articles: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2020/04/Canadarm2_robotic_arm https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/iss/canadarm2/about.asp https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/elements/remote-manipulator-system-canadarm2/ | |||
Space tether | |||
|---|---|---|---|
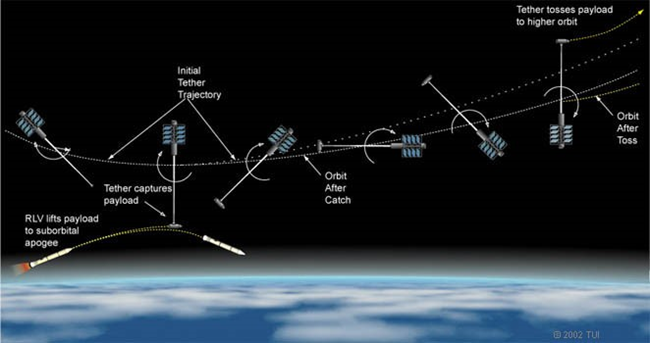 Source: https://www.colorado.edu/faculty/kantha/sites/default/files/attached-files/sandoval_space_tethers.pdf proposed catch and release cycle of a spinning space tether Short Definition: Space tethers are long cables attached to a counterweight. It has many applications in space such as propulsion and momentum exchange etc. This idea could help lowering the amount of money needed to transport payload into low earth orbit by hooking onto specialized spacecrafts in the future and either increasing the speed for space travel or decrease it to prepare for landing.
Detailed Definition:
Despite recent achievements in making spacecrafts fully reusable, space travel and space infrastructure continues to be quite expensive and only reserved for a few institutions and companies. The aim is to commercialize space, but to achieve that goal we still need to vastly decrease the amount of money to get payload into low earth orbit. Skyhooks, a special type of space tethers, could help lowering the cost of transportation into space. The idea is to attach cable hundreds or thousands of kilometres to a counterweight and the weight spins in a circle. The tether will be lowered to be 80-150 kilometres above the earth, where it can hook onto spacecrafts and let them go at the best point to maximize speed adjustment. This idea could make reusable rockets much lighter and cheaper by lowering the amount of rocket fuel needed. This idea acts as a “orbital battery”, where decreasing the spacecrafts speed will increase the amount of energy in the tether and increasing the spacecrafts speed will decrease the amount of energy in the tether.Etymology:
Space from Latinspatium Tether from proto-Germanic teudrą(“rope;cord;shaft”)Sample Sentence(s): Space tethers could revolutionize the space industry by lowering the money needed to get payload into low earth orbit. French: Links to Videos/Articles: https://science.nasa.gov/tether-space | |||
Space Weathering | |||
|---|---|---|---|
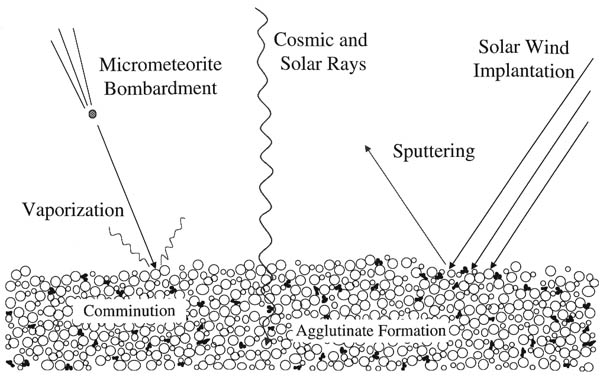 Source: https://planetfacts.org/space-weathering/ Short Definition: Space weathering is a general term used for different surface processes which happen to objects and celestial bodies in the harsh environment of outer space. Detailed Definition: Bodies in the outer space, which do not have atmospheres, are exposed to a number of devastating weathering processes, such as collisions of galactic or solar cosmic rays, the irradiation, implantation and spluttering from solar wind particles; the bombardment by different sizes of meteorites and micrometeorites. These phenomena are encompassed in the blanket term space weathering. The toll that space weathering takes on both the physical and optical properties of the surfaces of many celestial bodies is an important issue, as remotely sensed data needs to be processed appropriately. Etymology: "space" - Old French espace, Latin spatium - room, area, distance, stretch of time "weather" - Old English weder, Old Saxon wedar, Old Norse veðr, German wetar - wind, weather "we-" - Proto-Germanic wedra - to blow Sample Sentence(s): "Space weathering has to be accounted for during the design of space equipment." Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Altération de l'espace German: Weltraumverwitterung Polish: Wietrzenie kosmiczne Swedish: Rymdvittring Links to Videos/Articles: https://spaceweather.com https://sservi.nasa.gov/articles/space-weathering-on-airless-bodies/ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fdzZdFZrGHA | |||
Spacecraft | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: SpaceX (2016, September 25). SpaceX's proposed Interplanetary Spaceship, at Saturn.. wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=51812109 Definition:Vehicle, machine or other apparatus designed to fly or orbit outside the Earth’s atmosphere, i.e. above the Kármán line of 100 km.Etymology:Closed compound noun, consisting of ‘space’ and ‘craft’ Translations:
Note: the Russian translation has a slightly different meaning as it includes devices operating in atmospheres and on surfaces of other celestial bodies. | |||
Spacecraft Propulsion | ||
|---|---|---|
Short Definition: Spacecraft Propulsion is a method utilised to accelerate a spacecraft and artificial satellites. Different methods exist for this purpose, with each method having its advantages and drawbacks. Most spacecrafts nowadays are propelled by what is called a rocket engine, which propels the space probe by heating the reaction mass and allowing it to eject out from the rear of the vehicle. Detailed Definition: A spacecraft propulsion system has the purpose of changing the velocity (acceleration) of a spacecraft and artificial satellites. It is utilised to both leave earth and for orbit insertion. To launch a spacecraft from earth, the propulsion method must overcome a higher gravitational pull to provide a positive net acceleration. The difficulty of achieving this change is directly proportional to the size of the vehicle, which is why spacecraft performance is generally discussed in amount of change in momentum per unit of propellant consumed, known as “specific impulse”. The higher the specific impulse, the better the efficiency. Once launched, satellites and spacecrafts may need to be moved between orbits, thus requiring propulsion. When a satellite has exhausted its ability to adjust its orbit, its useful life is over. The methods areas are divided into four groups: (1.) chemical propulsion (reaction and rocket engines), (2.) electric propulsion (ion, electrothermal and electromagnetic thrusters), (3.) advanced propulsion technologies and (4) supporting technologies. Etymology:
Sample sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages:
Links to Videos/Articles: Space Propulsion: a Survey Study About Current and Future Technologies. DOI: 10.5028/jatm.v10.829 | ||
Spaceship | ||
|---|---|---|
cf. Spacecraft | ||
Special Purpose Dextrous Manipulator (SPDM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: Short Definition: A Special Purpose Dextrous Manipulator (SPDM), also called 'Dextre', is a system that is part of the Mobile Servicing System (MSS) mounted on the International Space Station (ISS). This robotic system is designed to assist astronauts in spaces where human reach and endurance are limited. Detailed Definition: It is a multi-talented robot added to Canadarm2 on March 16, 2008, by Nasa astronauts Mike Foreman and Richard Linnehan. Designed to withstand the harsh conditions of space, this robot supports astronauts for small tasks around the ISS. These tasks include installing and maintaining the various parts of the ISS's exterior, maintaining the Station's electrical system, and pre-testing new equipment to be added. This robot, which has two hands as sensitive as human hands, has a retractable motorized wrench, camera, light, and connection module in both hands. Sample Sentence(s):' 'This multi-talented robot can ride on the end of Canadarm2 to move from worksite to worksite, or be ferried on the Mobile Base System.'' ''Dextre is the most sophisticated space robot ever built.'' Translations: French: Manipulateur agile à usage spécial German: Geschickter Manipulator für besondere Zwecke Italian: Manipolatore abile per scopi speciali Polish: Zręczny manipulator do zadań specjalnych (SPDM) Turkish: Özel Amaçlı Hünerli Manipülatör Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/elements/special-purpose-dextrous-manipulator/ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_Servicing_System https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/iss/dextre/about.asp https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/iss/dextre/ https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/iss/dextre/data-sheet.asp https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nNcRDBK8zxY&ab_channel=CanadianSpaceAgency | |||
Star | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Kutsaev, R. (no data). Stars Galaxy Free Stock Image. stocksnap. https://stocksnap.io/photo/stars-galaxy-IJ5DPL13HR Definition:1) A natural luminous body that is visible in the night sky and can be used for navigation. 2) A large celestial body producing light and energy by means of nuclear reactions inside of it. EtymologyGreek “αστέρι”, Latin “stella” Translations:
| |||
Stellar wind | ||
|---|---|---|
Media Media ESO/Callingham et al. DefinitionsShort Definition Detailed Definition Etymology Stellar: from Latin stella"star" Sample Sentences Bright bow shocks form around stars when their stellar winds interact with the Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages Frenchle vent stellaire German
der Sternwind
Italian
il vento stellare
Polish
wiatr gwiazdowy
Swedish stjärnvind
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Languages Russian Ukrainian Links to Videos/Articles: Stellar Wind. ESA/Hubble. Retrieved [ 06.14.2023 ], from https://esahubble.org/wordbank/stellar-wind/
Holzer, T. E., & Axford, W. I. (1970). The theory of stellar winds and related flows. Annual review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 8(1), 31-60. Retrieved [ 06.17.2023 ], from https://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu//full/1982ApJ...259..282A/0000282.000.html | ||
Supernova | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 25). AI illustration of a supernova. Midjourney. midjourney Definition:Brief, bright illumination of a supermassive star at the end of its lifetime by an explosion in which the original star itself is destroyed. As it dies, a supermassive star goes through various stages of fusing different elements, forming a red supergiant. During this process, more and more heavy material is deposited onto the stellar core. Once the core’s mass tips past a certain threshold it collapses under its own gravity (meaning it cannot withstand its own gravitational force). The outer layers are blasted outwards in a supernova, the biggest explosion known to occur in the Universe. At its peak, a supernova can be brighter than an entire galaxy. Supernovae reach their peak luminosity in a matter of days, so their appearance and early decline can be observed in real time. Etymology:from Latin super “beyond”, “over and above” and stella nova “new star” Translations:English: supernova (neutr.) – [ˌsuːpərˈnoʊvə] French: supernova (f)– [] German: Supernova (f) – [ˈzuːpɐˌnoːva] Polish: supernowa () – [] Russian: сверхновая звезда () - [ˌsvʲerxˈnovəjə zvʲɪzˈda] Swedish: supernova () – [] | |||
Supernova Remnant | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short
Definition
Detailed Definition First, the ejecta expands freely, gradually shedding their mass into the circumstellar or interstellar medium. Subsequently, the remnant begins to gather and compress surrounding gas, forming a prominent shell. In the ensuing phase, the shell undergoes cooling, resulting in the formation of a thinner, more delicate outer layer enveloping the still-hot interior. As the interior continues to cool, the shell expands further under its own momentum. Finally, the remnant merges with the surrounding interstellar medium, culminating in the formation of a fully-fledged supernova remnant. Notable examples of supernova remnants include the Crab Nebula, the remnants of SN 1572, and Kepler, the remnants of SN 1604, named after Johannes Kepler. G1.9+0.3, discovered in the galactic centre, stands as the most recent known remnant within our galaxy.
Sample Sentence(s) “Supernova remnants are very important to the structure of galaxies.” Mathis, J. S. (Invalid Date). supernova remnant. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/supernova-remnant
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
French
German
Italian
Polish
Swedish
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Lang... Turkish Dutch Supernovarest Spanish resto de supernova Portuguese Remanescente de supernova
Links to Videos/Articles: Astrum. (2016a, January 29). Supernova Remnants | Hubble Images
4K | Episode 2 [Video]. YouTube. | ||
Surface | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 25). AI illustration of a planets surface. Midjourney. midjourney Definition:The exterior of an astronomical body that is in contact with outer space or an atmosphere.Etymology:From Latin superficies. Translations:
Links to videos/articles: | |||

