Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
P |
|---|
Parallax | ||
|---|---|---|
Media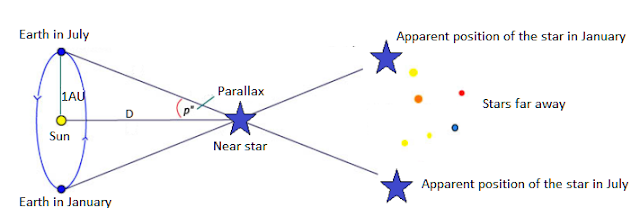 Insight Observatory (n.d.). Star Parallax. DefinitionsShort Definition Detailed Definition Etymology Sample Sentences Eyes of live creatures with binocular sight, humans included, exploit parallax to perceive depth and measure distances. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages Frenchla parallaxe
German
die Parallaxe
Italian la parallasse
Polish paralaksa
Swedish parallax
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other LanguagesRussian Ukrainian Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Parsec | |||
|---|---|---|---|
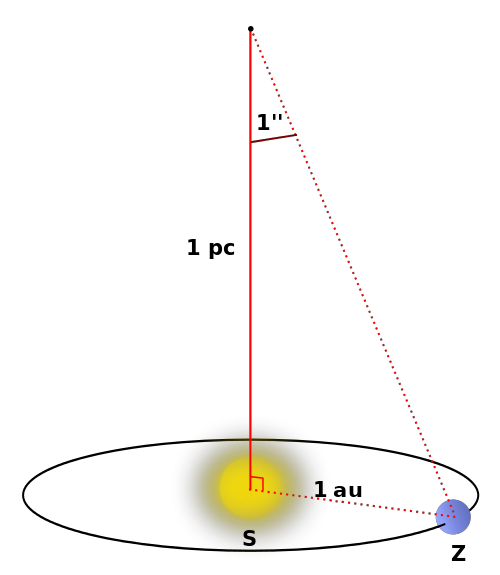 Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Parsek_pl.png Short Definition: The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System. Parsec is approximately equal to 3.26 light-years or 206,000 astronomical units (symbol: AU), or 30.9 trillion kilometers. As an example, the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is about 1.3 parsecs from the Sun. Most stars visible to the naked eye are within a few hundred parsecs of the Sun, with the most distant at a few thousand. Detailed Definition: A Parsec is the distance for which the annual parallax of the position of the Earth, viewed perpendicular to the plane of the orbit, is 1 arc second (arcsec). A parsec can equally be described as the distance from which half of the Earth's orbital major axis (equal to 1 AU) is visible as an arc of 1 arcsecond. Although distance equal to one parsec is tremendous still, multiples of parsecs are required for the larger scales in the universe, including kiloparsecs (kpc) for the more distant objects within and around the Milky Way, megaparsecs (Mpc) for mid-distance galaxies, and gigaparsecs (Gpc) for many quasars and the most distant galaxies. The term parsec is a combination of "parallax" and "arcsecond," which derives from the use of triangulation when measuring the distance between two stars. Etymology: Combination of words parallax and arcsecond Sample Sentence(s): "Distance to the nearest star is about 1.3 parsecs." Translations: French: Parsec German: Parsec Polish: Parsek Swedish: Parsec Links to Videos/Articles: https://earthsky.org/space/what-is-a-parsec/ | |||
Perihelion | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Diagram of a body's direct orbit around the Sun, with its nearest (perihelion) and farthest (aphelion) points. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apsis#/media/File:Perihelion-Aphelion.svg Short Definition: Perihelion is the farthest point in the orbit of a planetary body about the Sun. This point is present in every Solar System orbiting body orbit due to the fact all orbits are elliptical. Detailed Definition: Perihelion is the farthest point in the orbit of a planetary body about the Sun in the Solar System. In case of describing generic star orbiting system, such point is called an apsis as the farthest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For bodies moving around the Sun in a stable elliptical orbit, the perihelion is crossed at regular intervals, every orbital period. At perihelion, the Earth is 147.1 million km (0.9833 au) from the Sun. This usually takes place between 2nd and 4th January and occurs at a slightly different time each year due to interference from other celestial bodies. Etymology: From Proto-Indo-European *per- (“before, in front; first”) + ἥλιος (hḗlios, “sun”) + -on (suffix forming nouns) (from Ancient Greek -ον (-on)) Sample Sentence(s): "If the comet's perihelion (its closest point to the sun) coincides with the shower's peak, a rare meteor storm can occur, creating thousands of meteor showers per hour." - Skyler Caruso, Peoplemag, 4 Oct. 2022 "Earth makes its closest past on Jan. 4, which is called perihelion." - Dave Epstein, BostonGlobe.com, 4 July 2022 Translations: French: Périhélie German: Perihel Polish: Peryhelium Swedish: Perihelium Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.space.com/what-is-perihelion | |||
Perseids Meteor Shower | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Sutton, B. (2015, August 19). Perseid Meteor Shower over the Ocotillo Patch; 8/12/15. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/115357548@N08/20713070995 Definition:A meteor shower that recurs annually between the July 17th, and August 24th, with a peak of shooting stars in the days around August 12th. They have a high velocity (60 km/s) and, as so-called fireballs, can even reach the brightness of Venus. The radiant, apparent origin of this shower, lies in the eponymous constellation Perseus, near its border with Cassiopeia. Etymology:from Greek Περσείδαι “Perseidai”, the sons of Perseus in Greek mythology Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:Perseid meteor shower on NASA TV 2015 (4 hours)https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DIvVLyltJe8 | |||
Phobos | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:
Etymology:Named after Phobos, the ancient Greek god of fear, twin brother of Deimos, son of Ares (the equivalent of the Ancient Roman god of war Mars). Translations:
| |||
Photometer | |||
|---|---|---|---|
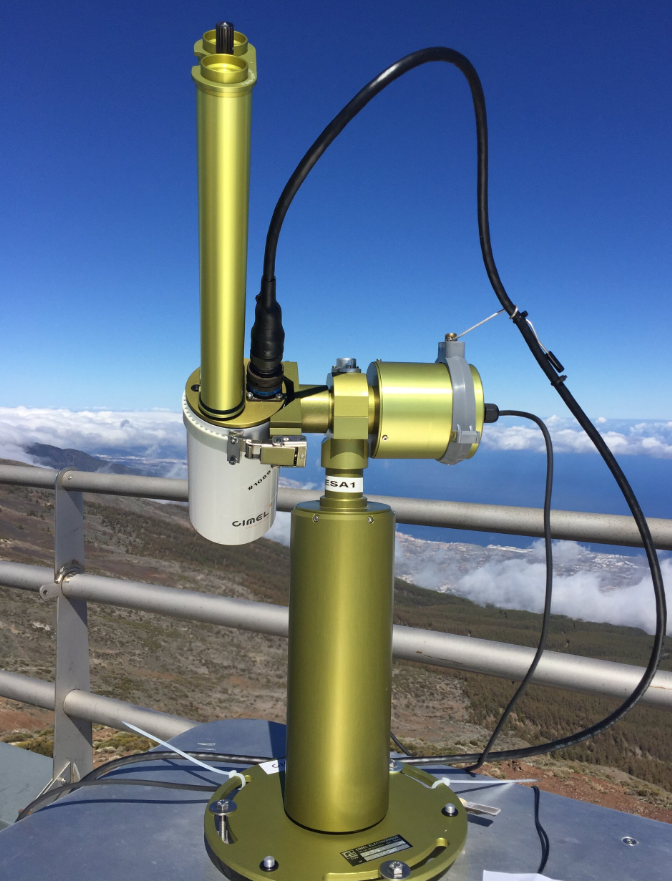 Source: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2018/04/Photometer Short Definition: A photometer is an instrument used to measure the strength of electromagnetic radiation. It is the primary tool used in the field of photometry, a field that focuses on the study of the emitted intensity of the electromagnetic radiation of an astronomical body. Detailed Definition: One of the devices used in the research electromagnetic radiation is the photometer. The most crucial component of the photometer is a photoresistor, photodiode, or photomultiplier, varying on the type of the photometer, which is responsible for the conversion of light into electric current. Among others, photometers most commonly measure illuminance, irradiance, light absorption, fluorescence, and luminescence. Most of the photometers measure light by the incoming flux, however, photon counting is also a viable technique. Light detection occurs after the light passes through a filter, which then distinguishes the respective wavelengths. Photometers are used in many medical, laboratory and industrial applications. Uses include the identification and quantification of chemical components, pharmaceutical quality control and astronomical calculations. Etymology: "photo-" - Greek, combining form of phōs (genitive phōtos) - word-forming element meaning "light" "-meter" - French -mètre, Greek metron - word-forming element meaning "a measure" Sample Sentence(s): "Photometers are used to gather data for improved lunar calibration of Earth-observing instruments." "A photometer is often used in conjunction with a telescope." Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Photomètre German: Fotometer Polish: Fotometr Swedish: Fotometer Links to Videos/Articles: https://planetfacts.org/photometer/ https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-photometry-definition-process-uses.html https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=95_yDQ9tAfs | |||
Pillars of Creation | ||
|---|---|---|
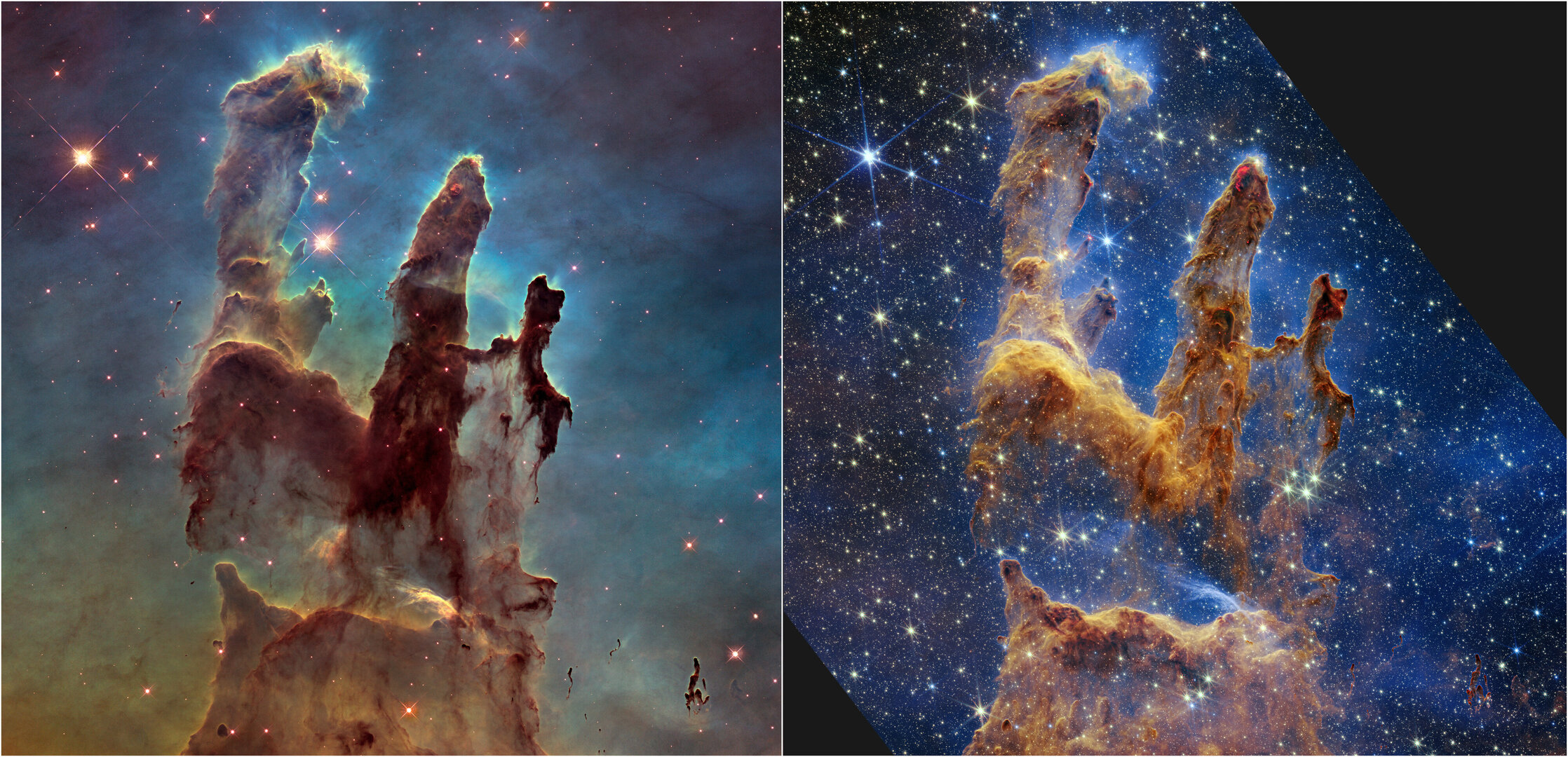 Short Definition The Pillars of Creation are a part of the Eagle Nebula that is located in constellation Serpens. They became popular when Hubble Telescope took first picture of them in 1995. The Pillars of Creation since then were revisited by various telescopes on multiple occasions throughout the years.
In Pillars of Creation, we can see new stars being formed. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
French
German
Italian
Polish
Swedish Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Planet | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Starkiteckt (2016, June 30). Icy Planet. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/141051222@N04/27966261236 Definition:A large round celestial body orbiting around a star. EtymologyFrom the Greek word “πλανήτης” (“wanderer”). Translations:
| |||
Planet Mars | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Term/Concept: Planet Mars Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| |||||||||||
Planetary geology | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short definition: Planetary geology is a science discipline that focuses on the geology of solid-surface celestial bodies, such as planets and their moons, asteroids and meteorites. It is also known as space geology, astrogeology or exogeology. Detailed definition: Planetary geology is a relatively new discipline, having appeared in the 1960s. Some topics that planetary geology is concerned with are: studying and analysing the composition of celestial bodies to better understand their origins and history; determining the properties and processes in the internal structure of astronomical objects, such as their volcanism, impact craters and fluvial processes; classifying exoplanets based on their geology and composition. Planetary geology is closely linked with the Earth’s geology, and many planetary geology studies are conducted by comparing the geology of the celestial body with the Earth’s geology. One of the main aims of these studies is trying to figure out whether other planets are capable of supporting life. Etymology: Even though the prefix -geo comes from Ancient Greek γῆ (gê, “earth”) and is mostly associated with topics related to the Earth, planetary geology is named as such for historical and convenience reasons. Sample sentence(s): Planetary geology researchers at Harvard contribute to robotic space missions to other planets. Translations:
French: Géologie planétaire German: Astrogeologie Italian: Esogeologia Polish: Geologia planetarna Swedish: Astrogeologi Links to Videos/Articles:
Byrne, P. K. (2021). Planetary Geology. In Elsevier eBooks (pp. 37–51). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-102908-4.00125-9 TAWNIA VANDERWOOD. (2019, August 20). Meet a Planetary Geologist [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/POMlppgXgM4 | ||
Point Nemo | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 25). AI illustration of point nemo. Midjourney. midjourney Space junkyard... Tags: space junkyard Keyword(s): Space Junkyard Probe (Last edited: Monday, 24 July 2023, 3:44 PM) Source: Todd, G. (October 2013). Mariner Space Probe. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/101561334@N08/10437025414 Space junkyard... | |||
Probe | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Todd, G. (October 2013). Mariner Space Probe. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/101561334@N08/10437025414 Short Definition: A probe is a smaller spacecraft meant to explore the space, but will return to a space station upon return from the exploration. Detailed Definition: A probe's role is to study other planets and moons, perform scientific observations and gather data about the universe. It's an unmanned spacecraft that can be remotely controlled and monitored during its mission. Some famous probes include Voyager, Pioneer and Galileo probes. Etymology: From latin proba - meaning "proof" Sample Sentence(s): Voyager 2 probe was launched in 1977. Translations: French: sonde German: Sonde Polish: Sonda Swedish: sond Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/parker-solar-probe https://www.space.com/40437-parker-solar-probe.html | |||
