Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Currently sorted By last update descending Sort chronologically: By last update
Accretion disc | |||
|---|---|---|---|
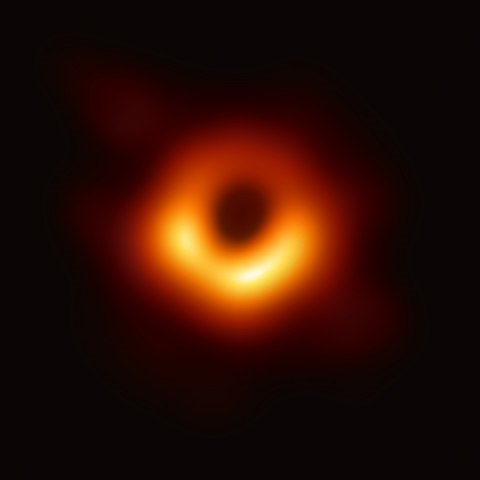

Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Black_hole_-_Messier_87_crop_max_res.jpg Short Definition: An accretion disk is a structure, which is an amalgamation of gas, plasma or particles around the black hole. It is attracted by the gravitational pull and orbits the black hole while it slowly spirals into it, so it is a phenomenon that describes the way how a big celestial body amasses matter like black holes. Detailed Definition: One can not observe black holes or their event horizon, but since black holes have accretion disks, which are a type of structure and accumulations of gas, plasma or particles that were attracted by the huge gravitational pull of black holes. Humans are able to see those accretion disks, because the spinning matter is so fast, which in turn generates heat and emits x-rays and gamma rays. The high amount of angular momentum makes it impossible for the matter to simply fall into the black hole like it would on earth or one would think. Angular momentum decreases despite there being no friction in space, because of turbulence, which is caused by the fact that rotation increases the effect of magnetic fields. Temperatures in the accretion disks tend to vary quite a bit, which is determined by the composition of the accretion disk and its source. Temperatures can go from a few thousand to a few million Kelvin. Etymology: Accretion from Latin ad+ crescere-->accrescere--->accretionem Disk from Latin discus
Sample Sentence(s):
The accretion disk is the natural consequence of how gravitational pull attracts matter and makes it impossible to simply fall into the black hole. Many people think they saw a picture of a black hole, but in reality they only saw a picture of its accretion disk.
French: disque d’accrétion German: Akkretionsscheibe Polish: Dysk akrecyjny Swedish: Accretionsskiva Links to Videos/Articles: GMS: Black Hole Accretion Disk Visualization (nasa.gov) | |||
White Dwarf | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio:  Image/Video/Audio: Picture: A white dwarf Image/Video/Audio Source: File:White dwarf.jpg - Wikimedia Commons. (2011, April 5). https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:White_dwarf.jpg Short Definition:
White dwarfs, or cold stars, is a term often used to describe stars in the final stages of their evolution. These stars, which lose their energy sources and cannot perform fusion reactions, are the stars that tend to squeeze into themselves due to the gravitational law. This phenomenon was firstly discovered by the British astronomer 'William Herschel' in 1783.
Detailed Definition:
As one of the densest stellar remnants in space, white dwarfs are stars that have run out of most of their nuclear fuel and tend to collapse inwards. These stars, which are relatively Earth-sized and composed entirely of carbon and oxygen mass, are less than 1.4 solar masses when their cores are stable, but they tend to suffer constant heat and radiation loss because they do not undergo any fusion process. According to NASA's calculations, the core temperatures of white dwarfs can reach up to 100,000 Kelvin. Apart from the carbon and oxygen mass that make up their core, their envelope are surrounded by thin helium and in some cases hydrogen atoms.
Etymology:
White - from Proto-Indo-European (ḱweydós) Dwarf - from Proto-Germanic (dwergaz) (white - Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/white) (dwarf - Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/dwarf)
Sample Sentence(s):
‘’White dwarfs evolve from stars with an initial mass of up to three or four solar masses or even possibly higher.’’ (The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (1998, July 20). White dwarf star | Definition, Size, Mass, Life Cycles, & Facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/white-dwarf-star) ‘’White
dwarfs reach this incredible density because they are collapsed so
tightly that their electrons are smashed together, forming what is
called "degenerate matter.’’ (Dobrijevic, D., & Tillman, N. T. (2022, March 4). White dwarfs: Facts about the dense stellar remnants. Space.com. https://www.space.com/23756-white-dwarf-stars.html)
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French:
Naine blanche German:
Weißer Zwerg Polish:
Biały karzeł Swedish:
Vit dvärg Turkish:
Beyaz Cüce Links to Videos/Articles:
Dobrijevic, D., & Tillman, N. T. (2022, March 4). White dwarfs: Facts about the dense stellar remnants. Space.com. https://www.space.com/23756-white-dwarf-stars.html Kurzgesagt
– In a Nutshell. (2017, May 4). The Last Light Before Eternal
Darkness – White Dwarfs & Black Dwarfs [Video]. YouTube.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qsN1LglrX9s The
Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (1998, July 20). White dwarf
star | Definition, Size, Mass, Life Cycles, & Facts. Encyclopedia
Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/white-dwarf-star White Dwarfs. (2021, May 4). Science. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/white-dwarfs | |||
Volcano | ||
|---|---|---|
Image: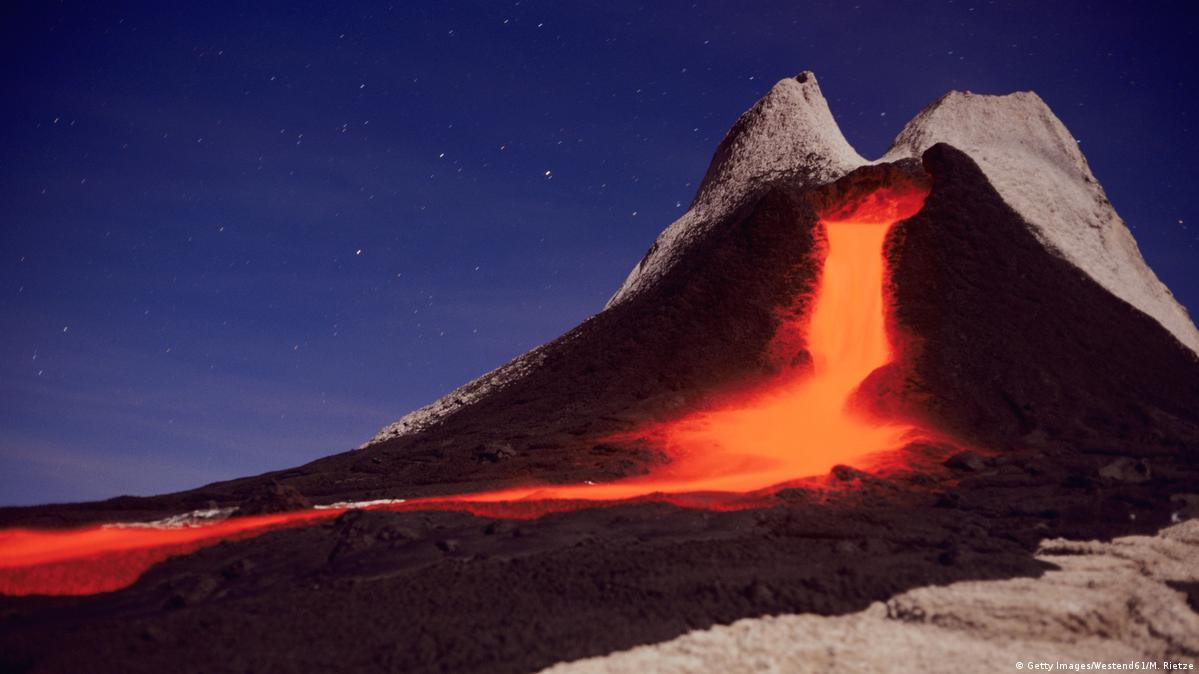  Image: Source: https://www.dw.com/en/volcanic-eruptions-can-cool-the-planet/a-40727123 Short Definition: A volcano is a hill or mountain with a hole where lava, rocks, or gas may be seen erupting from a planet or moon's interior. Detailed Definition: A crack in the earth's crust through which substances such as lava, steam, ashes, etc. are released continually or sporadically. Volcanoes are known to exist on the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, the Moon, Mars, and the moon Io of Jupiter. Only two of these bodies currently have active volcanoes: Earth and Io. However, Venus or Europa, the moon of Jupiter, may have volcanoes erupting. Etymology: Volcano comes from the Latin Vulcanus, which is the name of the fire god. Sample Sentence(s): The volcano's lava was pouring down the mountainside. On the seabed of Jupiter's moon Europa, there has been volcanic activity. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: volcan German: Vulkan Polish: wulkan Swedish: vulkan Links to Videos/Articles: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/topic/volcanoes https://chandra.harvard.edu/press/10_releases/press_081810.html | ||
Vacuum | ||
|---|---|---|
Image:
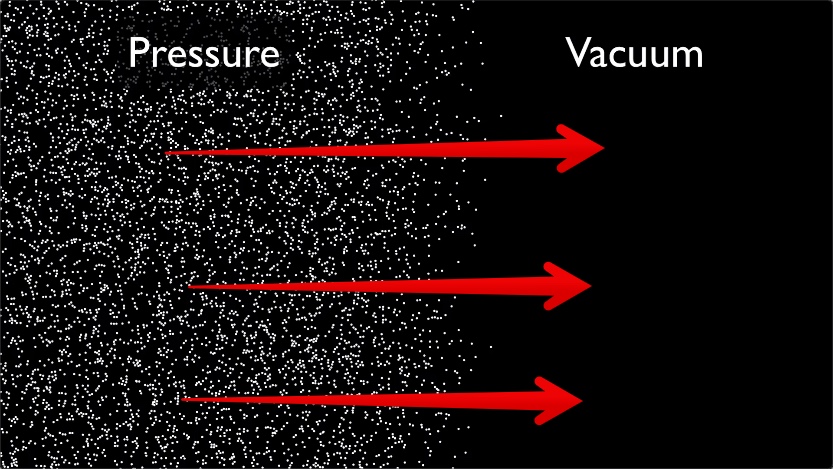 Image: Source: https://www.metabunk.org/attachments/metabunk-2018-10-31-08-37-23-jpg.34929/ Short Definition: A vacuum is a space in which there is no matter such as gas or particles. It is found in space or can be generated by machines. Detailed Definition: Space that does not contain any gas inside its boundaries. However, it is also required that there is not any matter in general in either state such as gas, liquid, or solid, among other complex definition states. Even though the vacuum is found naturally in space, it is used on earth for different machines such as vacuum pumps, and vacuum chambers, among others. Etymology: Vacum comes from the latin Vacuus, which means empty. Sample Sentence(s): Life cannot be found or developed in the vacuum of space. The dead body astronaut rambled in the vacuum of space. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: vide German: Vakuum Polish: próżnia Swedish: svenska Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/365382138_A_Review_of_Research_on_the_Vacuum_Plume DOI: 10.3390/aerospace9110706 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E43-CfukEgs&ab_channel=BBC | ||
Universe | |||
|---|---|---|---|

Source:Cajina, I. (2017, September 17). Milky Way from Max Patch. unsplash. https://unsplash.com/photos/asuyh-_ZX54 DefinitionThe totality of all existing matter, energy, space and time. The universe is approximately 13,8 years old and has emerged as a result of the Big Bang, in which it emerged from a single point and continues to expand. Translation
Links to Videos/Articles:https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/what-is-an-exoplanet/what-is-the-universe/ | |||
Time Dilation | ||
|---|---|---|
Media:  Media: File:Nonsymmetric velocity time dilation.gif - Wikimedia Commons . (2006, January 28). https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nonsymmetric_velocity_time_dilation.gif Short Definition: Time Dilation is a phenomenon observable through the change of measuring of elapsed time by two clocks. The change usually occurs due to the difference in velocity or gravitational potential. The faster you move relative to some object, the slower time seems to flow. Detailed Definition: Time Dilation is an occurrence which takes place due to the difference in velocity or gravitational potential of a given object. It occurs when one of the objects has higher velocity than the other (commonly called a reference frame). The reference frame is a coordinate system defined by certain characteristic points, this frame is stable while the other object travels with a certain velocity, different from the frame. What can be then observed is that the travelling object experiences time slower, than the reference frame (observer). This phenomenon is strictly connected to Einstein's theory of relativity, as the time passes differently, relative to the state (either gravitational or velocity) of the object. Time dilation has been observed and calculated on the International Space Station. The differences in time perception are virtually insignificant (in milliseconds) at small distances, but might increase to even years in difference. Etymology: Time, from Old English "tima" defined as limited space of time. Dilation from Late Latin "dilatationem" meaning widening of something. Sample Sentence(s) 1. The astronauts on the ISS experienced time dilation of around 20 milliseconds, compared to earth. 2. The time on ISS is lagging by about 0.01 seconds for every 12 months on earth, due to time dilation. Translation: French - dilatation du temps German- Zeitdilatation Italian - dilatazione del tempo Polish - dylatacja czasu Swedish - Tidsdilatation | ||
The Kuiper belt | ||
|---|---|---|
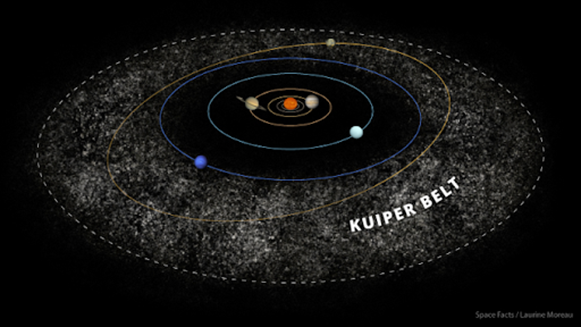 Image Source: https://theplanets.org/kuiper-belt/
Short Definition:
Detailed Definition: Etymology: Kuiper – Dutch
– Kuiper - cooper – from the name of the scientist Gerard Kuiper
Sample Sentence(s): French: German: Polish: Swedish: Spanish
Links to Videos/Articles: https://theplanets.org/kuiper-belt/ | ||
Terrestrial Planets | ||
|---|---|---|
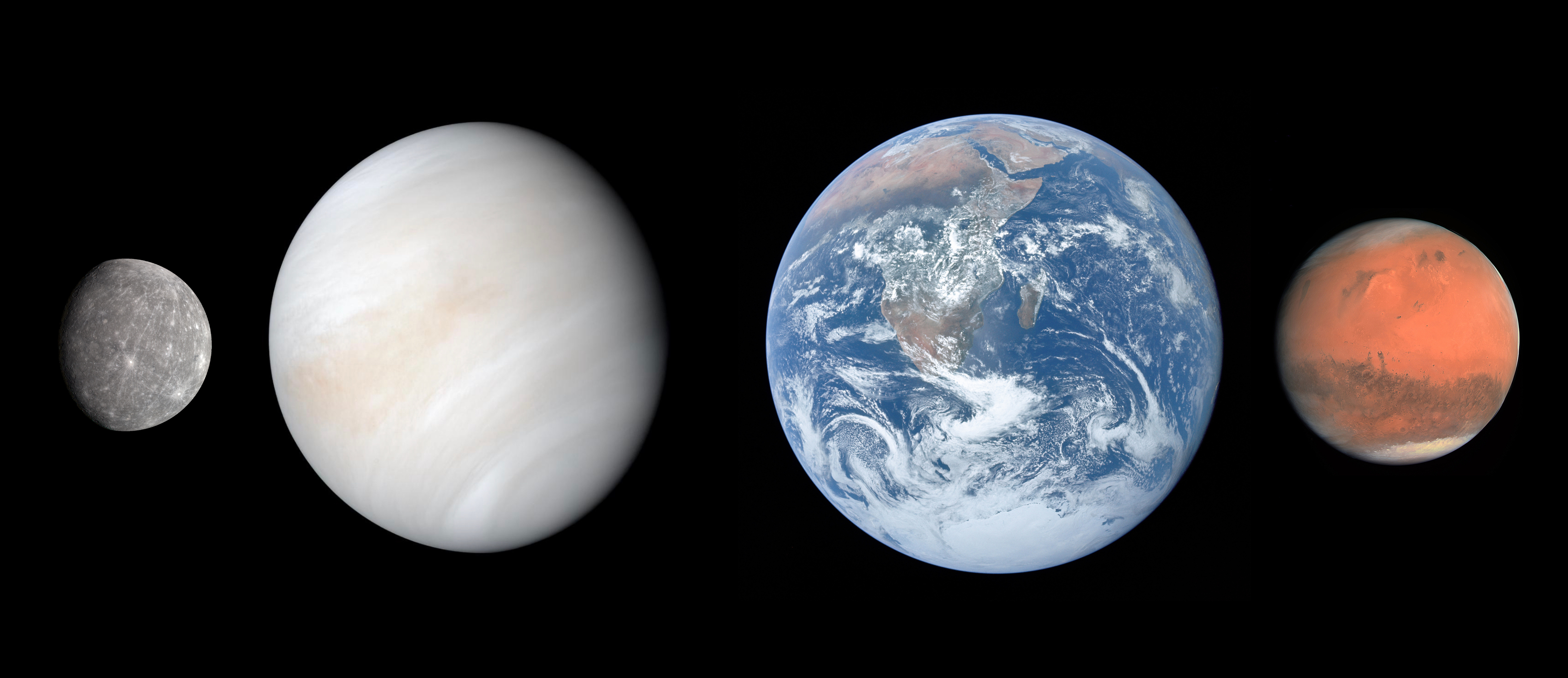 Short
Definition
The word "planet" has its roots in ancient Greek. It comes from the
Greek term "planētēs," which means "wanderer" or
"wandering star." Sample Sentence(s) "It's unclear what the dividing line is between a rocky planet and a terrestrial planet."
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
French
German
Italian
Polish
Swedish
Additional Translations Spanish Planeta terrestre Turkish Karasal gezegen Dutch Aardse planeten
Links to Videos/Articles
Dutfield, S., & Gammon, K. (2022). Terrestrial planets: Definition & facts about the inner planets and beyond. Space.com. https://www.space.com/17028-terrestrial-planets.html Morbidelli, A., Lunine, J. I., O’Brien, D. P., Raymond, S. N., & Walsh, K. J. (2012). Building Terrestrial Planets. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 40(1), 251–275. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-earth-042711-105319 Terrestrial | Planet Types – Exoplanet Exploration: Planets Beyond our Solar System. (n.d.). Exoplanet Exploration: Planets Beyond Our Solar System. https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/what-is-an-exoplanet/planet-types/terrestrial/ Cornerstone Television Network. (2015, October 8). Origins: The
Terrestrial Planets [Video]. YouTube.
MooMooMath and Science. (2019, August 22). Terrestrial Planets in Order
[Video]. YouTube. | ||
Telescope | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: http://catalog.archives.gov/OpaAPI/media/23486741/content/stillpix/255-sts/STS125/STS125_ESC_JPG/255-STS-s125e011848.jpg Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles: | |||||||||

