Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Currently sorted By last update ascending Sort chronologically: By last update
Black hole Horizon | |||
|---|---|---|---|
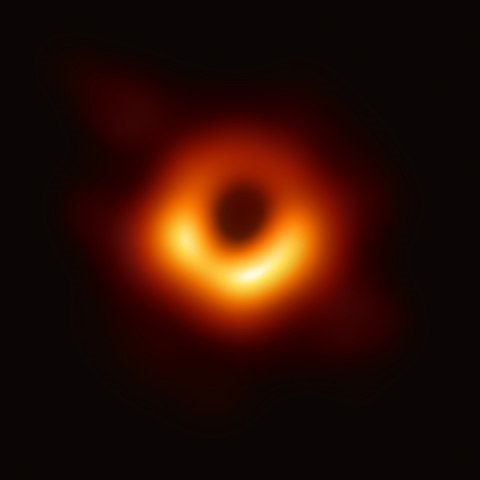 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Black_hole_-_Messier_87_crop_max_res.jpg Short Definition: The horizon of a black hole is called event horizon and is an astrophysical phenomenon, which describes the “point of no return” where matter and even light can not cross back according to our understandings of physics. The event horizon is a boundary in spacetime, where the gravitational pull becomes absolute. Detailed Definition: The astrophysical phenomenon of the event horizon defines the boundary of spacetime, where the ability of mass to deform spacetime is absolute. Near this event horizon time seems to work differently, because of gravitational time dilation, which appears to slow down clocks near the horizon more than those farther away and the clock would take an infinite amount of time to reach the black hole in itself. The huge amounts of gravitational pull causes any light to redshift in a process called gravitational redshift. A clock that is falling into a black hole would change from being visible from an outside perspective, to the light of it red shifting and then finally it would disappear from view and all this in a mere minute. On the contrary an indestructible observer that falls into a black hole would experience time normally and it would fall into the black hole in a finite amount of time.
Etymology: Black hole term was coined in astronomy in 1964 Horizon Greekhorizon (kyklos) àboundary
Sample Sentence(s): From an outside perspective an object falling into the black hole horizon would take an infinite amount of time to reach it.
The black hole horizon is the point of no
return, where matter or light are not able to cross back.
French:
Horizon du trou noir
German:
Schwarzes Loch-Horizont
Polish:
Horyzont czarnej dziury
Swedish:
Horisont för svarta hål
Links to Videos/Articles: | |||
Black Hole | ||
|---|---|---|

Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Black_hole_-_Messier_87_crop_max_res.jpg Short definition: A Black Hole is a region of spacetime where the gravitational field is so strong that nothing, not even light or other electromagnetic waves can escape its event horizon. An event horizon is “the point of no return”, meaning the boundary beyond which nothing can escape. Detailed definition: Since Black Holes can’t be observed directly with telescopes, they’re usually detected by other means, such as observing their gravitational influence on their surroundings. Most Black Holes are formed from large stars that die in a supernova explosion - these Black Holes are usually around 20 times as massive as the Sun. However, there also exist Black Holes that are incredibly large, called Supermassive Black Holes, which can be millions or even billions times as massive as the Sun. Scientists believe that at the centre of almost every big galaxy lies a Supermassive Black Hole, for example Sagittarius A* at the centre of the Milky Way. Etymology: Presumably in December 1967, a student suggested the phrase "black hole" at a lecture by John Wheeler; Wheeler adopted the term for its brevity and "advertising value", and it quickly caught on. (Source: Siegfried, T. (2019, August 9). 50 years later, it’s hard to say who named Black Holes. Science News. https://www.sciencenews.org/blog/context/50-years-later-its-hard-say-who-named-black-holes) Sample sentence(s): Some Black Holes apparently have nonstellar origins. (Source: Lohnes, K. (n.d.). How Do Black Holes Really Work? Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/story/how-do-black-holes-really-work ) Translations: French: Trou noir German: Schwarzes Loch Italian: buco nero Polish: Czarna dziura Swedish: Svart hål Links to Videos/Articles:
The Economist. (2022, July 12). Black holes: why they matter [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/qqMAFtIGaq4 Black Holes | Science Mission Directorate. (n.d.). https://science.nasa.gov/astrophysics/focus-areas/black-holes | ||
Blazar | |||
|---|---|---|---|
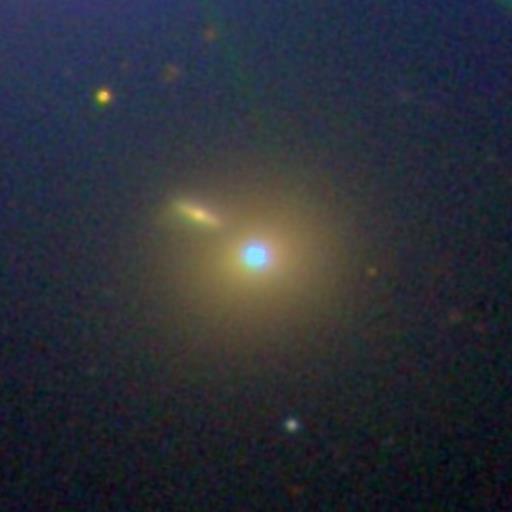 Sloan Digital Sky Survey image of blazar Markarian 421. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Markarian_421#/media/File:SDSS_Mrk_421.jpg Short Definition: A blazar is a type of active galaxy nucleus with a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light, which direction is nearly towards an observer. Due to the jet almost directly shooting towards Earth, a blazar appears much brighter on observations than in case of facing another direction. Blazars are a source of powerful radiation in all electromagnetic spectrum, especially in high-energy gamma rays. Blazars are among the most energetic phenomena in the universe and are an important subject to research. Detailed Definition: Blazars are an extremely bright, starlike object characterized by rapid changes in luminosity and a flat spectrum caused by a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light directed at the observer. Blazars emit electromagnetic radiation over a very wide range of frequencies, but mostly distinguished by amount of radio and gamma rays. Due to blazar's instabilities its properties change over time, specifically the variability and intensity of their observable brightness, which is distinguishing blazars from another class of active galactic nucleus, quasars. Blazars are important topics of research in astronomy and astrophysics. Blazar research includes investigation of the properties of accretion disks and jets, the central supermassive black holes and surrounding host galaxies, and the emission of high-energy photons, cosmic rays, and neutrinos. Etymology: Coined by 1978 by astronomer Edward Spiegel from BL Lac object and quasar. Sample Sentence(s): "Blazars are thought to be active galactic nuclei, with relativistic jets oriented close to the line of sight with the observer." Translations: French: Blazar German: Blazare Polish: Blazar Swedish: Blazar Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/blazar | |||
Constellation | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Term/Concept: constellation Image/Video/Audio:  Term/Concept: constellation Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: Sullivan, R. (2017, June 12). Constellations map. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/47430793@N08/35249283965 Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||||||||||
CubeSat | ||
|---|---|---|
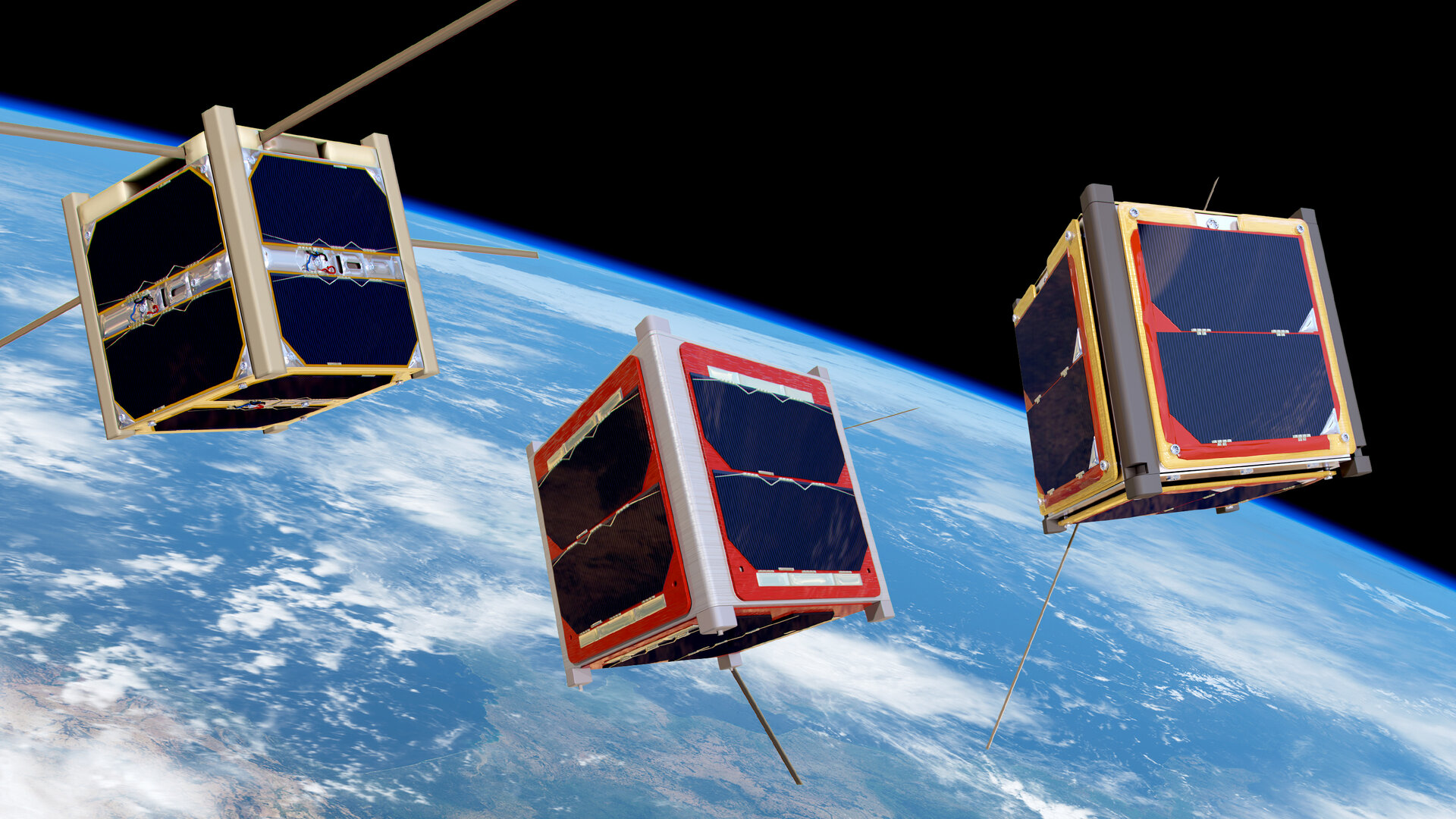 The European Space Agency. (2022, March). CubeSats orbiting Earth. Retrieved from https://www.esa.int/var/esa/storage/images/esa_multimedia/images/2016/04/cubesats_orbiting_earth/15950521-1-eng-GB/CubeSats_orbiting_Earth_pillars.jpg Short definition: CubeSat (Cube Satellite) is a spacecraft that is meant to be a planet's artificial satellite and is designed as a cubic case. The purpose of such case is to carry its payload. Detailed Definition CubeSat is a nanosatellite. It is built as a cube with standard dimension, length of each side is a multiple of 10cm or 1U. They can contain arbitrary payload, usually scientific equipment such as small cameras. Their usual weight is about 1.3 kilograms, what makes them relatively cheap to launch and hence widely accessible. Their accessibility allows smaller players in space industry such as companies and even universities to deploy their space exploration tools into space. Etymology Cube SatelliteCube – from Latin cubusSatellite – from Latin satellitem– an attendant Sample Sentences "These CubeSats are flown as auxiliary payloads on previously planned missions."NASA. (2018, February). CubeSats Overview. Retrieved from https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/cubesats/overview Translations in our Alliance languages: French: CubeSatGerman: CubeSat Italian: CubeSat Polish: CubeSat Swedish: CubeSat Translations in other languages: Russian: КубСат References The European Space Agency. (2022, March). CubeSats. Retrieved from https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Preparing_for_the_Future/Discovery_and_Preparation/CubeSats Cal Poly SLO. (2014, February). CubeSat Design Specification Rev. 13. Retrieved from https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5418c831e4b0fa4ecac1bacd/t/56e9b62337013b6c063a655a/1458157095454/cds_rev13_final2.pdf | ||
Dark Nebula | ||
|---|---|---|
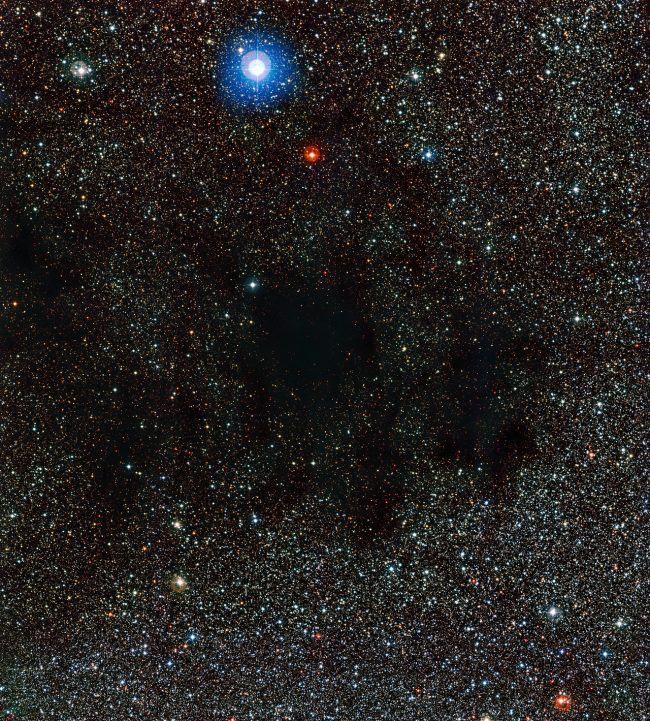 Short DefinitionA dark nebula, also known as an absorption nebula, is a form of interstellar cloud. It is so thick that it obscures visible wavelengths of light from things behind it, such as reflection nebulae or background stars and emission. Interstellar dust grains in molecular clouds' coldest, densest portions produce light extinction. Detailed DefinitionSometimes the light from the background stars or reflection nebulas can be obscured by an interstellar cloud composed of gas, plasma and galaxy dust, creating irregular shapes without defined boundaries. This results in the formation of a black nebula or absorption nebula. The naked eye has seen large dark nebulas, often seen as shadows falling from the sky. The development of stars and meteors is crucial in the black nebula. Because of the difference in density, it is impossible to form stars during condensation. Enormous molecular clouds often surround the black nebulas, while the small ones can be called Bok globulos. Half of the world's famous Bang globules have been discovered to contain new stars. Etymologymid-15c., nebule "a cloud, mist," from Latin nebula, plural nebulae, "mist, vapor, fog, smoke, exhalation," figuratively "darkness, obscurity," from PIE root *nebh- "cloud." Sample Sentence(s) 1. Later, when I looked to my left, there was a black nebula. It had initially been an implacable cloud. 2. In general, the detections best suited the concept of a collision between a star and an interstellar nebula. 3. We've seen enough evidence to believe our solar system began with a cold black nebula spinning in slow motion. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages Swedish: mörk nebulosa 1. Kurzgesagt - In a Nutwchell. 2017. The Last Light Before Eternal Darkness – White Dwarfs & Black Dwarfs. Retrieved on June 6, 2023 from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qsN1LglrX9s&ab_channel=Kurzgesagt%E2%80%93InaNutshell 2. Encyclopedia Britannica Contributors. February 23. 2023. Nebula. Retrieved June 15, 2023 from https://www.britannica.com/science/nebula | ||
Dwarf Galaxy | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Picture: Fornax Dwarf Galaxy Image/Video/Audio Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Fornax_dwarf_galaxy.jpg
Short Definition:
A dwarf galaxy is one that contains fewer stars than larger galaxies. A dwarf galaxy is a galaxy made up of material and dark matter ejected from larger galaxies by the force of gravity. Although a dwarf galaxy is defined by astronomers by the number of stars it contains, and hence its size, it is also defined as dwarf by its shape, content, and even appearance.
Detailed Definition:
Dwarf galaxies, formed from fragments of larger galaxies, are the most abundant type of galaxy in the universe. Dwarf galaxies are galaxies that break apart due to their relatively small size to their neighbors, causing stellar streams and galaxy mergers. However dynamic these relationships with neighboring galaxies may be, they are difficult to detect by astronomers due to their low light, mass and small size. The astronomical importance of these dwarf galaxies actually comes from their tendency to form from other large galaxies and merge again with larger galaxies. Their difference from the usual galaxy shape is that they have low metallicity and gas in abundance. This situation is used by astronomers as evidence to interpret the motion and evolution of galaxies. Dwarf galaxies are basically divided into three groups: Dwarf elliptical galaxies, dwarf spheroidal galaxies, and dwarf irregular galaxies.
Etymology:
From Old English ‘Dweorg’ + From Latin ‘Galaxias’
Sample Sentence(s):
‘’The most powerful space telescope currently operating has zoomed in on a lonely dwarf galaxy in our galactic neighborhood, imaging it in stunning detail.’’ (Lea, R. (2022, November 11). James Webb Space Telescope peers into lonely dwarf galaxy with sparkling results. Space.com. https://www.space.com/james-webb-space-telescope-wlm-dwarf-galaxy-image) ‘’This Living Collection starts with an introductory Comment and continues with a series of articles on the science of dwarf galaxies, their properties and their theoretical modelling and simulations.’’ (It’s time for some plane speaking. (2021, December 13). Nature. https://www.nature.com/collections/bgegjajcec error=cookies_not_supported&code=03e197b7-7ba4-4db9-a0c7-ee3cf2730af7)
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French: Galaxie Naine German: Zwerggalaxie Polish: Galaktyka karłowata Swedish: DvärggalaxTurkish: Cüce Gökada
Links to Videos/Articles:
https://esahubble.org/wordbank/dwarf-galaxy/ https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/D/dwarf+galaxy https://www.sciencealert.com/webb-is-giving-us-a-stunning-new-look-into-this-lonely-dwarf-galaxy https://esawebb.org/images/WLMb/ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hcDrvX6vy0k&ab_channel=EuropeanSouthernObservatory%28ESO%29 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gez1RSHQvDE&ab_channel=Engadget | |||
EVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
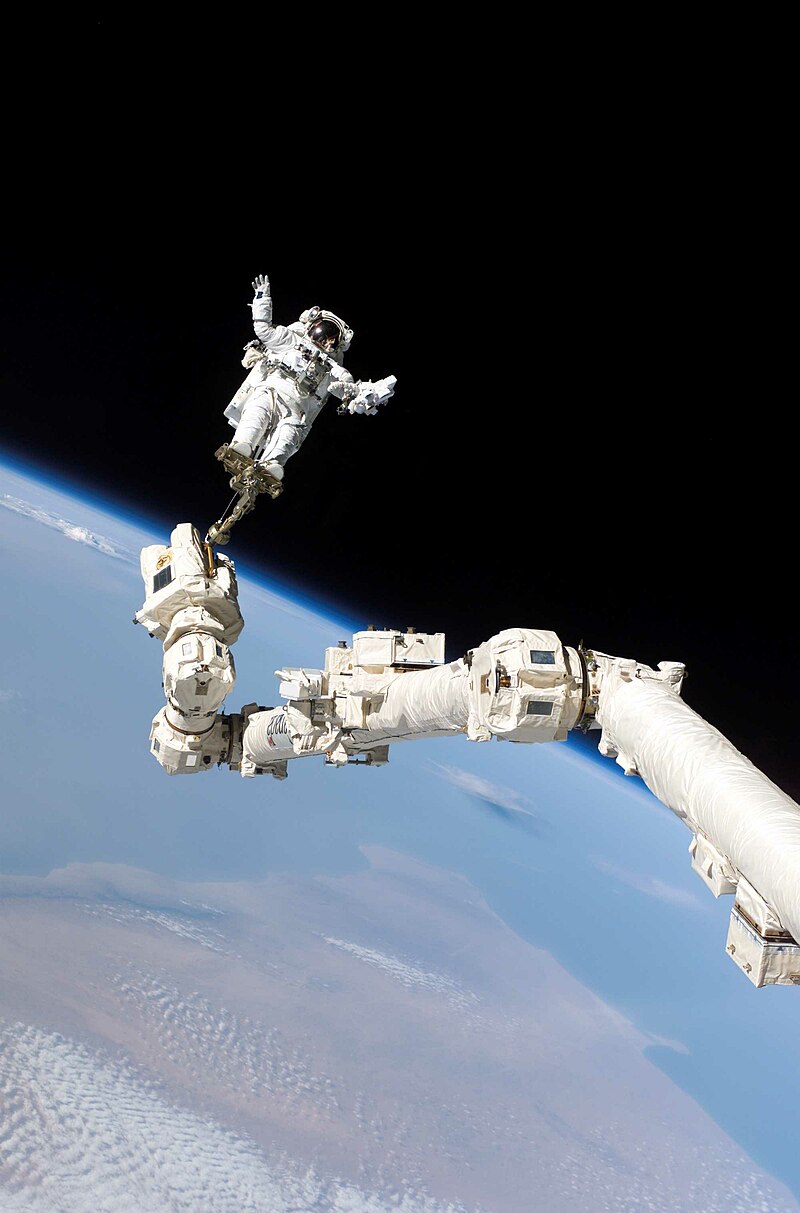 Astronaut Steve Robinson performing an EVA during STS-114 mission. Source: Wikipedia/NASA Short Definition: EVA is an act of performing different activities outside your spaceship while in orbit. This could include repairing, attaching or other experiments. Detailed Definition: Performing an EVA can refer to activities such as spacewalks, where astronauts leave the spacecraft to work in the vacuum of space, as well as other tasks such as inspections or repairs on the exterior of the spacecraft. EVAs are a common part of space exploration and are conducted by astronauts in a variety of different settings, including the International Space Station and during lunar, or in the future, planetary missions. Etymology: EVA stands for Extravehicular Activity Sample Sentence(s): Astronauts on the ISS are preparing to perform an EVA. Yesterday's EVA was completed successfully. Translations: French: Sortie extravéhiculaire German: Außenbordeinsatz Polish: Spacer kosmiczny Swedish: Rymdpromenad Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nasa.gov/content/extravehicular-activities/ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extravehicular_activity | |||
ExoMars Programme | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 DefinitionA programme created in cooperation between ESA and Roscosmos, which is trying to find signs of biological processes on Mars indicating whether life has ever existed on that planet. The programme includes two missions:
The Trace Gas Orbiter’s task is to look for trace atmospheric gases, including methane, which would indicate the presence of biological processes, whereas the Rosalind Franklin rover is supposed to look for evidence of life on the surface and underground. Etymology:“Exo” in ExoMars refers to “exobiology”, a branch of sciences investigating life beyond Earth. A rover involved in this mission is named after Rosalind Franklin, who was an English chemist known in particular for her contribution to DNA research. The platform Kazachok is named after a Russian folk dance. Sources:https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Exploration/ExoMars More about the mission:https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Exploration/ExoMars/ExoMars_Factsheet | |||

