Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
R |
|---|
Reaction engine | ||
|---|---|---|
Image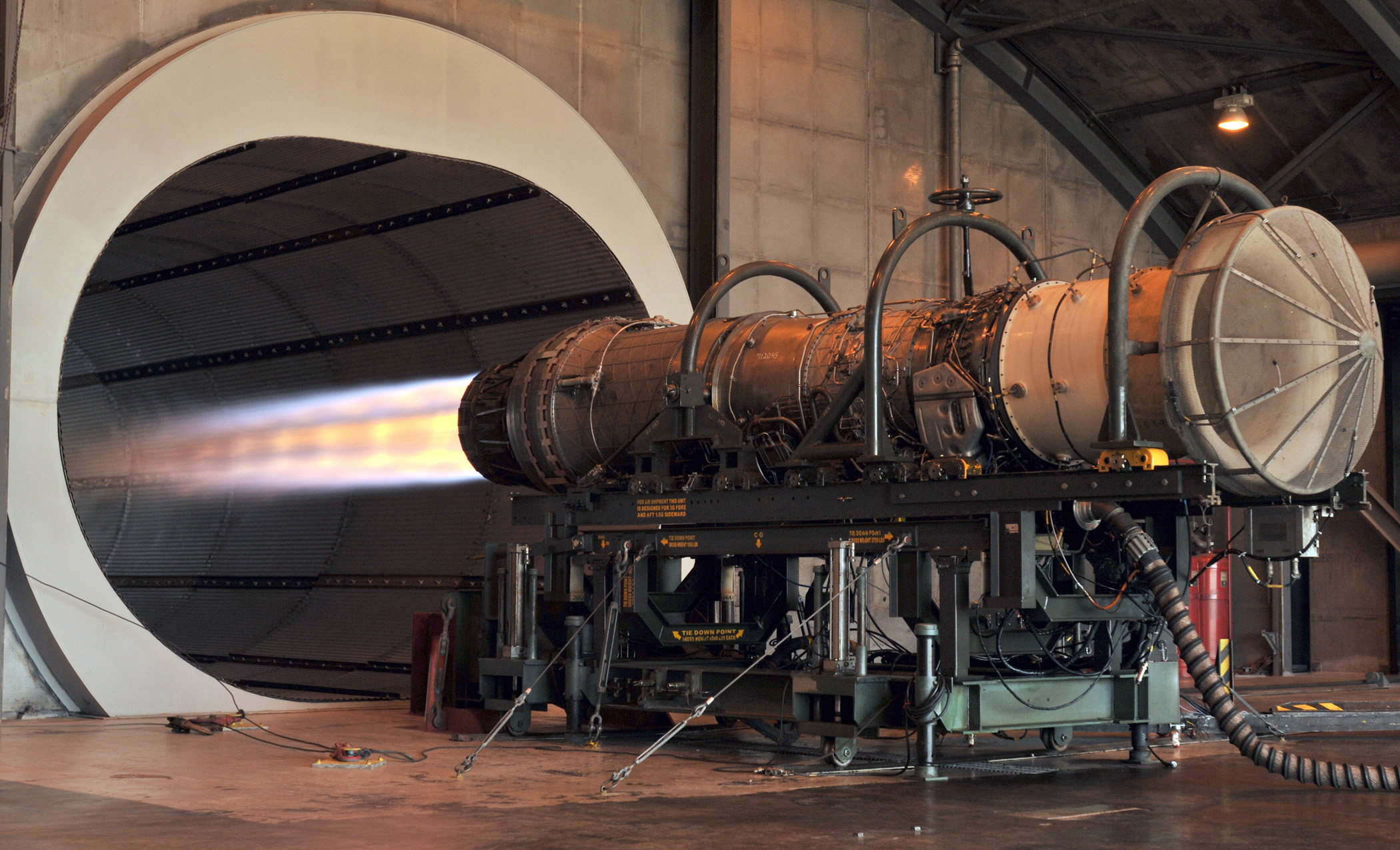  Image U.S. Air Force. (2010, November). F100 F-15 engine. Retrieved from https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/69/F100_F-15_engine.JPG Short Definition A reaction engine is an engine that produces thrust by expelling reaction mass. It works in accordance with the third Newton's law of motion. Detailed Definition Reaction engines work in accordance with the third Newton's law of motion, stating that for every action force there is an equal by magnitude, but opposite in direction, reaction force. Thus, reaction engines apply force to the reaction mass, under which reaction mass accelerates and leaves the engine. As a result, the engine together with the vehicle are accelerated by the reaction force that makes the vehicle move. Jet engines and different types of rocket engines are reaction engines. In fact, this is the only engine capable of working in a vacuum, since there is nothing to propel a vehicle besides the fuel (reaction mass) carried by the vehicle itself, which makes those engines the only applicable to spacecrafts. Reaction engines have a broad application area that is not limited to space. For example, boats and ferries are often powered by reaction engines. But instead of a jet of heated gas, they expel water. Etymology Reaction – re- (back, again, anew) + action (from French réaction)Engine – from Middle English engyn or Anglo-Norman engine or Old French engin– skill, cleverness, war machine Sample Sentences The reaction engine utilized a combination of fuel and oxidizer to generate thrust for propulsion. Translations from alliance partner languages: French: Moteur de réactionGerman: Rückstoßantrieb Italian: Motore a reazione Polish: Silnik reakcyjny Swedish: Reaktionsmotor Translations from other languages: Belarusian: Рэактыўны рухавік References The European Space Agency. (2020, December). System study results for SABRE-powered reusable launcher. Retrieved from https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Transportation/Future_space_transportation/System_study_results_for_SABRE-powered_reusable_launcher Petrescu, R. V., Aversa, R., Apicella, A., Petrescu, F. I. T. (2018, January). Romanian Engineering, "On the Wings of the Wind". Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.3844/jastsp.2018.1.18 | ||
RemoveDEBRIS Mission | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:A mission under the supervision of the Surrey Space Centre of the University of Surrey (supported by Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd., Airbus Defense and Space, Innovative Solutions in Space, CSEM, Inria and Stellenbosch University) that aimed to find the best method of capturing and removing space debris. The project was based on a satellite containing several pieces of equipment (a net, a harpoon, a drag sail and vision-based navigation equipment, as well as a set of targets simulating space debris), which remained in orbit between 2018 and 2021. The satellite platform for the project RemoveDEBRIS was launched using SpaceX Falcon 9, was delivered to the International Space Station and later deployed into orbit, where a series of experiments on debris removal were conducted, using several pieces of equipment:
Translations:
Links to Videos:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XLuHk5gWx3k https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_QUhCLTfXf0 Articles:https://www.surrey.ac.uk/surrey-space-centre/missions/removedebris https://www.airbus.com/en/products-services/space/in-space-infrastructure/removedebris https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/r/removedebris | |||
Rocket engine | ||
|---|---|---|
Image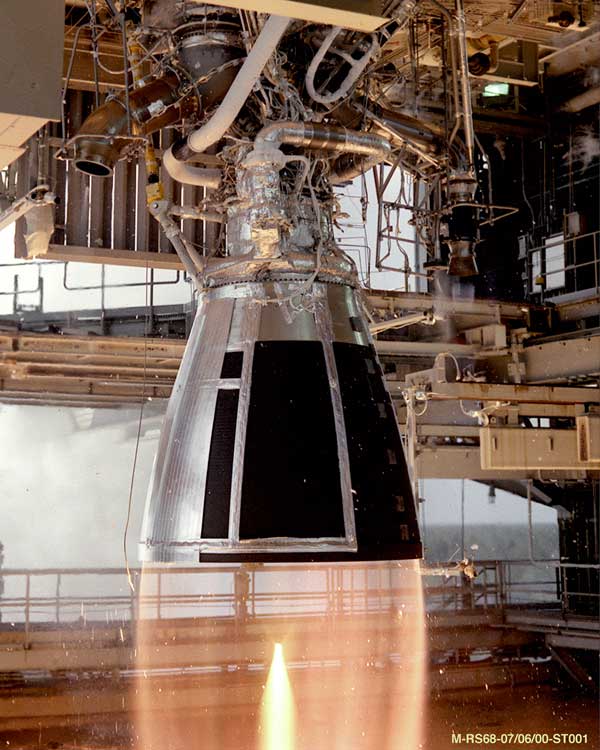  Image NASA. (2000, January). RS-68 being tested at NASA's Stennis Space Center. Retrieved from https://www.nasa.gov/images/content/148709main_d4_testing_08.jpg Photograph of a rocket engine in operation, with a converging plume of hot gas streaming out from the nozzle Short Definition A rocket engine is a jet engine that discharges a jet of high-temperature gas as reaction mass, which was acquired from the propellant stored internally in a vehicle. Rocket engines, unlike general jet engines, can only use internally stored propellant to create a jet, because they have to operate in space, where there is no medium like air or water which can be used as a reaction mass in jet engines on Earth. Detailed Definition A rocket engine is an internal combustion jet engine that discharges a jet of high-temperature gas as reaction mass, which was acquired from the propellant stored internally in a vehicle. Rocket engines, unlike general jet engines, can only use internally stored propellant to create a jet of gas as a result of chemical reactions, because they have to operate in space, where there is no medium like air or water which can be used as a reaction mass in jet engines on Earth. The nozzle is always an integral part of a rocket engine because it makes the jet accelerate as gas moves through the nozzle, and the higher the speed of a discharged jet, the more efficient the engine. The de Laval nozzle is the most common type of nozzles used in rocket engines, as it accelerates the gas passing through it most efficiently. Gas, when burnt, moves at a low subsonic speed and accelerates as it moves through the nozzle, reaching supersonic speed by the moment it leaves the nozzle. Etymology Rocket – from Old Italian rochetto– a bobbinEngine – from Middle English engyn or Anglo-Norman engine or Old French engin– skill, cleverness, war machine Sample Sentences The rocket engine ignited with a powerful roar, propelling the spacecraft into space. Translations from our alliance partners' languages: French: Moteur-fuséeGerman: Raketentriebwerk Italian: Motore a razzo Polish: Silnik rakietowy Swedish: Raketmotor Other language translations: Russian: Ракетный двигатель Ukrainian: Раĸетний двигун Belarusian: Ракетны рухавік References Braeunig, R. A. (2012). Rocket propulsion. Retrieved from http://www.braeunig.us/space/propuls.htm Oberth, H. (1972, January). Ways to spaceflight. Retrieved from https://archive.org/details/nasa_techdoc_19720008133/page/n35/mode/2up | ||
Roscosmos | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:Russian state corporation formed in 2015 and responsible for various aspects of the country’s space exploration activities (space equipment, infrastructure, international cooperation, etc.). The corporation is a legal successor of the Soviet space program which existed from 1955 to 1991 and Russian Space Agency founded in 1992. EtymologyThe name of the corporation “Роскосмос” consists of two elements: “Рос” (abbreviation for “Russian”) and “космос” (“space”). Translations:
| |||
Rover | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Image/Video/Audio Source: Author: Kamila Kopacz Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Other sources: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GMMQUXrcOGY https://www.britannica.com/topic/Mars-Exploration-Rover | |||||||||
S |
|---|
Satellite data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: NOAA Images (2015, August 18). Hurricane Katrina as seen by NOAA satellite. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/77790740@N08/20676559362 Definition:Satellite data, also referred to as satellite imagery, provides information about Earth and other planets in space, which are collected by man-made satellites in their orbits. Satellite data allow us to observe the Earth, as satellites deliver information about the surface and weather changes on the planet Earth. Satellite data is generated via remote sensing technologies. In fact, it is very useful for providing authentic information about the atmospheres, oceans and land masses by constantly collecting data from joined satellites. Etymology:The english word satellite derives from Latin satelles which means "accomplice, follower, attendant, or guard." There are natural satellites, e.g. the planet Moon which is following the Earth on a fix route, but also several artificial satellites which fulfill certain task, e.g. scientific or commercial. Data is the classical plural of Latin datum which means (thing) given. In classical use originally ". From 1897 the term is referred to as "numerical facts collected for future reference." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles: | |||
Solar Eclipse | ||
|---|---|---|
Short Definition
Sample Sentence(s) A solar eclipse cannot be visible from all the places on Earth all at once. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
French
German
Italian
Polish
Swedish Links to Videos/Articles: Hocken, V. (n.d.), What Are Solar Eclipses?, Retrieved from https://www.timeanddate.com/eclipse/solar-eclipse.htmlNASA Science SpacePlace Explore Earth and Space (n.d.), What Is Solar Eclpise?, Retrieved from https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/eclipse-snap/en/ Dobrijevic, D. (n.d.), What is a solar eclipse?, Retrieved from https://www.space.com/15584-solar-eclipses.html Online Etymology Dictionary (n.d.), eclipse (n.), Retrieved from https://www.etymonline.com/word/eclipse Online Etymology Dictionary (n.d.), solar (adj.), Retrieved from https://www.etymonline.com/word/solar#etymonline_v_23841 ESA (2015), Europe’s solar eclipse seen from Proba-2, Retrieved from https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Videos/2015/03/Europe_s_solar_eclipse_seen_from_Proba-2 | ||
Solar sail | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 31). . midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition: Solar sails (also known as light sail or photon sail) are a method of spacecraft propulsion using radiation pressure exerted by starlight on large mirrors. Solar sails can be used instead of traditional fuel consumption. First proposed in the 1980s as alternative propulsion method for low-weight long-distance spacecrafts, the first real usage of the solar sail system was in JAXA’s IKAROS mission, launched in 2010. Detailed Definition: The Solar sails use a phenomenon called solar pressure, which is the force produced by the impact of sunlight photons on the surface of the spacecraft. Normally, solar pressure is affecting all spacecrafts during flights and must be accounted for in trajectory planning, but in that specific case it is used as thrust. Vessels using solar sails must be lightweight as the total force exerted on an eight hundred by eight hundred meters solar sail is about 5 Newtons at Earth's distance from the Sun, so this propulsion method requires specially constructed spacecraft. If solar sails are implemented in space vessel it can produce propulsion without need of fuel usage and thus can be great for small satellites to travel to distant objects without great amount of storage for fuel and engines. The negative side of this technology is significantly small force compared to traditional liquid fuel engines and fragile sail build. Also, this system cannot be used far away from “propulsion” star, as thrust generated by the solar sail is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. Etymology: Solar
- From Latin sōlāris, from sōl (“sun”), Sample Sentence(s): “The IKAROS probe is the world's first spacecraft to use solar sailing as the main propulsion system.” Translations: French: Voile solaire German: Sonnensegel Polish: Żagiel słoneczny Swedish: Sol segel Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305884757_Solar_sail_technology-A_state_of_the_art_review | |||
Solar Storm | ||
|---|---|---|
Media: 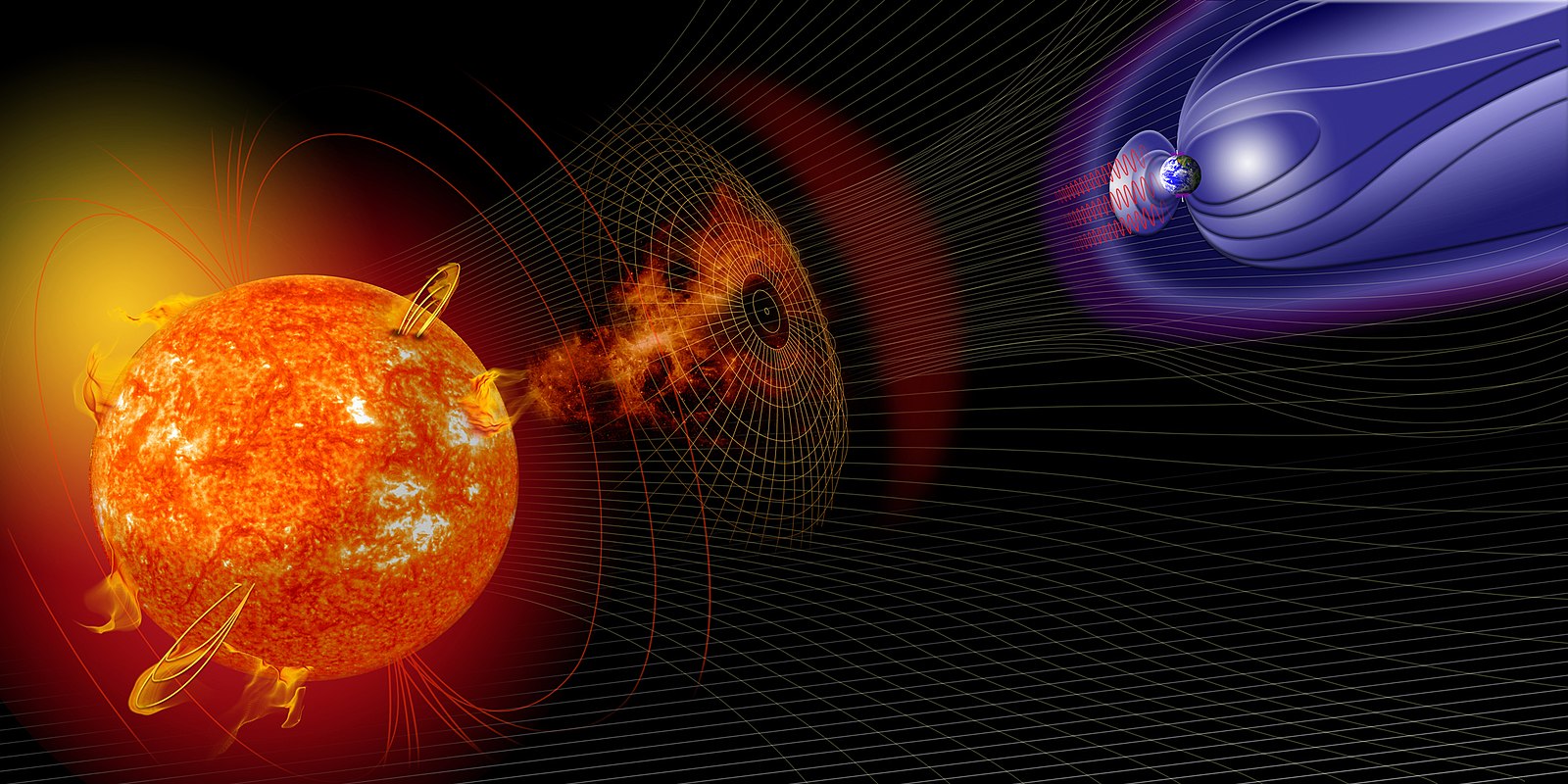 Media: File:Storms From the Sun (6819077978).jpg - Wikimedia Commons . (2005, April 24). https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Storms_From_the_Sun_%286819077978%29.jpg Short Definition: A solar storm is a magnetic eruption happening on a star, causing a large burst of particles at very high speeds. This event is usually associated with visible arches on the sun. Detailed Definition: A solar storm is a phenomenon which is caused by a magnetic eruption on the Sun, which in hand happens due to increasing velocity of charged particles in the Sun's magnetic field. Such eruption, called a solar flare, shoots out mostly protons, which achieve speeds close to the speed of light. Such protons, while reaching the Earth's magnetosphere, they get guided towards both poles and lose their speeds. The occurrence of solar storm, has some negative effects on the earth, but most of the bursts, are light enough to be neutralized by the magnetosphere. The protons that manage to reach earth, usually disturb radio communications or other services and technologies which utilize waves. Etymology solar from Latin "solaris" or "sol" meaning "the sun". Storm from Middle/Old English "storm" meaning "a disturbed state of the atmosphere, especially as affecting the earth's surface". Sample Sentence(s) - The Solar storm is depending on the solar cycle, which lasts around 11 years. - The solar storm disturbed the TV, I couldn't finish watching the game!
Translations: French - tempête solaire German - Sonnensturm Italian - tempesta solare Polish - Burza słoneczna Swedish - solstorm | ||