Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
M |
|---|
Manipulator | |||
|---|---|---|---|
source of image: Short definition: A robot manipulator is a multi-segmented electronically controlled mechanism that performs tasks by interacting with its surroundings. They are also commonly known as robotic arms. They are widely used in the industry to assist workers to deal with radioactive or biological hazard materials, moving or lifting objects that are too heavy. Detailed Definition: A manipulator is a tool used in robotics to move objects around without the operator having to touch them directly. They have been used in a variety of applications, including robotic surgery, welding automation, and space travel. It is an arm-like device made up of several sliding or jointed segments known as cross-slides that can grip and move items with a variety of degrees of freedom. A manipulator is a lift-assist device used in industrial ergonomics to assist workers in lifting, moving, and placing objects that are too heavy, too hot, too big, or otherwise too challenging for one worker to handle manually. A column boom manipulator is utilized in welding to improve deposition rates, decrease human error, and lower costs in a manufacturing environment. Furthermore, manipulator tooling allows the lift assist to pitch, roll, or spin the part for proper placement. For example, removing a part from a horizontal press and pitching it up for vertical placement in a rack, or rolling a part over to expose the back of the part. Sample sentence: 6-axis robotic manipulators are the most commonly seen in industry because their range of motion is similar to the human arm.Chinese: French: Manipulatrice (feminine)Manipulateur (masculine) German: Manipulator Polish: Manipulator Swedish: Manipulator Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figure-1-1-Standard-robot-manipulators-1_fig1_330599518 | |||
Mars Habitat | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio Source: Short Definition: A Mars habitat is a proposed idea to colonize Mars and establish an autonomous
colony. The horrid conditions of Mars will pose an almost insurmountable problem, where concrete solutions still elude us. In theory, Elon Musk said that a crewed
landing would occur in 2029, which Is still 6 years away, but this seems to be
an unachievable goal in the near future. Detailed Definition: A Mars habitat would be a habitat on Mars where humans’ strife to be self-sufficient. In some ways, Mars is even similar to the Earth, but it just differs in too many life essential conditions. The mean temperature on Mars only reaches -63°C and the average natural radiation levels are 40-50 times higher than on Earth due to the missing Ozone layer on Mars. These conditions would be enough to classify it as horrid, but the list goes on. Breathing normally is impossible due to the wrong gas composition, and even the ground you would walk on is cancerous. Another negative is the different gravitational pull, because Mars’ gravity only reaches 38% of the gravity on Earth, which will lead to muscle atrophy and the necessity of intensive sport programs. These conditions would make an underground base under frozen CO2 that could be harvested from Mars and another layer of Mars soil a necessity to decrease the chance of getting cancer. At the start of the colony, only nuclear could be used as an energy option, because the varying conditions make others not effective and Mars as a whole is relatively energy poor. To achieve self-sufficiency proves to be an insurmountable problem, because even food will be hard to produce, because the soil does not have the needed nitrogen compounds and the soil would have to be decontaminated. To make a Mars habitat is certainly possible, but the feasibility and the ethicality have to be called into question.Etymology: Mars come from older Latin (older than 75 BCE) Māvors which was used as god of war from Middle English Habitat comes from Latin habitareà meaning habitat (it dwells) Sample Sentence(s): Mars habitats would have to contend with surface conditions that include almost no oxygen in the air, extreme cold, low pressure, and high radiation. (Wikipedia) French: Habitat mars German: Mars-Habitat Polish: habitat marsjański Swedish: Mars livsmiljö Links to Videos/Articles: | |||
Mercury | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| |||||||||||
Meridian | ||
|---|---|---|
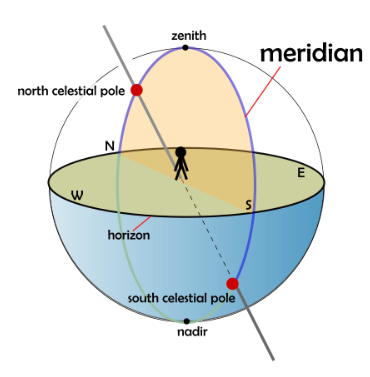 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Meridian_(astronomy) Short definition: An imaginary line in the sky running from due north to due south through the observer's location and the zenith.Detailed Definition:
In astronomy, a meridian is an imaginary line in the sky that runs from due north to due south, passing through the observer's location and the zenith. The zenith is the point in the sky that is directly overhead. The meridian is used to measure the altitude of objects in the sky, as well as their right ascension and declination. The meridian also marks the boundary between the eastern and western halves of the sky, with objects east of the meridian being in the morning sky and those west of the meridian being in the evening sky. Etymology: Latin - medius ‘middle’ + dies ‘day’. Sample Sentence(s):
"The planet Venus will cross the meridian at 8:00 pm tonight." "The altitude of the North Star above the horizon can be measured relative to the observer's meridian." "The meridian passage of a celestial object is the time it crosses the observer's meridian." Translations: French: Le Meridien German: Höhepunkt Polish: Południk Links to videos/articles: https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/m/meridian https://www.britannica.com/science/celestial-meridian | ||
Meteor Crater (Barringer Crater) | ||
|---|---|---|
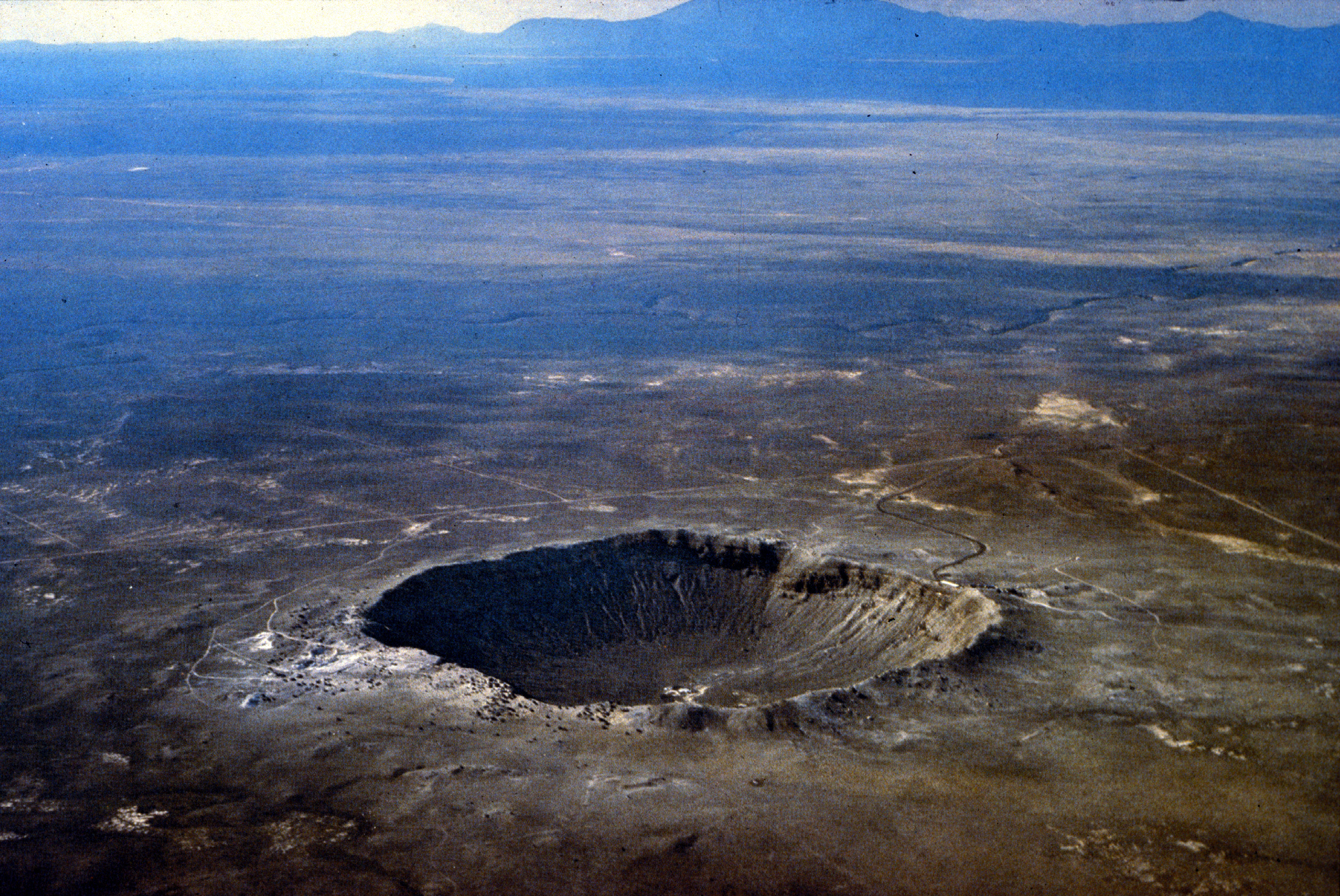 Short Definition Meteor Crater, also known under the name Barringer Meteor Crater, is the first crater known to be caused by the impact of a meteorite. The crater caused 50,000 years ago was long thought to be volcanic until it was proven in 1961 that it was caused by the impact of an asteroid hitting earth.
Found pieces of the asteroid are known under the Canyon Diablo Meteorite and can be seen among other things at the museum nearby. To this day, it is the best-preserved crater caused by impact to be found. Because of that, scientist have done much research inside and astronauts have been trained there. Today it is part of a museum and can be visited. Etymology Sample Sentence(s): Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
Other sources/links: ● Meteor Crater Natural Landmark. (2023a, May 23). Meteor Crater | Barringer Space Museum | Winslow, AZ. Meteor Crater | Barringer Space Museum. https://meteorcrater.com/ ●
AZFamily, Arizona News. (2019, July 22). How Arizona’s meteor crater was
created [Video]. YouTube. ● Meteor Crater, Arizona, USA | NASA Solar System Exploration. (n.d.). NASA Solar System Exploration. https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/resources/2257/meteor-crater-arizona-usa/
| ||
Meteorite | ||
|---|---|---|
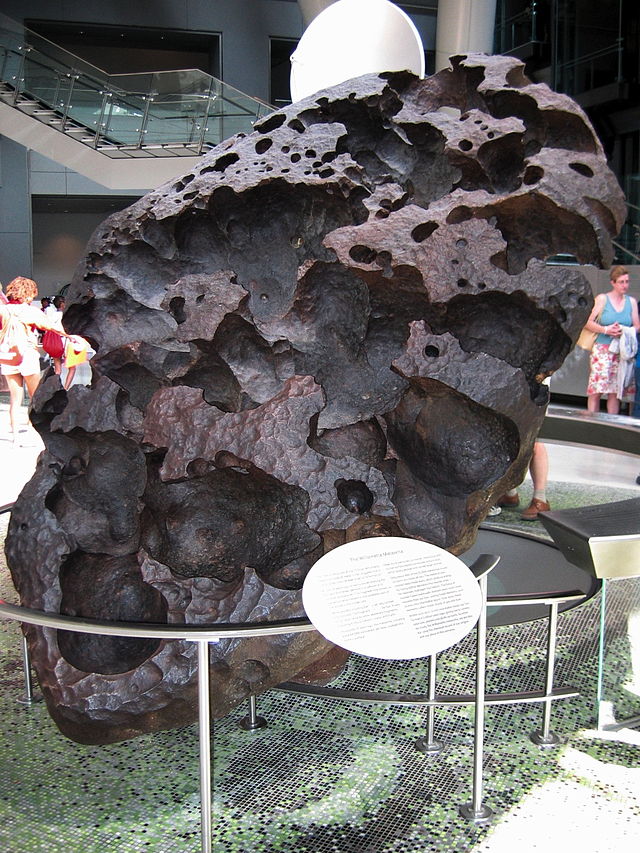 Short definition: A meteorite is a piece of rock or metal originating from space that has landed on the Earth’s surface. Before a meteorite enters the Earth’s atmosphere, it’s called a meteoroid. The phenomenon of a meteoroid burning up and leaving a glowing trail behind is called a meteor. Detailed definition: A meteorite is a piece of debris, usually of a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that has survived its passage through the Earth’s atmosphere and reached the surface. Meteorites vary greatly in size: some, that are called micrometeorites, are less than 1mm in size, and very few are large enough to leave an impact crater. The biggest meteorite ever found - the Hoba meteorite in Namibia - weighs about 60 tons. Most meteorites are stony, and only about 6% of meteorites are iron meteorites or a mix of stone and metal. Etymology: meteor (from Greek ta meteōra"the celestial phenomena, things in heaven above") + -ite Sample sentence(s): Commonly, chondrules can make up 75% of the volume of the meteorites in which they occur. (Source: Cambridge English Corpus | Cambridge University Press | ELT. (n.d.). Cambridge.es. https://www.cambridge.es/en/) Translations: French: météorite German: Meteorit Italian: meteorite Polish: Meteoryt Swedish: Meteorit Links to Videos/Articles: Alexander, C. M., & Wetherill, G. W. (2023, May 11). Meteorite | Definition, Types, Identification, & Facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/meteorite meteorite. (n.d.). https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/meteorite/ Science with Thomas Stevenson. (2022, August 9). What is a Meteorite? [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/Cv82yiksbl8 | ||
Meteoroid | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short definition: A meteoroid is a small rocky or metallic body in space that has not yet entered the Earth's atmosphere. When a meteoroid enters the Earth’s atmosphere at a high speed and burns up, it leaves a glowing trail, which is called a meteor. Detailed definition: Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than meteoroids are called micrometeoroids or space dust. Most meteoroids are fragments from comets or asteroids, containing extraterrestrial nickel and iron. Etymology: Meteoroid comes from meteor + -oid. -oid is a suffix coming from Ancient Greek εἶδος (eîdos, “form, likeness”), which means “resembling; having the likeness of”. Sample sentence(s): It was found that meteoroids from cometary sources were typically of porous, aggregate compositions with relatively low densities. (Source: Cambridge English Corpus | Cambridge University Press | ELT. (n.d.). https://www.cambridge.es/en/) Translations: French: Météoroïde German: Meteoroid Italian: Meteoroide Polish: Meteoroid Swedish: Meteoroid Links to Videos/Articles:Atkinson, N. (2018, April 8). What Is The Difference Between Asteroids and Meteorites? - Universe Today. Universe Today. https://www.universetoday.com/36398/what-is-the-difference-between-asteroids-and-meteorites/ Meteors & Meteorites. (n.d.). NASA Solar System Exploration. https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/asteroids-comets-and-meteors/meteors-and-meteorites/overview/?page=0&per_page=40&order=id+asc&search=&condition_1=meteor_shower%3Abody_type Encyclopaedia Britannica. (2019, January 2). DEMYSTIFIED: What’s the difference — meteoroids, meteors, & meteorites | Encyclopaedia Britannica [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/tXfjUxdzqBY | ||
Microgravity | ||
|---|---|---|
Short definition: Microgravity, also known as micro-g environment, is when a person or object appear to be weightless but the g-forces are never exactly zero. A clear example of microgravity can be seen when astronauts or objects float in space. Detailed definition: Microgravity, also known as micro-g environment, is a condition in which an object or a person appear to be weightless, though the g-forces are never exactly zero. "Micro" means “very small”, so microgravity refers to the phenomenon in which gravity appears to be very small. The effects of this condition can be seen when objects and astronauts float inside a spacecraft or outside, while on a spacewalk. Microgravity has a variety of effects on the human body. Muscles and bones, for example, can become weaker without having to work as hard. Furthermore, many things appear to behave differently in microgravity. Fire burns in different ways. Flames are more round when the pull of gravity is absent. There is a better growth of crystals. Their shapes are more perfect without gravity. Etymology: “Micro” from ancient greek mikrós/“small” + “gravity” from Latin gravitās/“weight” Sample sentences:
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages:
Sources: https://www.nasa.gov/audience/forstudents/5-8/features/nasa-knows/what-is-microgravity-58.htmlhttps://www.snexplores.org/article/explainer-gravity-and-microgravity https://www.britannica.com/video/163292/aspects-life-microgravity-Earth | ||
Milky Way | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Milchstraße#/media/Datei: Artist's_impression_of_the_Milky_Way_(updated_-_annotated).jpg 5th November 2021 Definition:A large spiral galaxy consisting of several hundred billion stars, dust and gas.The galaxy that includes our solar system, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. Etymology:The term Milky Way is a translation of the Latin via lactea, from the Greek γαλακτικός κύκλος (galaktikos kýklos), meaning "milky circle”. Translations:
| |||

