Dictionary of Space Concepts
Welcome to the Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space", students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
R |
|---|
Radiation | ||
|---|---|---|
Image: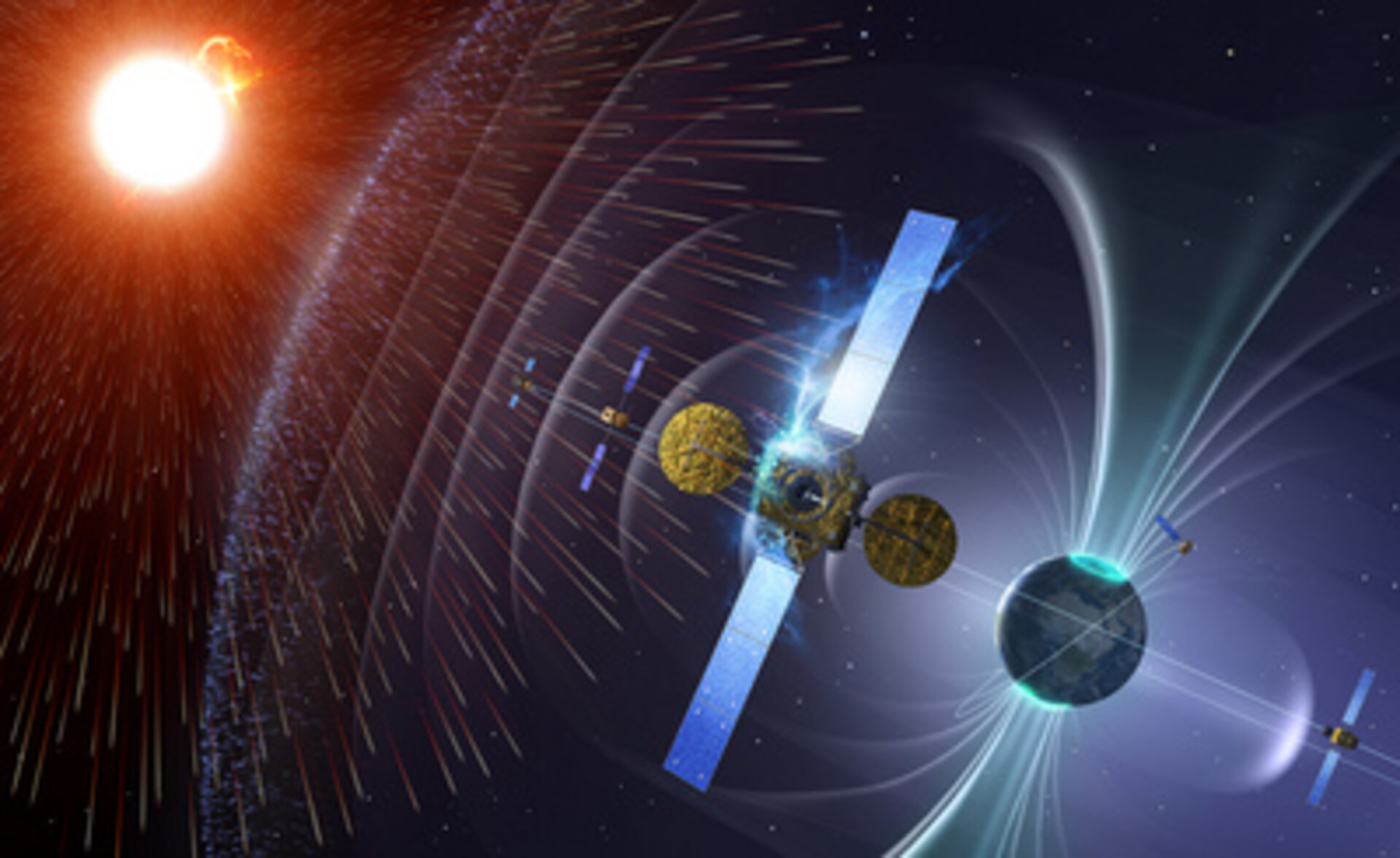  Image: Source: https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Engineering_Technology/Proba_Missions/Detecting_radiation Short Definition: Generation of strong and hazardous energy that results from atoms being broken up. Detailed Definition: The full process through which energy is released by one body, transported across a space or other intermediary, and then absorbed by another body. The universe is full of radiation as it is a form of energy that is emitted in the form of rays, electromagnetic waves, and/or particles, which are found all over the cosmos. Radiation may be utilized cautiously to learn more about biological and mechanical systems, despite the fact that it can also be harmful to both of these systems. Etymology: Radiation comes from the Latin radiare, which means emit rays. Sample Sentence(s): High radiation doses are administered to patients during cancer therapy. Alpha particles are an illustration of ionizing radiation. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: radiation German: Strahlung Polish: promieniowanie Swedish: strålning Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nasa.gov/feature/how-nasa-prepares-spacecraft-for-the-harsh-radiation-of-space https://www.nasa.gov/analogs/nsrl/why-space-radiation-matters | ||
Reaction control system | ||
|---|---|---|
Image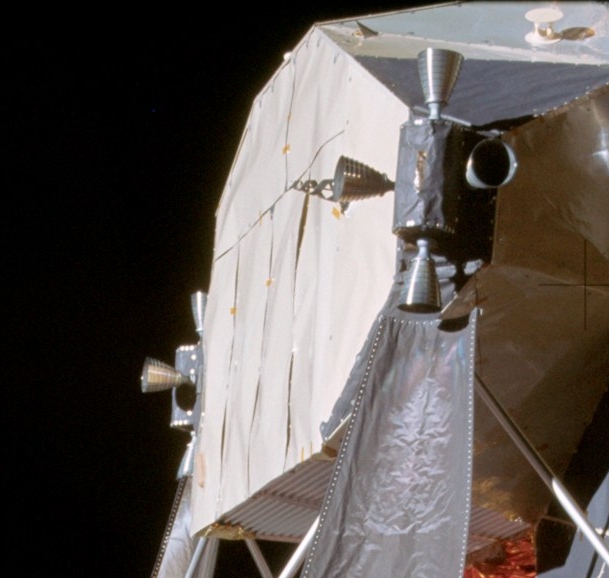 Image Shepard, A., NASA. (1972, December). Apollo 14 LM RCS quads. Retrieved form https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/2d/LM_RCS.jpg Short Definition Reaction control system (RCS) is a system of low-thrust engines that is used to control orientation of a spacecraft in space (attitude control) and for fine position and velocity adjustments. Detailed Definition The reaction control system of a spacecraft consists of multiple low-thrust engines that are placed symmetrically on the spacecraft equidistantly from its barycentre to ensure even force and torque distribution. Thrusters can provide thrust in any direction and combining thrusters in different positions allows acquiring force in any direction or torque in any plane, which enables the spacecraft to perform translational motion in any direction and any of roll, pitch and yaw rotations. RCS is used for attitude control (for example, to keep a telescope pointed at one object for a long time), precise manoeuvring (for example, while spacecraft docking), orbit correction and other purposes. Etymology Reaction – re- (back, again, anew) + action (from French réaction)Control – from Anglo-French contreroller– exert authoritySystem – from Late Latin or Greek systema– an arrangement, organized whole, a whole compounded of parts Sample Sentences The spacecraft's reaction control system precisely adjusts the orientation and stability of the vehicle during maneuvers in the microgravity environment of space. Translations in partner languages: German: Reaktionskontrollsystem (RCS) French: système de contrôle de la réaction (RCS) Swedish: seaktionskontrollsystem (RCS) Polish: system sterowania reakcyjnego (RCS) Italian: sistema di controllo della reazione (RCS) Translations in other languages: Russian: Реактивная система управления Ukrainian: Реактивна система керування References Colas, A. L., Valenzuela, J. G. (2020, August). Reaction Control System Performance Characterization using Vacuum Chamber Thrust Stand. Retrieved form https://arc.aiaa.org/doi/10.2514/6.2020-3526 Boeing. (2006, November). ISS Motion Motion Control System. Retrieved from http://forum.nasaspaceflight.com/index.php?action=dlattach;topic=34777.0;attach=586775 | ||
Reaction engine | ||
|---|---|---|
Image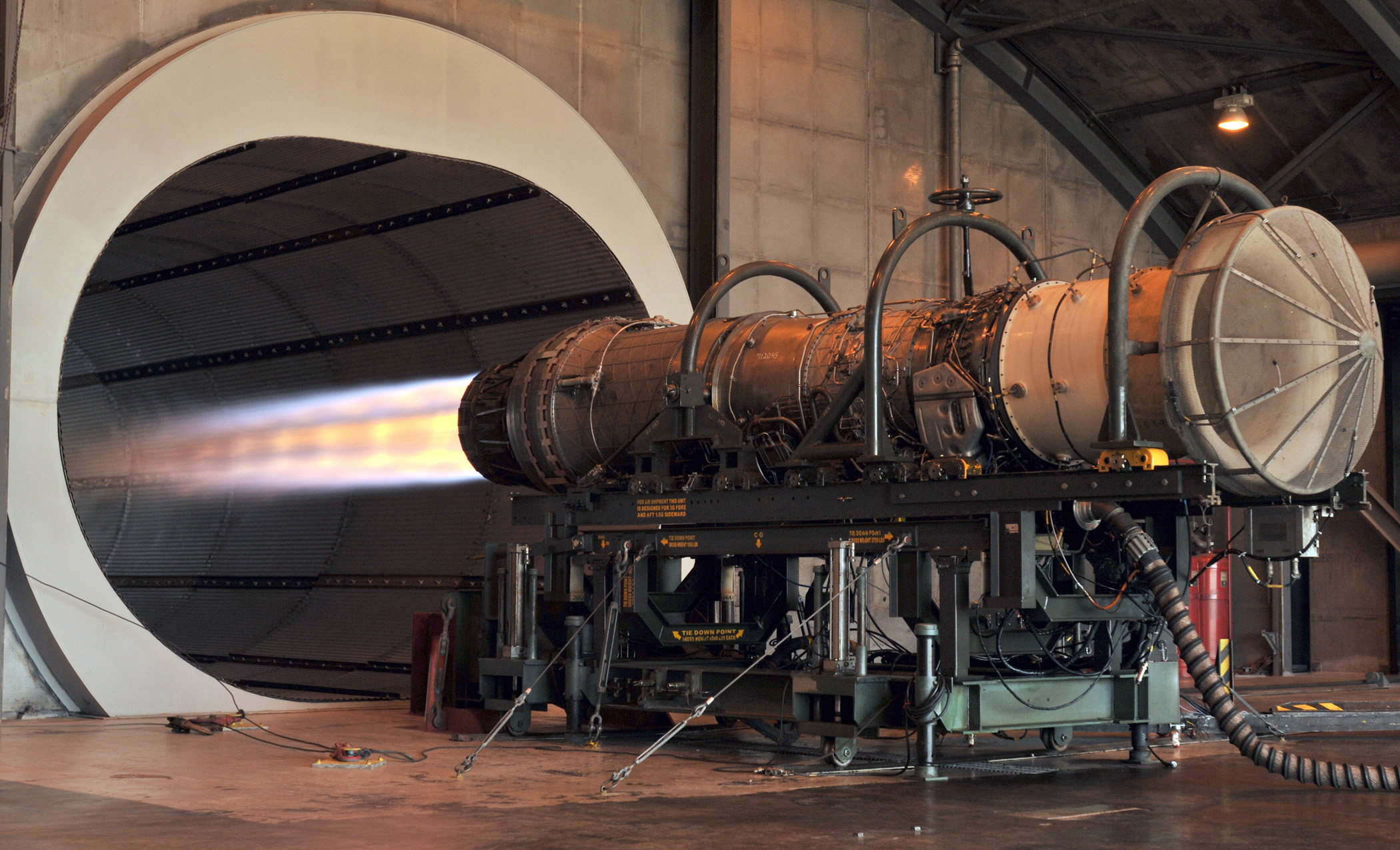  Image U.S. Air Force. (2010, November). F100 F-15 engine. Retrieved from https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/69/F100_F-15_engine.JPG Short Definition A reaction engine is an engine that produces thrust by expelling reaction mass. It works in accordance with the third Newton's law of motion. Detailed Definition Reaction engines work in accordance with the third Newton's law of motion, stating that for every action force there is an equal by magnitude, but opposite in direction, reaction force. Thus, reaction engines apply force to the reaction mass, under which reaction mass accelerates and leaves the engine. As a result, the engine together with the vehicle are accelerated by the reaction force that makes the vehicle move. Jet engines and different types of rocket engines are reaction engines. In fact, this is the only engine capable of working in a vacuum, since there is nothing to propel a vehicle besides the fuel (reaction mass) carried by the vehicle itself, which makes those engines the only applicable to spacecrafts. Reaction engines have a broad application area that is not limited to space. For example, boats and ferries are often powered by reaction engines. But instead of a jet of heated gas, they expel water. Etymology Reaction – re- (back, again, anew) + action (from French réaction)Engine – from Middle English engyn or Anglo-Norman engine or Old French engin– skill, cleverness, war machine Sample Sentences The reaction engine utilized a combination of fuel and oxidizer to generate thrust for propulsion. Translations from alliance partner languages: French: Moteur de réactionGerman: Rückstoßantrieb Italian: Motore a reazione Polish: Silnik reakcyjny Swedish: Reaktionsmotor Translations from other languages: Belarusian: Рэактыўны рухавік References The European Space Agency. (2020, December). System study results for SABRE-powered reusable launcher. Retrieved from https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Transportation/Future_space_transportation/System_study_results_for_SABRE-powered_reusable_launcher Petrescu, R. V., Aversa, R., Apicella, A., Petrescu, F. I. T. (2018, January). Romanian Engineering, "On the Wings of the Wind". Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.3844/jastsp.2018.1.18 | ||
RemoveDEBRIS Mission | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:A mission under the supervision of the Surrey Space Centre of the University of Surrey (supported by Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd., Airbus Defense and Space, Innovative Solutions in Space, CSEM, Inria and Stellenbosch University) that aimed to find the best method of capturing and removing space debris. The project was based on a satellite containing several pieces of equipment (a net, a harpoon, a drag sail and vision-based navigation equipment, as well as a set of targets simulating space debris), which remained in orbit between 2018 and 2021. The satellite platform for the project RemoveDEBRIS was launched using SpaceX Falcon 9, was delivered to the International Space Station and later deployed into orbit, where a series of experiments on debris removal were conducted, using several pieces of equipment:
Translations:
Links to Videos:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XLuHk5gWx3k https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_QUhCLTfXf0 Articles:https://www.surrey.ac.uk/surrey-space-centre/missions/removedebris https://www.airbus.com/en/products-services/space/in-space-infrastructure/removedebris https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/r/removedebris | |||
Rocket engine | ||
|---|---|---|
Image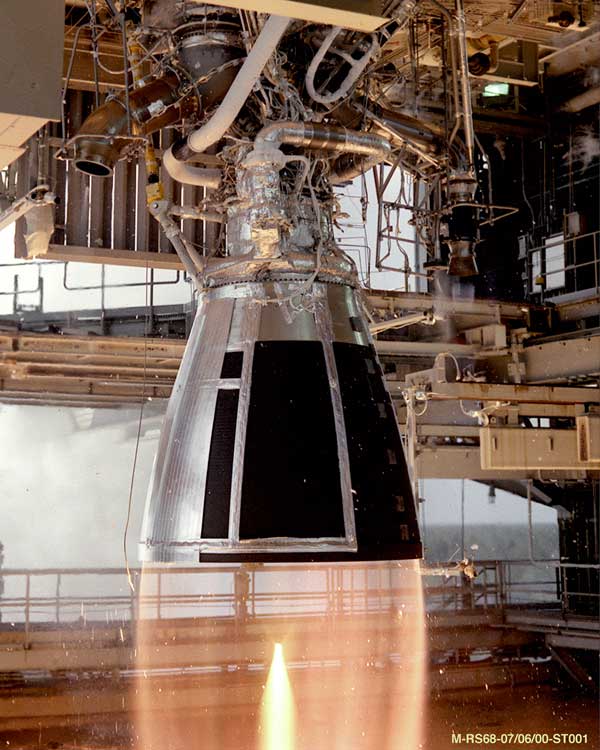  Image NASA. (2000, January). RS-68 being tested at NASA's Stennis Space Center. Retrieved from https://www.nasa.gov/images/content/148709main_d4_testing_08.jpg Photograph of a rocket engine in operation, with a converging plume of hot gas streaming out from the nozzle Short Definition A rocket engine is a jet engine that discharges a jet of high-temperature gas as reaction mass, which was acquired from the propellant stored internally in a vehicle. Rocket engines, unlike general jet engines, can only use internally stored propellant to create a jet, because they have to operate in space, where there is no medium like air or water which can be used as a reaction mass in jet engines on Earth. Detailed Definition A rocket engine is an internal combustion jet engine that discharges a jet of high-temperature gas as reaction mass, which was acquired from the propellant stored internally in a vehicle. Rocket engines, unlike general jet engines, can only use internally stored propellant to create a jet of gas as a result of chemical reactions, because they have to operate in space, where there is no medium like air or water which can be used as a reaction mass in jet engines on Earth. The nozzle is always an integral part of a rocket engine because it makes the jet accelerate as gas moves through the nozzle, and the higher the speed of a discharged jet, the more efficient the engine. The de Laval nozzle is the most common type of nozzles used in rocket engines, as it accelerates the gas passing through it most efficiently. Gas, when burnt, moves at a low subsonic speed and accelerates as it moves through the nozzle, reaching supersonic speed by the moment it leaves the nozzle. Etymology Rocket – from Old Italian rochetto– a bobbinEngine – from Middle English engyn or Anglo-Norman engine or Old French engin– skill, cleverness, war machine Sample Sentences The rocket engine ignited with a powerful roar, propelling the spacecraft into space. Translations from our alliance partners' languages: French: Moteur-fuséeGerman: Raketentriebwerk Italian: Motore a razzo Polish: Silnik rakietowy Swedish: Raketmotor Other language translations: Russian: Ракетный двигатель Ukrainian: Раĸетний двигун Belarusian: Ракетны рухавік References Braeunig, R. A. (2012). Rocket propulsion. Retrieved from http://www.braeunig.us/space/propuls.htm Oberth, H. (1972, January). Ways to spaceflight. Retrieved from https://archive.org/details/nasa_techdoc_19720008133/page/n35/mode/2up | ||
Roscosmos | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:Russian state corporation formed in 2015 and responsible for various aspects of the country’s space exploration activities (space equipment, infrastructure, international cooperation, etc.). The corporation is a legal successor of the Soviet space program which existed from 1955 to 1991 and Russian Space Agency founded in 1992. EtymologyThe name of the corporation “Роскосмос” consists of two elements: “Рос” (abbreviation for “Russian”) and “космос” (“space”). Translations:
| |||
Rover | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
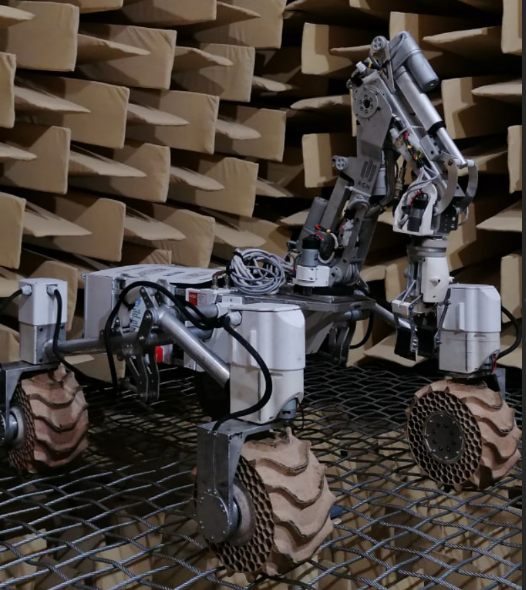 Image/Video/Audio Source: Author: Kamila Kopacz Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Other sources: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GMMQUXrcOGY https://www.britannica.com/topic/Mars-Exploration-Rover | |||||||||
UNIVERSEH is an alliance of:
All rights reserved. Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Education and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA). Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.