Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
S |
|---|
Spacecraft | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: SpaceX (2016, September 25). SpaceX's proposed Interplanetary Spaceship, at Saturn.. wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=51812109 Definition:Vehicle, machine or other apparatus designed to fly or orbit outside the Earth’s atmosphere, i.e. above the Kármán line of 100 km.Etymology:Closed compound noun, consisting of ‘space’ and ‘craft’ Translations:
Note: the Russian translation has a slightly different meaning as it includes devices operating in atmospheres and on surfaces of other celestial bodies. | |||
Spacecraft Propulsion | ||
|---|---|---|
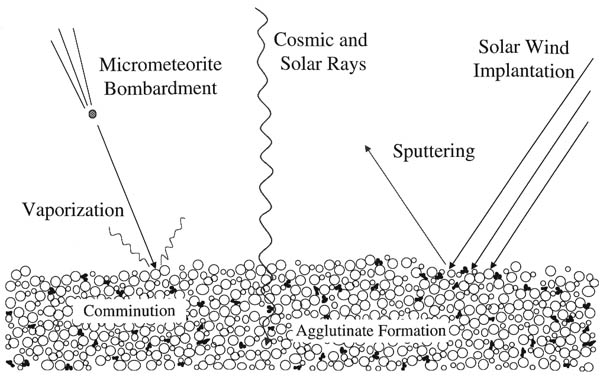
Short Definition: Spacecraft Propulsion is a method utilised to accelerate a spacecraft and artificial satellites. Different methods exist for this purpose, with each method having its advantages and drawbacks. Most spacecrafts nowadays are propelled by what is called a rocket engine, which propels the space probe by heating the reaction mass and allowing it to eject out from the rear of the vehicle. Detailed Definition: A spacecraft propulsion system has the purpose of changing the velocity (acceleration) of a spacecraft and artificial satellites. It is utilised to both leave earth and for orbit insertion. To launch a spacecraft from earth, the propulsion method must overcome a higher gravitational pull to provide a positive net acceleration. The difficulty of achieving this change is directly proportional to the size of the vehicle, which is why spacecraft performance is generally discussed in amount of change in momentum per unit of propellant consumed, known as “specific impulse”. The higher the specific impulse, the better the efficiency. Once launched, satellites and spacecrafts may need to be moved between orbits, thus requiring propulsion. When a satellite has exhausted its ability to adjust its orbit, its useful life is over. The methods areas are divided into four groups: (1.) chemical propulsion (reaction and rocket engines), (2.) electric propulsion (ion, electrothermal and electromagnetic thrusters), (3.) advanced propulsion technologies and (4) supporting technologies. Etymology:
Sample sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages:
Links to Videos/Articles: Space Propulsion: a Survey Study About Current and Future Technologies. DOI: 10.5028/jatm.v10.829 | ||
Spaceship | ||
|---|---|---|
cf. Spacecraft | ||
Special Purpose Dextrous Manipulator (SPDM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: Short Definition: A Special Purpose Dextrous Manipulator (SPDM), also called 'Dextre', is a system that is part of the Mobile Servicing System (MSS) mounted on the International Space Station (ISS). This robotic system is designed to assist astronauts in spaces where human reach and endurance are limited. Detailed Definition: It is a multi-talented robot added to Canadarm2 on March 16, 2008, by Nasa astronauts Mike Foreman and Richard Linnehan. Designed to withstand the harsh conditions of space, this robot supports astronauts for small tasks around the ISS. These tasks include installing and maintaining the various parts of the ISS's exterior, maintaining the Station's electrical system, and pre-testing new equipment to be added. This robot, which has two hands as sensitive as human hands, has a retractable motorized wrench, camera, light, and connection module in both hands. Sample Sentence(s):' 'This multi-talented robot can ride on the end of Canadarm2 to move from worksite to worksite, or be ferried on the Mobile Base System.'' ''Dextre is the most sophisticated space robot ever built.'' Translations: French: Manipulateur agile à usage spécial German: Geschickter Manipulator für besondere Zwecke Italian: Manipolatore abile per scopi speciali Polish: Zręczny manipulator do zadań specjalnych (SPDM) Turkish: Özel Amaçlı Hünerli Manipülatör Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/elements/special-purpose-dextrous-manipulator/ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_Servicing_System https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/iss/dextre/about.asp https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/iss/dextre/ https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/iss/dextre/data-sheet.asp https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nNcRDBK8zxY&ab_channel=CanadianSpaceAgency | |||
Star | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Kutsaev, R. (no data). Stars Galaxy Free Stock Image. stocksnap. https://stocksnap.io/photo/stars-galaxy-IJ5DPL13HR Definition:1) A natural luminous body that is visible in the night sky and can be used for navigation. 2) A large celestial body producing light and energy by means of nuclear reactions inside of it. EtymologyGreek “αστέρι”, Latin “stella” Translations:
| |||
Stellar wind | ||
|---|---|---|
Media Media ESO/Callingham et al. DefinitionsShort Definition Detailed Definition Etymology Stellar: from Latin stella"star" Sample Sentences Bright bow shocks form around stars when their stellar winds interact with the Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages Frenchle vent stellaire German
der Sternwind
Italian
il vento stellare
Polish
wiatr gwiazdowy
Swedish stjärnvind
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Languages Russian Ukrainian Links to Videos/Articles: Stellar Wind. ESA/Hubble. Retrieved [ 06.14.2023 ], from https://esahubble.org/wordbank/stellar-wind/
Holzer, T. E., & Axford, W. I. (1970). The theory of stellar winds and related flows. Annual review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 8(1), 31-60. Retrieved [ 06.17.2023 ], from https://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu//full/1982ApJ...259..282A/0000282.000.html | ||
Supernova | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 25). AI illustration of a supernova. Midjourney. midjourney Definition:Brief, bright illumination of a supermassive star at the end of its lifetime by an explosion in which the original star itself is destroyed. As it dies, a supermassive star goes through various stages of fusing different elements, forming a red supergiant. During this process, more and more heavy material is deposited onto the stellar core. Once the core’s mass tips past a certain threshold it collapses under its own gravity (meaning it cannot withstand its own gravitational force). The outer layers are blasted outwards in a supernova, the biggest explosion known to occur in the Universe. At its peak, a supernova can be brighter than an entire galaxy. Supernovae reach their peak luminosity in a matter of days, so their appearance and early decline can be observed in real time. Etymology:from Latin super “beyond”, “over and above” and stella nova “new star” Translations:English: supernova (neutr.) – [ˌsuːpərˈnoʊvə] French: supernova (f)– [] German: Supernova (f) – [ˈzuːpɐˌnoːva] Polish: supernowa () – [] Russian: сверхновая звезда () - [ˌsvʲerxˈnovəjə zvʲɪzˈda] Swedish: supernova () – [] | |||
Supernova Remnant | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short
Definition
Detailed Definition First, the ejecta expands freely, gradually shedding their mass into the circumstellar or interstellar medium. Subsequently, the remnant begins to gather and compress surrounding gas, forming a prominent shell. In the ensuing phase, the shell undergoes cooling, resulting in the formation of a thinner, more delicate outer layer enveloping the still-hot interior. As the interior continues to cool, the shell expands further under its own momentum. Finally, the remnant merges with the surrounding interstellar medium, culminating in the formation of a fully-fledged supernova remnant. Notable examples of supernova remnants include the Crab Nebula, the remnants of SN 1572, and Kepler, the remnants of SN 1604, named after Johannes Kepler. G1.9+0.3, discovered in the galactic centre, stands as the most recent known remnant within our galaxy.
Sample Sentence(s) “Supernova remnants are very important to the structure of galaxies.” Mathis, J. S. (Invalid Date). supernova remnant. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/supernova-remnant
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
French
German
Italian
Polish
Swedish
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Lang... Turkish Dutch Supernovarest Spanish resto de supernova Portuguese Remanescente de supernova
Links to Videos/Articles: Astrum. (2016a, January 29). Supernova Remnants | Hubble Images
4K | Episode 2 [Video]. YouTube. | ||
Surface | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 25). AI illustration of a planets surface. Midjourney. midjourney Definition:The exterior of an astronomical body that is in contact with outer space or an atmosphere.Etymology:From Latin superficies. Translations:
Links to videos/articles: | |||