Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Spécial | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Tout
S |
|---|
Space debris | ||
|---|---|---|
 Image source: Midjourney (2023, June 01). AI illustration of space debris in earths orbit. midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition:
Detailed Definition: space -> spatium from Latin - meaning: space debris -> débriser from French - meaning: break down Sample Sentence(s): French: Débris spatiaux German: Weltraummüll / Weltraumschrott Polish: kosmiczne śmieci Swedish: Rymdskepp Spanish: Desechos espaciales Links to Videos/Articles: https://youtu.be/f513HPs24VM [Space Debris by the European Space Agency, ESA] https://www.nasa.gov/news/debris_faq.html https://www.nasa.gov/centers/hq/library/find/bibliographies/space_debris | ||
Space graveyard | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:S4-space-junk-045.jpg Definition:An area on Earth's surface or orbit in which decommissioned spacecrafts or satellites are discarded. Etymology:Translations:
| |||
Space rendezvous | |||
|---|---|---|---|
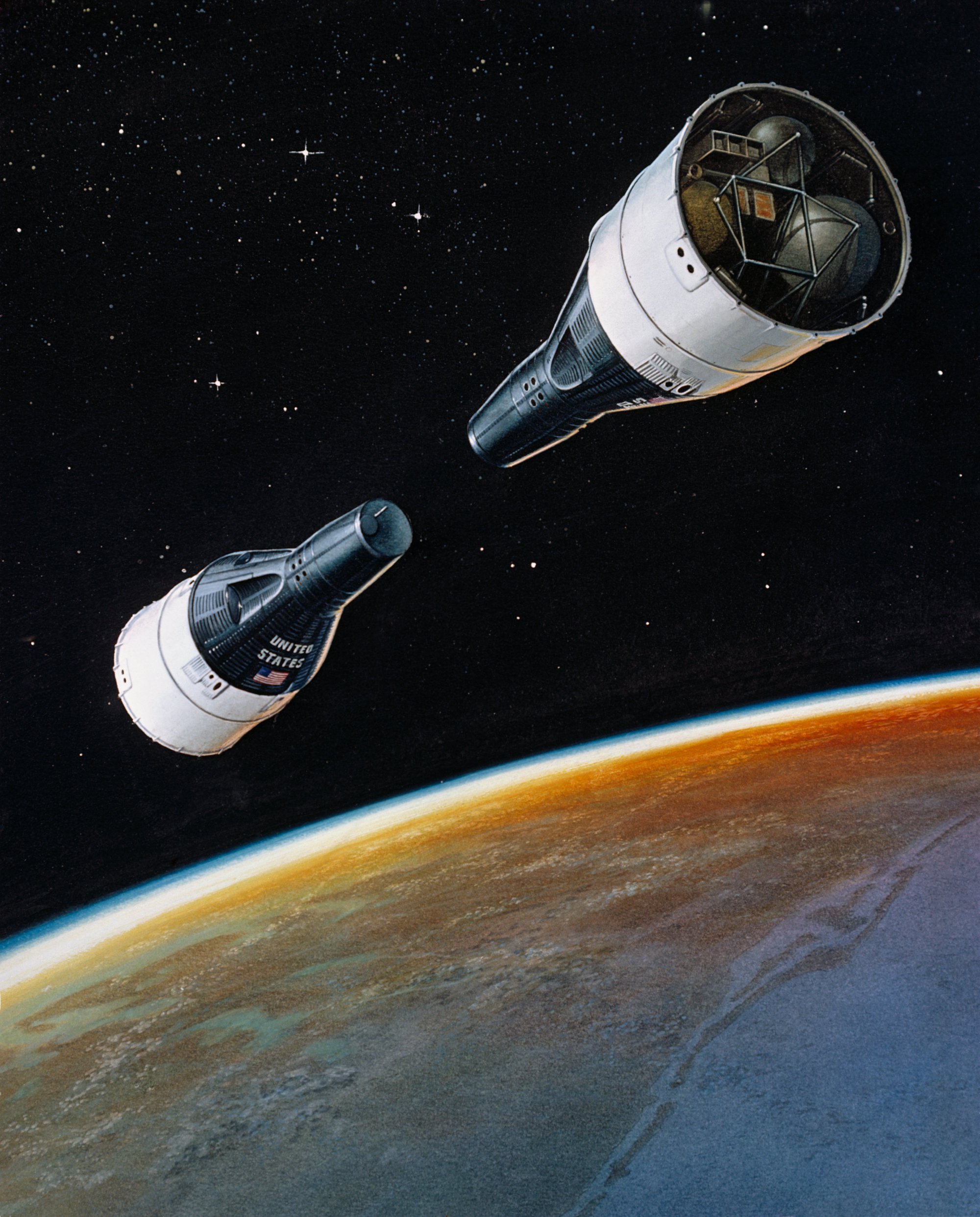 Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:RENDEZVOUS_-_ARTIST_CONCEPT_-_GEMINI-TITAN_GT-VI_and_GT-VII.jpg Short Definition: A space rendezvous is a series of orbital maneuvers focused on bringing together two orbiting spacecrafts. In most cases, a space rendezvous occurs between a space station and a spaceship trying to dock to it. Rendezvous requires a precise match of the orbital velocities and position vectors of spacecrafts, allowing them to remain at a constant distance during final maneuvers or docking. Detailed Definition: A space rendezvous is an approach in space to a very close distance (e.g. within visual contact) between spacecrafts or between a spacecraft and a celestial object at zero or very low relative speed. The space rendezvous requires carrying out complex orbital maneuvers, which must be completed in a minimum time without excessive consumption of the propellant. Rendezvous may or may not be followed by docking or berthing, procedures which bring the spacecraft into physical contact and usually create a link between them. NASA's first attempt at rendezvous was made on June 3, 1965, when astronaut Jim McDivitt tried to maneuver his Gemini 4 spacecraft to meet the Titan II launch vehicle's upper stage. Rendezvous was first successfully accomplished by NASA on December 15, 1965, and then lead to success of Apollo's program and moon landing. Etymology: Space - From Middle English space, from Anglo-Norman space, variant of espace, espas et al., and spaze, variant of espace, from Latin spatium(“to stretch, to pull”). Sample Sentence(s): The first space rendezvous was in 1965 during Gemini program Translations: French: Rendez-vous spatial German: der Raumfahrt Rendezvous Polish: dokowanie, połączenie się statków w przestrzeni kosmicznej Swedish: Rymdmöte Links to Videos/Articles: https://airandspace.si.edu/stories/editorial/worlds-first-space-rendezvous https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oNXPtZDS-cg | |||
Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
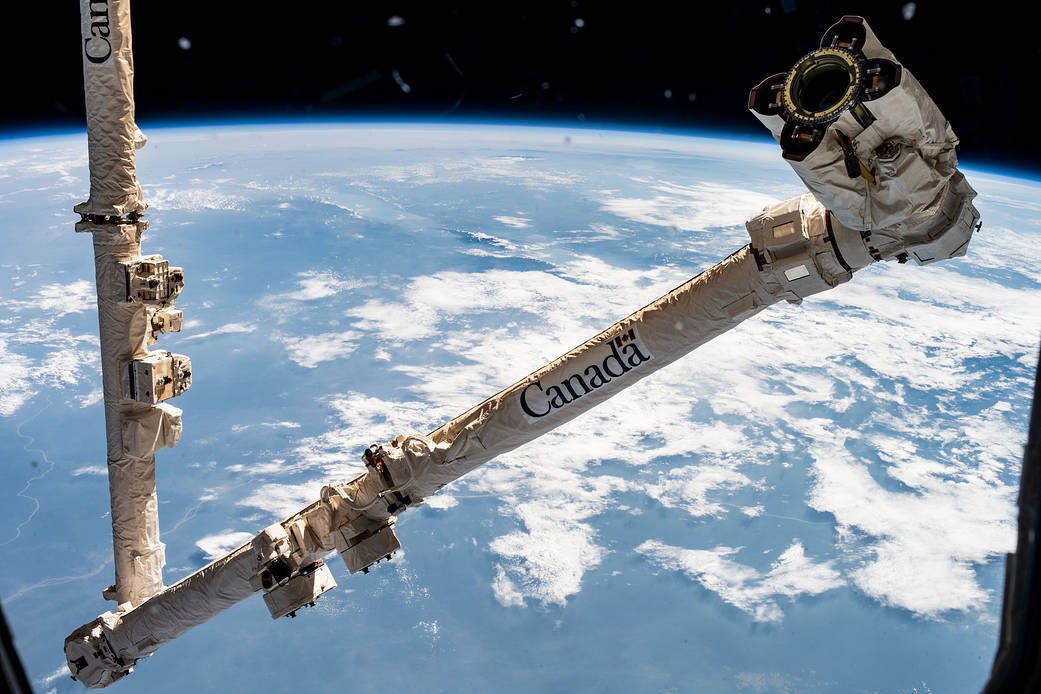 Source: https://www.nasa.gov/image-feature/the-canadarm2-robotic-arm-is-poised-to-capture-cygnus Short Definition: Ssrms is a manipulator system equipped with two long arms, seven attachment points, and various precision robotic equipment is also known as 'Canadarm2', it is a second-generation robotic arm system in the Mobile Servicing System of the International Space Station, whose main purpose is to take part in high-tonnage/cosmic catching missions. It is the most efficient heavy-duty robotic system (Up to 116 tons) left on the ISS after the Canadarm1 was retired in July 2011. Detailed Definition: It is a space manipulator attached to the international space station.As an improved version of the Canadarm 1, the Canadarm 2 is aimed at enhancing; size, load-carrying capacity, arm reach, durability, and increased mobility. It is a robotic system that assists astronauts with payload handling, approach and docking of space shuttles, making Cosmic catches, and maintenance of the station. The robotic arm, which can be managed by the astronauts on the ISS and the NASA and CSA centers on the world, is also adorned with advanced imaging-light systems. It is also used as an anchor point by attaching it to other robotic equipment itself. Sample Sentence(s): ''Canadarm2 is made up of parts that can be replaced while in space.'' ''Canadarm 2 will also help to berth the Axiom Space Station modules to the ISS.'' Translations: French Système de manipulateur à distance de la station spatiale Italian Sistema di manipolazione remota della stazione spaziale Polish System zdalnie sterowanego manipulatora stacji kosmicznej Turkish Uzay İstasyonu Uzaktan Manipülatör Sistemi
German Fernmanipulatorsystem der Raumstation Links to Videos/articles: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2020/04/Canadarm2_robotic_arm https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/iss/canadarm2/about.asp https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/elements/remote-manipulator-system-canadarm2/ | |||
Space tether | |||
|---|---|---|---|
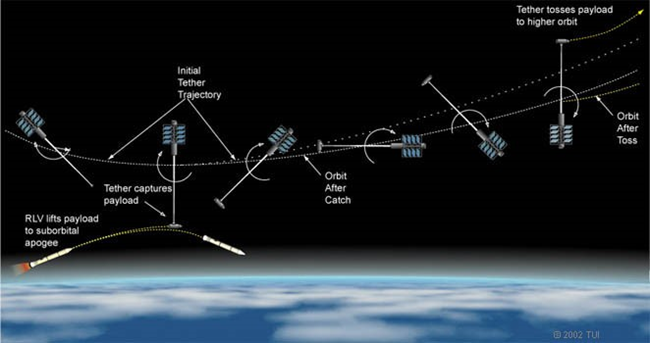 Source: https://www.colorado.edu/faculty/kantha/sites/default/files/attached-files/sandoval_space_tethers.pdf proposed catch and release cycle of a spinning space tether Short Definition: Space tethers are long cables attached to a counterweight. It has many applications in space such as propulsion and momentum exchange etc. This idea could help lowering the amount of money needed to transport payload into low earth orbit by hooking onto specialized spacecrafts in the future and either increasing the speed for space travel or decrease it to prepare for landing.
Detailed Definition:
Despite recent achievements in making spacecrafts fully reusable, space travel and space infrastructure continues to be quite expensive and only reserved for a few institutions and companies. The aim is to commercialize space, but to achieve that goal we still need to vastly decrease the amount of money to get payload into low earth orbit. Skyhooks, a special type of space tethers, could help lowering the cost of transportation into space. The idea is to attach cable hundreds or thousands of kilometres to a counterweight and the weight spins in a circle. The tether will be lowered to be 80-150 kilometres above the earth, where it can hook onto spacecrafts and let them go at the best point to maximize speed adjustment. This idea could make reusable rockets much lighter and cheaper by lowering the amount of rocket fuel needed. This idea acts as a “orbital battery”, where decreasing the spacecrafts speed will increase the amount of energy in the tether and increasing the spacecrafts speed will decrease the amount of energy in the tether.Etymology:
Space from Latinspatium Tether from proto-Germanic teudrą(“rope;cord;shaft”)Sample Sentence(s): Space tethers could revolutionize the space industry by lowering the money needed to get payload into low earth orbit. French: Links to Videos/Articles: https://science.nasa.gov/tether-space | |||
Space Weathering | |||
|---|---|---|---|
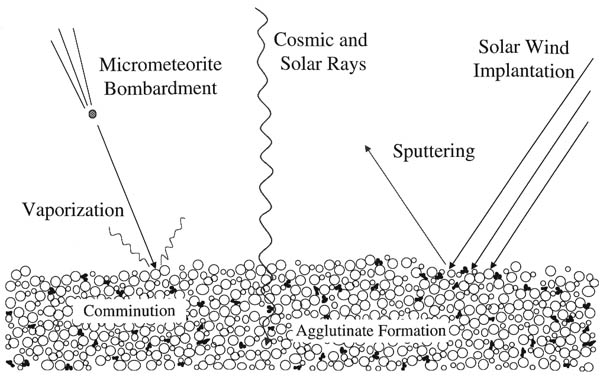 Source: https://planetfacts.org/space-weathering/ Short Definition: Space weathering is a general term used for different surface processes which happen to objects and celestial bodies in the harsh environment of outer space. Detailed Definition: Bodies in the outer space, which do not have atmospheres, are exposed to a number of devastating weathering processes, such as collisions of galactic or solar cosmic rays, the irradiation, implantation and spluttering from solar wind particles; the bombardment by different sizes of meteorites and micrometeorites. These phenomena are encompassed in the blanket term space weathering. The toll that space weathering takes on both the physical and optical properties of the surfaces of many celestial bodies is an important issue, as remotely sensed data needs to be processed appropriately. Etymology: "space" - Old French espace, Latin spatium - room, area, distance, stretch of time "weather" - Old English weder, Old Saxon wedar, Old Norse veðr, German wetar - wind, weather "we-" - Proto-Germanic wedra - to blow Sample Sentence(s): "Space weathering has to be accounted for during the design of space equipment." Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Altération de l'espace German: Weltraumverwitterung Polish: Wietrzenie kosmiczne Swedish: Rymdvittring Links to Videos/Articles: https://spaceweather.com https://sservi.nasa.gov/articles/space-weathering-on-airless-bodies/ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fdzZdFZrGHA | |||
Spacecraft | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: SpaceX (2016, September 25). SpaceX's proposed Interplanetary Spaceship, at Saturn.. wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=51812109 Definition:Vehicle, machine or other apparatus designed to fly or orbit outside the Earth’s atmosphere, i.e. above the Kármán line of 100 km.Etymology:Closed compound noun, consisting of ‘space’ and ‘craft’ Translations:
Note: the Russian translation has a slightly different meaning as it includes devices operating in atmospheres and on surfaces of other celestial bodies. | |||
Spacecraft Propulsion | ||
|---|---|---|
Short Definition: Spacecraft Propulsion is a method utilised to accelerate a spacecraft and artificial satellites. Different methods exist for this purpose, with each method having its advantages and drawbacks. Most spacecrafts nowadays are propelled by what is called a rocket engine, which propels the space probe by heating the reaction mass and allowing it to eject out from the rear of the vehicle. Detailed Definition: A spacecraft propulsion system has the purpose of changing the velocity (acceleration) of a spacecraft and artificial satellites. It is utilised to both leave earth and for orbit insertion. To launch a spacecraft from earth, the propulsion method must overcome a higher gravitational pull to provide a positive net acceleration. The difficulty of achieving this change is directly proportional to the size of the vehicle, which is why spacecraft performance is generally discussed in amount of change in momentum per unit of propellant consumed, known as “specific impulse”. The higher the specific impulse, the better the efficiency. Once launched, satellites and spacecrafts may need to be moved between orbits, thus requiring propulsion. When a satellite has exhausted its ability to adjust its orbit, its useful life is over. The methods areas are divided into four groups: (1.) chemical propulsion (reaction and rocket engines), (2.) electric propulsion (ion, electrothermal and electromagnetic thrusters), (3.) advanced propulsion technologies and (4) supporting technologies. Etymology:
Sample sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages:
Links to Videos/Articles: Space Propulsion: a Survey Study About Current and Future Technologies. DOI: 10.5028/jatm.v10.829 | ||
Spaceship | ||
|---|---|---|
cf. Spacecraft | ||

