Dictionary of Space Concepts
Welcome to the Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space", students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC.
@ | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Alle
A |
|---|
Absolute Magnitude | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio:
Short Definition:
Absolute magnitude is the measurement of the brightness of celestial bodies using inverse logarithmic calculations in astronomical calculations and expressed as a mathematical value. This process involves mathematically expressing their luminosity, as a hypothesis, by placing objects at an equal distance from the observer (10 parsecs that equals to 32.6 light years).
Detailed Definition:
Absolute magnitude is also called absolute visual magnitude, which is a hypothesis that predicts the mathematical calculation of the luminosity of different celestial bodies, taking into account fixed distances, and comparing the luminosities of these objects. The mathematical formula used to calculate this luminosity is as follows; Mv: Absolute magnitude m: Apparent magnitude d: Distance in 10 parsecs Mv = m – 2.5 log [d/10]² The apparent magnitude here, on an inverse scale, indicates how bright celestial objects appear to our eyes. Because it's an inverted scale, high numbers indicate dim objects and low numbers indicate bright objects. The brightest object known and measured on this scale has a value of -10, while the star Sirius has a luminosity of 1.4, and our sun has a luminosity of 4.8.
Etymology:
Absolute -from old Latin (absolūtus) (Absolute – Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/absolute) Magnitude -from old Latin (Magnus) (Magnitude – Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/magnitude)
Sample Sentence(s):
‘’When comet 289P/Blanpain was discovered in 1819, its absolute magnitude was estimated as {\displaystyle M_{1}=8.5}{\displaystyle M_{1}=8.5}’’ (Wikipedia contributors. (2023, January 13). Absolute magnitude. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Absolute_magnitude) ‘’Colour–magnitude diagram, in astronomy, graph showing the relation between the absolute magnitudes (brightnesses) of stars and their colours, which are closely related to their temperatures and spectral types.’’ (The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (1998, July 20). Colour–magnitude diagram | astronomy. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/colour-magnitude-diagram) Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages:
French:
Magnitude absolue German:
Absolute Helligkeit Polish:
wielkość absolutna Swedish:
Absolut magnitud Turkish: Mutlak Kadir
Links to Videos/Articles:
Absolute magnitude | astronomy. (n.d.-a). Encyclopaedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/absolute-magnitude Absolute Magnitude | COSMOS. (n.d.-a). https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/a/Absolute+Magnitude Apparent and Absolute Magnitudes. (n.d.-b). https://www.phys.ksu.edu/personal/wysin/astro/magnitudes.html Michel van Biezen. (2014, April 9). Astronomy - Measuring Distance, Size, and Luminosity (18 of 30) Absolute Magnitude [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yfsUhOPCMaM | |||
Accretion disc | |||
|---|---|---|---|
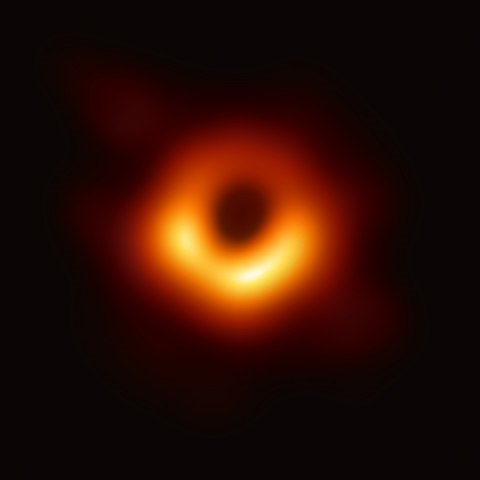

Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Black_hole_-_Messier_87_crop_max_res.jpg Short Definition: An accretion disk is a structure, which is an amalgamation of gas, plasma or particles around the black hole. It is attracted by the gravitational pull and orbits the black hole while it slowly spirals into it, so it is a phenomenon that describes the way how a big celestial body amasses matter like black holes. Detailed Definition: One can not observe black holes or their event horizon, but since black holes have accretion disks, which are a type of structure and accumulations of gas, plasma or particles that were attracted by the huge gravitational pull of black holes. Humans are able to see those accretion disks, because the spinning matter is so fast, which in turn generates heat and emits x-rays and gamma rays. The high amount of angular momentum makes it impossible for the matter to simply fall into the black hole like it would on earth or one would think. Angular momentum decreases despite there being no friction in space, because of turbulence, which is caused by the fact that rotation increases the effect of magnetic fields. Temperatures in the accretion disks tend to vary quite a bit, which is determined by the composition of the accretion disk and its source. Temperatures can go from a few thousand to a few million Kelvin. Etymology: Accretion from Latin ad+ crescere-->accrescere--->accretionem Disk from Latin discus
Sample Sentence(s):
The accretion disk is the natural consequence of how gravitational pull attracts matter and makes it impossible to simply fall into the black hole. Many people think they saw a picture of a black hole, but in reality they only saw a picture of its accretion disk.
French: disque d’accrétion German: Akkretionsscheibe Polish: Dysk akrecyjny Swedish: Accretionsskiva Links to Videos/Articles: GMS: Black Hole Accretion Disk Visualization (nasa.gov) | |||
Additive manufacturing | ||
|---|---|---|
DefinitionsShort Definition Detailed Definition Etymology Sample Sentence(s)Extensive use of additive manufacturing in aerospace industry will result in more frequent launches, as this technology greatly shortens the expenses. The most common and well-known example of additive manufacturing is 3-D printing models from melted plastic. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner LanguagesFrench la fabrication additive German Italian Polish Swedish Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other LanguagesRussian аддитивное производство Ukrainian Links to Videos/Articles:2. Additive manufacturing, explained | MIT Sloan. (2017b, December 7). MIT Sloan. Retrieved [ 06.14.2023 ], from https://mitsloan.mit.edu/ideas-made-to-matter/additive-manufacturing-explained 3. SAE Media Group. (2020, January 17). 3D Printing and Space Exploration: How NASA Will Use Additive Manufacturing. Tech Briefs. Retrieved [ 06.20.2023 ], from https://www.techbriefs.com/component/content/article/tb/stories/blog/35871 | ||
Aerolite | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 31). AI image of an aerolite meteorite. midjourney. midjourney.com Short definition: An Aerolite is a stony meteorite that
comes from the asteroid belt. Detailed Definition: In astronomy, an aerolite
is a type of meteorite that is composed primarily of rock and minerals. They
are believed to originate from the asteroid belt, a region between Mars and
Jupiter where many small bodies orbit the Sun. Aerolites are formed from the
debris of collisions between asteroids and are made up of a variety of minerals,
including silicates and oxides. They are different from iron meteorites, which
are composed primarily of iron and nickel. Etymology: aero - air+ -lite - (used to from names of rocks and minerals) Sample Sentence(s):
"The museum's collection includes a small aerolite from the asteroid belt." "The aerolite that landed in the farmer's field was later determined to be a piece of the asteroid Vesta." "Many scientists study aerolites to learn more about the composition of the early solar system." Translations: French: aérolithe German: Steinmeteorit Polish: aerolit Links to videos/articles: https://www.britannica.com/science/stony-meteorite | ||
Almucantar | ||
|---|---|---|
Media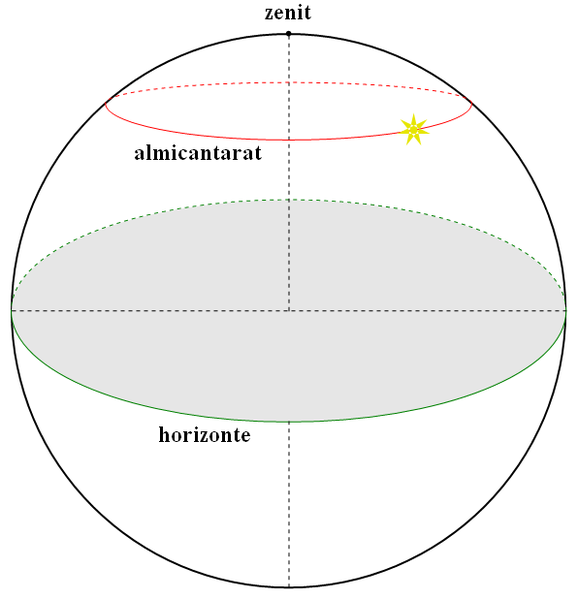 DefinitionsAlmucantar (also known as almucantarat, almacantara) is a circle of the celestial sphere parallel to the horizon. Stars belonging to the same almucantar have the same altitude. Detailed Definition
Almucantar is commonly defined by the arc on the celestial sphere, characterized by the zenith angle, which represents half of its angular magnitude. The almucantar plane refers to a plane within the celestial sphere that is formed by the almucantar. A solar almucantar specifically denotes an almucantar plane used for measuring the irradiance of the Sun. Etymology
From French almucantarat, from Arabic almuqanṭarāt"circles of celestial latitude" , from qanṭara"arch" Sample Sentence(s)The Sun and the Moon seized their almucantar and remained there for a moment, dividing the world into day and night.
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner LanguagesFrench
l'almicantarat German
der Almukantarat Italian
l’almucantarat Polish
almukantar, almukantarat Swedish
almicantarat Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other LanguagesRussian
альмукантарат
Ukrainian
альмукантарат
Links to Videos/Articles:The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (1998a, July 20). Almucantar | astronomy. Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved [ 06.14.2023 ], from https://www.britannica.com/science/almucantar | ||
Analog habitat | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Mars Desert Research Station - an analog habitat in the middle of a desert in Utah Source: Wikipedia An analog habitat is a facility that is set up to imitate martian or lunar conditions on earth. Detailed Definition: An analog habitat is a base meant to simulate a space habitat or colony. It is designed to test and study the feasibility of living in such a habitat. Analog habitats are used to test technologies and systems that could be used in a real space habitat, and to study the psychological and social effects of living in a closed environment without the risks and cost of an actual space mission. Etymology: From Latin habitō (“I live or I dwell”). Sample Sentence(s): An analog habitat was set up in the middle of a desert. Translations: French: habitat analogique German: analoger Lebensraum Polish: habitat analogowy Swedish: analog livsmiljö Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352309321000018 | |||
Antimatter | ||
|---|---|---|
Media: 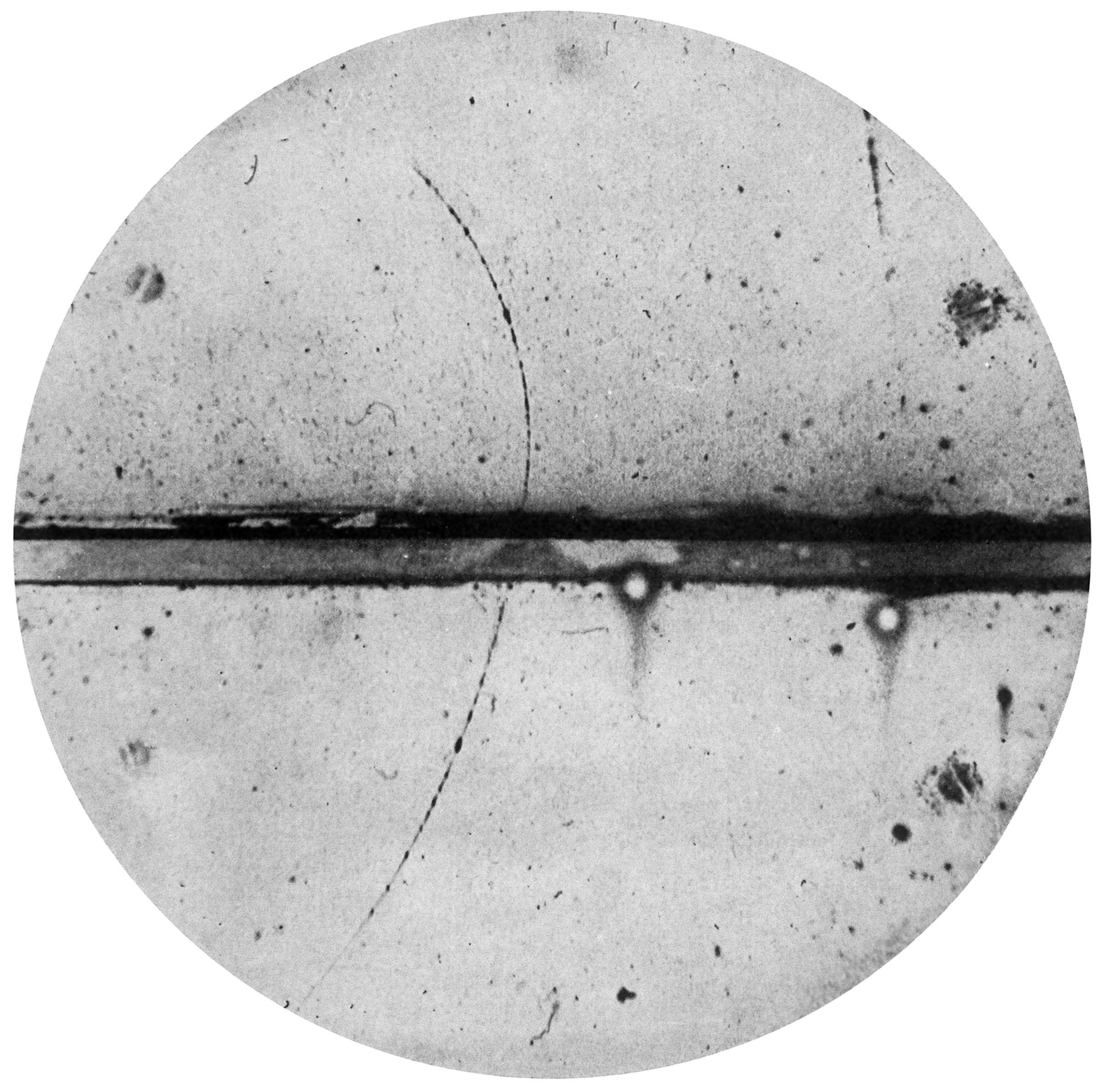 Media: Carl D. Anderson (1905–1991) - Anderson, Carl D. (1933). "The Positive Electron". Physical Review 43 (6): 491–494. DOI:10.1103/PhysRev.43.491. Short Definition: Antimatter is a type of matter which takes on exactly reverse properties to normal matter, considering charge, parity and time in a symmetric matter. Properties such as mass and acceleration are the same to regular matter, even though some are exactly opposite. Where in normal matter electrons have negative charge, antimatter has its own 'positrons' which behave the same as electrons but are positively charged. Detailed Definition: Antimatter is a type of matter which has certain properties flipped. As matter is all around us and is a building block of our universe, antimatter also has a place in our universe. This type of matter has an obvious relation with regular matter. When the two come into contact, they are both annihilated and turn into pure energy. Antimatter has been in our universe since the beginning according to the Big Bang theory. There is far less antimatter in the universe than regular matter, but it constantly gets created through radiation, decay and even lightnings, to shortly after being destroyed by contact with electrons. Antimatter is a well-defined concept in physics and is used in medical PET (Positron emission tomography) scans to form images of our bodies. The term is connected to many other concepts with 'anti-' prefix, as Antimatter is a general concept describing particles with inverse properties to the regular ones. Etymology: The prefix 'anti' from Greek, meaning 'something opposite' and 'matter' from Anglo-French 'materie' meaning 'a substance'. Sample Sentence(s): 1. At CERN, physicists make antimatter to study in experiments. The starting point is the Antiproton Decelerator, which slows down antiprotons so that physicists can investigate their properties. 2. Antimatter and regular matter annihilate each other at contact into pure energy. Translations: French - Antimatière German - Antimaterie Italian - Antimateria Polish - antymateria Swedish - Antimateria | ||
Aphelion | ||
|---|---|---|
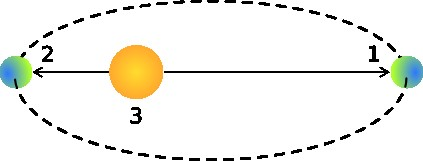 Source: Vitalik1986 (2011, March 26). Perihelios-aphelion. wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=14702160 Short definition: The point in the orbit of a planet or other celestial body that is farthest from the sun. Detailed Definition: Aphelion is the point in the orbit of a celestial body where it is farthest from the sun. It is the opposite of perihelion, which is the point in the orbit where the celestial body is closest to the sun. The distance between a celestial body and the sun varies during its orbit due to the elliptical shape of the orbit. The aphelion is the point where the distance is at a maximum. Etymology: aphelios - far from the sun aph - from and helion - the sun Sample Sentence(s):
"Mars reaches its aphelion in July, when it is about 250 million miles from the sun." "The aphelion of Earth's orbit occurs in July, when it is about 3.1 million miles farther from the sun than at perihelion in January." "The aphelion of Pluto's orbit is about 49.3 billion kilometres, while its perihelion is about 29.7 billion kilometres." Translations: French: aphélie German: Aphel Polish: aphelium Links to videos/articles: https://www.britannica.com/science/aphelion https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/videos/whats-up-january-2021 | ||
Apogee | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: Short Definition: An apogee is a point in an elliptical orbit, which is considered to be the farthest point from Earth. Detailed Definition: There are two sides in any elliptical orbit, with the names referring to the primary body in the orbit. The closest and farthest points are referred to by, respectively, the prefixes peri- and apo-. The suffix is determined by the primary body, which in the case of Earth is -gee. Therefore, an apogee is the term describing the farthest point on the elliptical orbit of Earth. A satellite is at its slowest when travelling through the apogee. Etymology: "apogee" - French apogée, Latin apogaeum, Greek apogaion - point at which the Moon is farthest from the Earth "apo-" - Greek apo, Avestan apa, Latin ab - off, away, away from "Gaia" / "ge" - Greek Gaia / gaia - a titan, personification of Earth Sample Sentence(s): A satellite that travel around a celestial body is at its slowest whenever the satellite is at its apogee. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Apogée German: Höhepunkt Polish: apogeum Swedish: Höjdpunkt Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.allthescience.org/what-is-an-apogee.htm | |||
UNIVERSEH is an alliance of:
All rights reserved. Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Education and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA). Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.