Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Currently sorted By last update ascending Sort chronologically: By last update
Active galactic nucleus | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short definition: An active galactic nucleus, or an AGN, is an extremely bright compact region in the center of a galaxy. The brightest, most powerful AGNs are classified as quasars. The galaxy hosting an AGN is called an active galaxy. Detailed definition: Active galactic nuclei have a much higher luminosity than any star could produce. They emit radiation across the whole electromagnetic spectrum, from gamma rays to radio waves. Due to their extreme luminosity they can be used as a means of detecting distant objects in space. Etymology: AGN is the commonly used acronym for Active Galactic Nucleus. Sample sentence(s): Using active galactic nuclei to measure cosmic distances could lead to a breakthrough in cosmology. Translations: French: Galaxie active German: Aktiver Galaxienkern Italian: Galassia attiva Polish: aktywne jądro galaktyczne Swedish: Aktiv galaxkärna Links to Videos/Articles: Active Galactic Nucleus. ESA/Hubble | ESA/Hubble. https://esahubble.org/wordbank/active-galactic-nucleus/ What Are Active Galactic Nuclei? (n.d.). WebbTelescope.org. https://webbtelescope.org/contents/articles/what-are-active-galactic-nuclei | ||
Aerolite | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 31). AI image of an aerolite meteorite. midjourney. midjourney.com Short definition: An Aerolite is a stony meteorite that
comes from the asteroid belt. Detailed Definition: In astronomy, an aerolite
is a type of meteorite that is composed primarily of rock and minerals. They
are believed to originate from the asteroid belt, a region between Mars and
Jupiter where many small bodies orbit the Sun. Aerolites are formed from the
debris of collisions between asteroids and are made up of a variety of minerals,
including silicates and oxides. They are different from iron meteorites, which
are composed primarily of iron and nickel. Etymology: aero - air+ -lite - (used to from names of rocks and minerals) Sample Sentence(s):
"The museum's collection includes a small aerolite from the asteroid belt." "The aerolite that landed in the farmer's field was later determined to be a piece of the asteroid Vesta." "Many scientists study aerolites to learn more about the composition of the early solar system." Translations: French: aérolithe German: Steinmeteorit Polish: aerolit Links to videos/articles: https://www.britannica.com/science/stony-meteorite | ||
Antimatter | ||
|---|---|---|
Media: 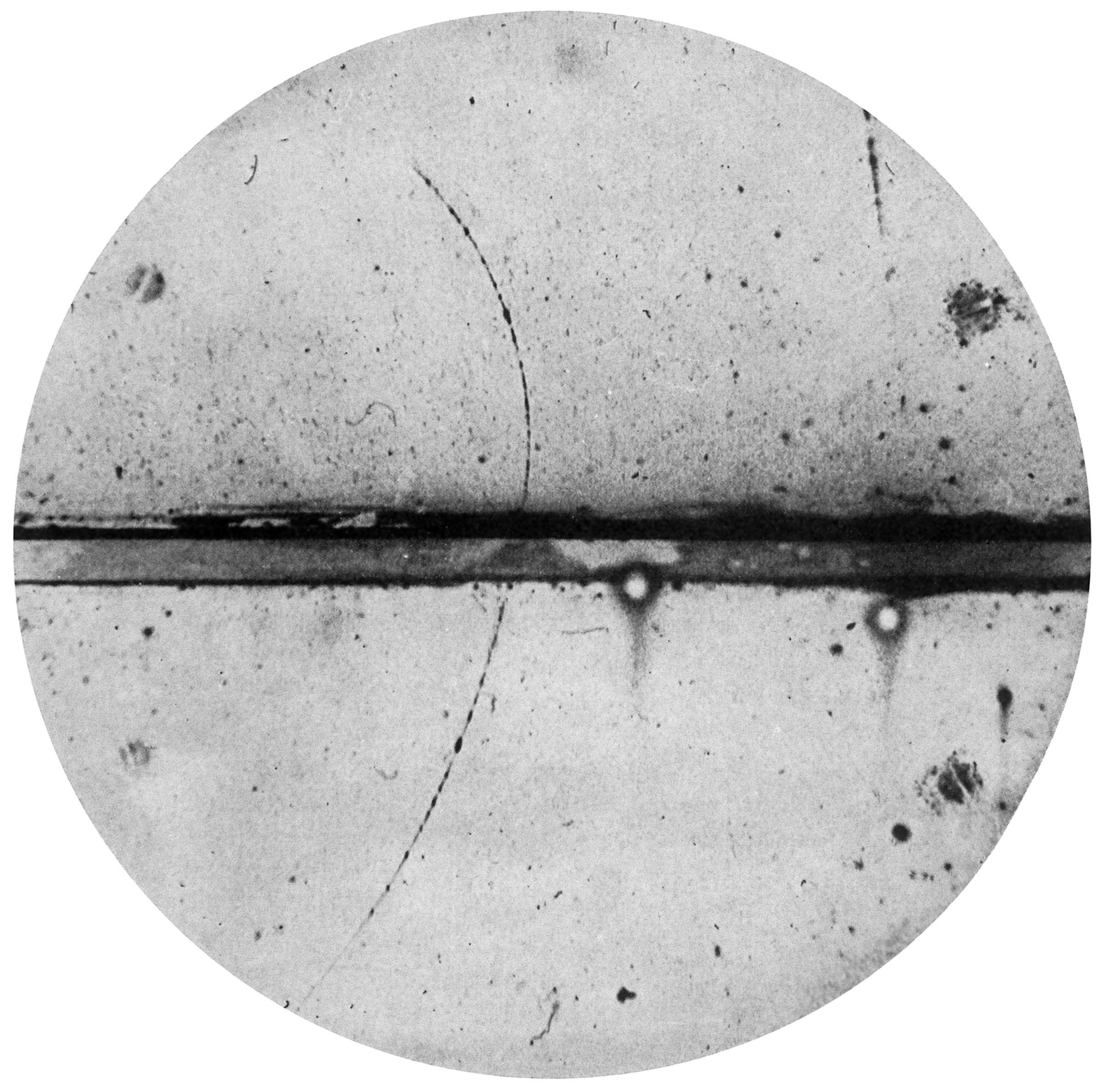 Media: Carl D. Anderson (1905–1991) - Anderson, Carl D. (1933). "The Positive Electron". Physical Review 43 (6): 491–494. DOI:10.1103/PhysRev.43.491. Short Definition: Antimatter is a type of matter which takes on exactly reverse properties to normal matter, considering charge, parity and time in a symmetric matter. Properties such as mass and acceleration are the same to regular matter, even though some are exactly opposite. Where in normal matter electrons have negative charge, antimatter has its own 'positrons' which behave the same as electrons but are positively charged. Detailed Definition: Antimatter is a type of matter which has certain properties flipped. As matter is all around us and is a building block of our universe, antimatter also has a place in our universe. This type of matter has an obvious relation with regular matter. When the two come into contact, they are both annihilated and turn into pure energy. Antimatter has been in our universe since the beginning according to the Big Bang theory. There is far less antimatter in the universe than regular matter, but it constantly gets created through radiation, decay and even lightnings, to shortly after being destroyed by contact with electrons. Antimatter is a well-defined concept in physics and is used in medical PET (Positron emission tomography) scans to form images of our bodies. The term is connected to many other concepts with 'anti-' prefix, as Antimatter is a general concept describing particles with inverse properties to the regular ones. Etymology: The prefix 'anti' from Greek, meaning 'something opposite' and 'matter' from Anglo-French 'materie' meaning 'a substance'. Sample Sentence(s): 1. At CERN, physicists make antimatter to study in experiments. The starting point is the Antiproton Decelerator, which slows down antiprotons so that physicists can investigate their properties. 2. Antimatter and regular matter annihilate each other at contact into pure energy. Translations: French - Antimatière German - Antimaterie Italian - Antimateria Polish - antymateria Swedish - Antimateria | ||
Apogee | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: Short Definition: An apogee is a point in an elliptical orbit, which is considered to be the farthest point from Earth. Detailed Definition: There are two sides in any elliptical orbit, with the names referring to the primary body in the orbit. The closest and farthest points are referred to by, respectively, the prefixes peri- and apo-. The suffix is determined by the primary body, which in the case of Earth is -gee. Therefore, an apogee is the term describing the farthest point on the elliptical orbit of Earth. A satellite is at its slowest when travelling through the apogee. Etymology: "apogee" - French apogée, Latin apogaeum, Greek apogaion - point at which the Moon is farthest from the Earth "apo-" - Greek apo, Avestan apa, Latin ab - off, away, away from "Gaia" / "ge" - Greek Gaia / gaia - a titan, personification of Earth Sample Sentence(s): A satellite that travel around a celestial body is at its slowest whenever the satellite is at its apogee. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Apogée German: Höhepunkt Polish: apogeum Swedish: Höjdpunkt Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.allthescience.org/what-is-an-apogee.htm | |||
Asteroid | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Burned Pineapple Productions (2018, June 14). asteroid. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/51686021@N07/42075207904 Short definition: An asteroid is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the sun, also known as a “minor planet”. They can be rocky, metallic, or icy bodies with no atmosphere and range in a wide spectrum of sizes and shapes. Long definition: An asteroid is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the sun, also known as a “minor planet”. They can be rocky, metallic, or icy bodies with no atmosphere and vary greatly in shape and size, from 1000 km to 1 m across. The three largest asteroids (Ceres, Vesta and Pallas) look very much like miniature planets by being almost spherical and containing some partly differentiated interiors. They are thought to be surviving protoplanets. Nevertheless, a wide majority of asteroids are smaller and irregularly shaped and are thought to be shattered remnants of planetesimals, which are bodies that never grew large enough to become planets within the formation of the solar system (solar nebula) or fragments of bigger bodies. The physical composition of asteroids is in most cases still poorly understood and varies from asteroid to asteroid. They are classified by their emission spectra and are divided generally in three big groups: C-type, M-type, and S-Type, named after their compositions carbon-rich, metallic, and salicaceous, respectively. In the main asteroid belt there are two primary types of asteroids: dark, volatile-rich asteroid consisting of the C-type and P-type, and dense, volatile-poor asteroids consisting of the S-type and M-type asteroids.Etymology: From Greek asteroeidēs ‘starlike’, from astēr ‘star’. Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Astrobiology | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 11). Artistic AI Illustration of Astrobiology. midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition:Astrobiology is an interdisciplinary field of research concerned with the origin, evolution, distribution and future of life in the universe. It encompasses research in astronomy, biology, chemistry, geology, and physics. Detailed Definition:The goal of this study is to understand more about the origin and evolution of life on Earth, planetary system formation, organic compounds in space, and whether or not life exists or might exist elsewhere. Especially the frozen moons of the outer solar system, particularly Europa and Enceladus, as well as Mars, are of significant astrobiological interest. These solar system bodies are the focus of current and future multinational space missions, for example in the DLR. Etymology:
astro - Ancient Greek - ἄστρον (astron) "star" bio – Ancient Greek - βίος (bíos) “life” logy – Ancient Greek -λογία (logía) “branch of study” or “to speak” Sample Sentence(s):
“The research field of astrobiology is gaining more and more importance in the last decades.” “Did you see the documentary on astrobiology last week?” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:
https://www.dlr.de/me/en/desktopdefault.aspx/tabid-2016/ | ||
Astronomy | |||
|---|---|---|---|
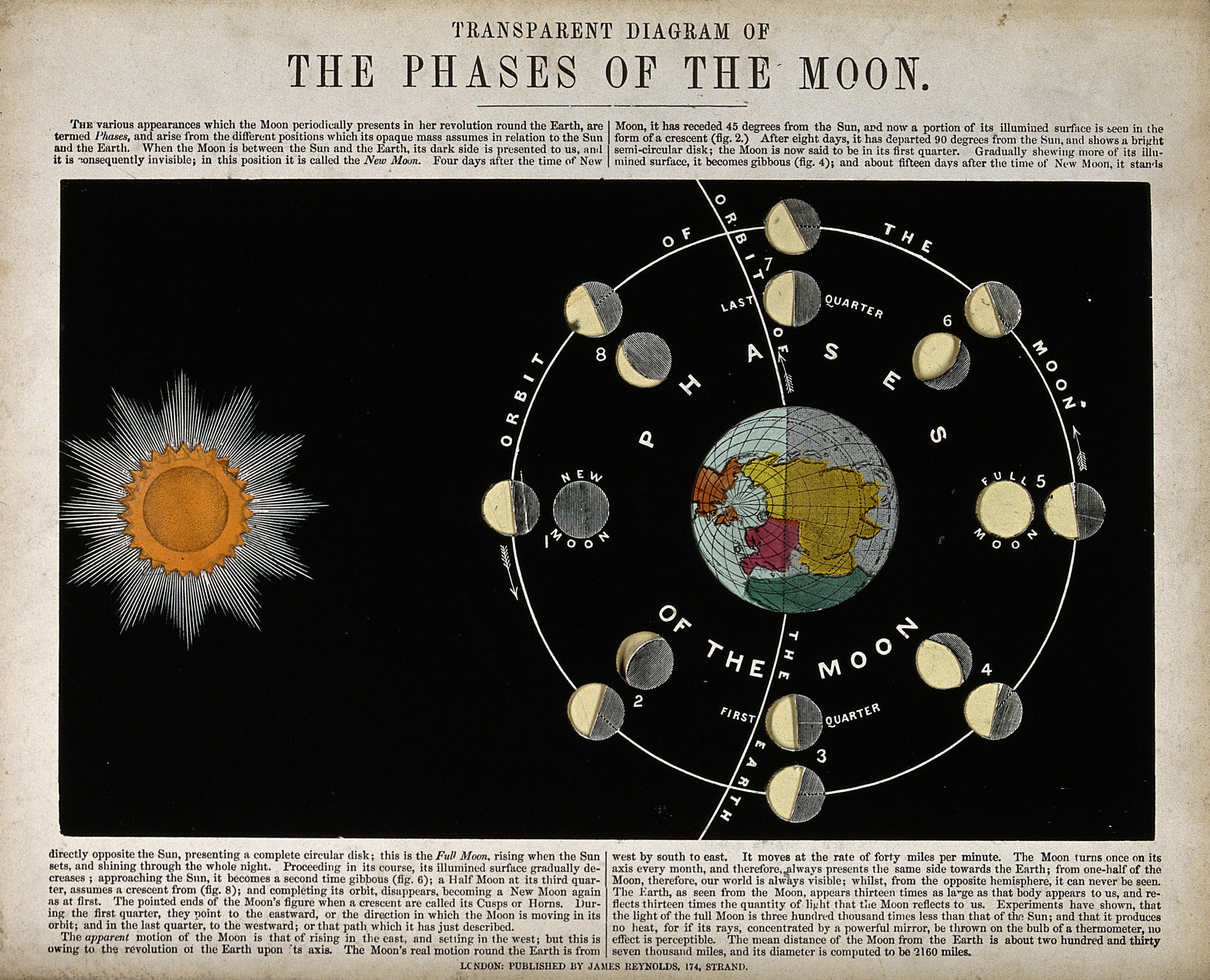 Image/Video/Audio: Diagram: Phases of the Moon Image/Video/Audio Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/8b/Astronomy%3B_a_diagram_of_the_phases_of_the_moon._Engraving._Wellcome_V0024718.jpg Short Definition:
Astronomy is a positive science that includes the discovery, observation, interpretation and recording of all objects and phenomena in space. Before 17th century, astronomy, which worked only to observe and interpret the positions and motion capabilities of observable celestial bodies due to technological inadequacies, after advanced its agenda in all space with the advancement of technology. Detailed Definition:
Astronomy, which aims to investigate first our galaxy and then the whole space in the light of the physics and chemistry sciences that have developed since the 19th century, it also includes to investigate structures and movements of celestial bodies, the formation of galaxies and the chemical analysis of this formation, and the distances and brightness levels of these objects and phenomena. There are 4 main sub-branches of today's contemporary astronomy. These are; Astrophysics: Examines the harmony and application of defined laws of physics in space. Astrometry: It deals with mapping the locations of space objects and their distances from each other. Astrogeology: It deals with the elucidation and understanding of the structure and reserves of materials in space. Astrobiology: Examines possible extraterrestrial life. All these sub-domains contain more of an observable method besides being experimental due to he lack of possibilities we have today in regards with technology.
Etymology:
‘Astron’ (star) – From Ancient Greek ‘Nomos’ (rule, law) – From Ancient Greek
Sample Sentence(s):
''Astronomy has expanded to include astrophysics, the application of physical and chemical knowledge to an understanding of the nature of celestial objects and the physical processes that control their formation, evolution, and emission of radiation.'' (Evans, J. (2023, January 5). Astronomy | Definition, History, Discoveries, & Facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/astronomy) ‘’Astrology can be fun to think about, but it’s different from astronomy. Astrology is not science!’’ (Cloudflare CAPTCHA. (n.d.). https://www.amnh.org/explore/ology/astronomy/what-is-astronomy) Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French:
Astronomie German:
Astronomie Polish:
astronomia Swedish:
Astronomi Turkish: Astronomi
Links to Videos/Articles:
Astronomic. (2015, July 7). Astronomy: Explained | Astronomic [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XinkicMVzLs Cloudflare CAPTCHA. (n.d.). https://www.amnh.org/explore/ology/astronomy/what-is-astronomy E., E. (2022, May 12). 17 branches of astronomy. Earth How. https://earthhow.com/what-is-astronomy/ Evans, J. (2023, January 5). Astronomy | Definition, History, Discoveries, & Facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/astronomy | |||
Biomining | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 24). AI illustration of microorganisms on ore. midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition:A process involving the extraction of a resource using biological tools. For example, with bacteria or algea. Detailed Definition:Biomining is an environmentally friendly and energy efficient way of extracting useful elements by using microbes to break down rocks to make soil or provide nutrients. Microbes are tiny organisms, such as bacteria and fungi, that have a wide variety of functions. Some microbes have abilities that could be beneficial to humans, such as biomining. Etymology:Bio: From Ancient Greek βίο- (bo-), combining form and stem of βίος (bíos, “life”). Mining: Any activity that extracts or unearths minerals. Sample Sentence:You can use biomining to extract minerals from asteroids using bacteria or fungi." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.sciencedirect.com/referencework/9780080885049/comprehensive-biotechnology | ||
Chandrasekhar limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|
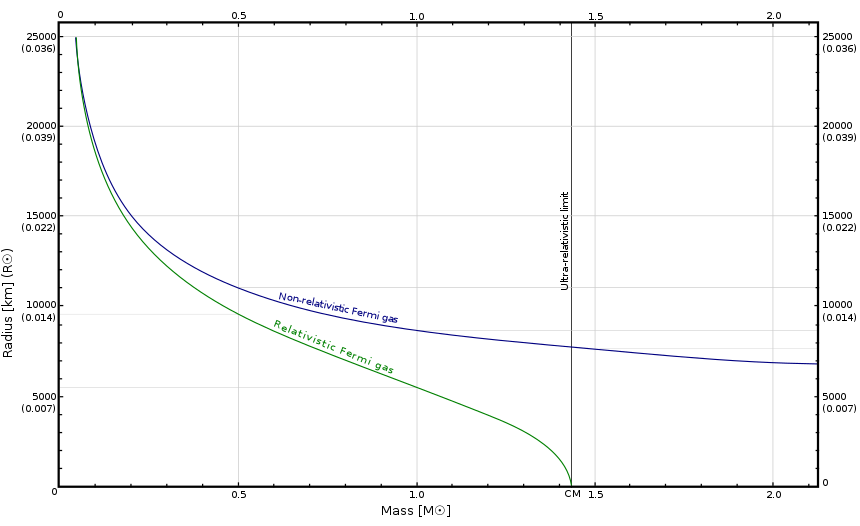 Creator : Unknown Year: (n.d.) Title of image: White Dwarf Mass-Radius Relationship Description of image: Graph illustrating the mass-radius relationship of white dwarf stars Retrieved from URL: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/14/WhiteDwarf_mass-radius_en.svg/860px-WhiteDwarf_mass-radius_en.svg.png Definitions
Sample Sentence(s)
Author : Staff, Space.com Year: (n.d.) Title of the article: Chandrasekhar Limit: Definition, Facts & Equation Title of the Website: Space.com Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023 URL: https://www.space.com/chandrasekhar-limit
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Lang...
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.toppr.com/guides/physics/astronomy/chandrasekhar-limit/ Author(s): Unknown Year: (n.d.) Title of the article: Chandrasekhar Limit Title of the Website: Toppr.com Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, URL: https://www.toppr.com/guides/physics/astronomy/chandrasekhar-limit/
| |||
