Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
A |
|---|
Asteroid | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Burned Pineapple Productions (2018, June 14). asteroid. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/51686021@N07/42075207904 Short definition: An asteroid is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the sun, also known as a “minor planet”. They can be rocky, metallic, or icy bodies with no atmosphere and range in a wide spectrum of sizes and shapes. Long definition: An asteroid is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the sun, also known as a “minor planet”. They can be rocky, metallic, or icy bodies with no atmosphere and vary greatly in shape and size, from 1000 km to 1 m across. The three largest asteroids (Ceres, Vesta and Pallas) look very much like miniature planets by being almost spherical and containing some partly differentiated interiors. They are thought to be surviving protoplanets. Nevertheless, a wide majority of asteroids are smaller and irregularly shaped and are thought to be shattered remnants of planetesimals, which are bodies that never grew large enough to become planets within the formation of the solar system (solar nebula) or fragments of bigger bodies. The physical composition of asteroids is in most cases still poorly understood and varies from asteroid to asteroid. They are classified by their emission spectra and are divided generally in three big groups: C-type, M-type, and S-Type, named after their compositions carbon-rich, metallic, and salicaceous, respectively. In the main asteroid belt there are two primary types of asteroids: dark, volatile-rich asteroid consisting of the C-type and P-type, and dense, volatile-poor asteroids consisting of the S-type and M-type asteroids.Etymology: From Greek asteroeidēs ‘starlike’, from astēr ‘star’. Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Astrobiology | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 11). Artistic AI Illustration of Astrobiology. midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition:Astrobiology is an interdisciplinary field of research concerned with the origin, evolution, distribution and future of life in the universe. It encompasses research in astronomy, biology, chemistry, geology, and physics. Detailed Definition:The goal of this study is to understand more about the origin and evolution of life on Earth, planetary system formation, organic compounds in space, and whether or not life exists or might exist elsewhere. Especially the frozen moons of the outer solar system, particularly Europa and Enceladus, as well as Mars, are of significant astrobiological interest. These solar system bodies are the focus of current and future multinational space missions, for example in the DLR. Etymology:
astro - Ancient Greek - ἄστρον (astron) "star" bio – Ancient Greek - βίος (bíos) “life” logy – Ancient Greek -λογία (logía) “branch of study” or “to speak” Sample Sentence(s):
“The research field of astrobiology is gaining more and more importance in the last decades.” “Did you see the documentary on astrobiology last week?” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:
https://www.dlr.de/me/en/desktopdefault.aspx/tabid-2016/ | ||
Astronomy | |||
|---|---|---|---|
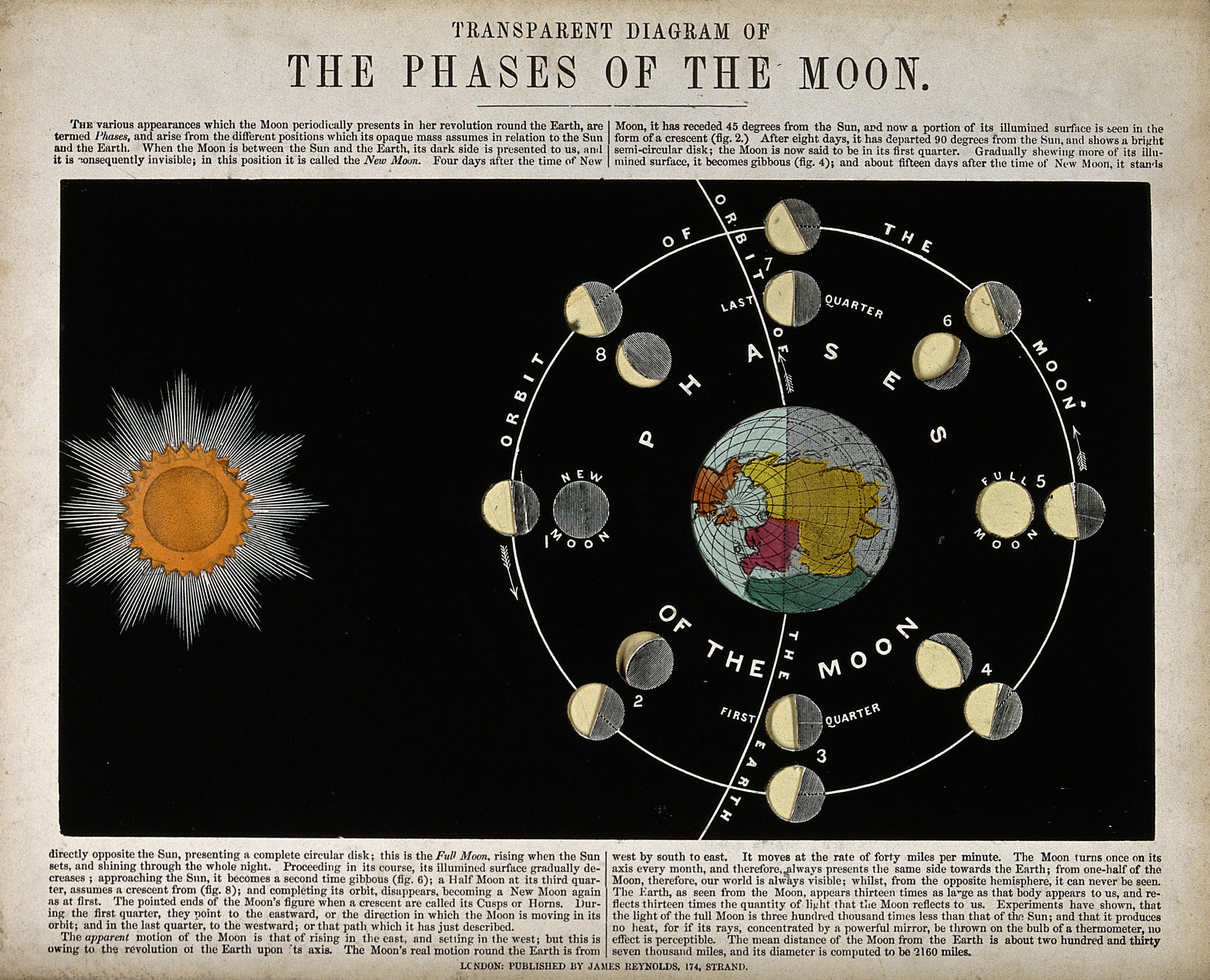 Image/Video/Audio: Diagram: Phases of the Moon Image/Video/Audio Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/8b/Astronomy%3B_a_diagram_of_the_phases_of_the_moon._Engraving._Wellcome_V0024718.jpg Short Definition:
Astronomy is a positive science that includes the discovery, observation, interpretation and recording of all objects and phenomena in space. Before 17th century, astronomy, which worked only to observe and interpret the positions and motion capabilities of observable celestial bodies due to technological inadequacies, after advanced its agenda in all space with the advancement of technology. Detailed Definition:
Astronomy, which aims to investigate first our galaxy and then the whole space in the light of the physics and chemistry sciences that have developed since the 19th century, it also includes to investigate structures and movements of celestial bodies, the formation of galaxies and the chemical analysis of this formation, and the distances and brightness levels of these objects and phenomena. There are 4 main sub-branches of today's contemporary astronomy. These are; Astrophysics: Examines the harmony and application of defined laws of physics in space. Astrometry: It deals with mapping the locations of space objects and their distances from each other. Astrogeology: It deals with the elucidation and understanding of the structure and reserves of materials in space. Astrobiology: Examines possible extraterrestrial life. All these sub-domains contain more of an observable method besides being experimental due to he lack of possibilities we have today in regards with technology.
Etymology:
‘Astron’ (star) – From Ancient Greek ‘Nomos’ (rule, law) – From Ancient Greek
Sample Sentence(s):
''Astronomy has expanded to include astrophysics, the application of physical and chemical knowledge to an understanding of the nature of celestial objects and the physical processes that control their formation, evolution, and emission of radiation.'' (Evans, J. (2023, January 5). Astronomy | Definition, History, Discoveries, & Facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/astronomy) ‘’Astrology can be fun to think about, but it’s different from astronomy. Astrology is not science!’’ (Cloudflare CAPTCHA. (n.d.). https://www.amnh.org/explore/ology/astronomy/what-is-astronomy) Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French:
Astronomie German:
Astronomie Polish:
astronomia Swedish:
Astronomi Turkish: Astronomi
Links to Videos/Articles:
Astronomic. (2015, July 7). Astronomy: Explained | Astronomic [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XinkicMVzLs Cloudflare CAPTCHA. (n.d.). https://www.amnh.org/explore/ology/astronomy/what-is-astronomy E., E. (2022, May 12). 17 branches of astronomy. Earth How. https://earthhow.com/what-is-astronomy/ Evans, J. (2023, January 5). Astronomy | Definition, History, Discoveries, & Facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/astronomy | |||
Atmosphere | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Gatley, R. (2018, January 27). Cruising at 47000 feet over Kazakhstan. Shot with an 8mm fisheye lens.. unsplash. https://unsplash.com/photos/oxgK2f_rxDc Definition:The mass of gas that surrounds an astronomical body, such as a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of this body. Etymology:From Greek ατμός (atmos)'vapor' + σφαιρα (sphaira)'sphere' Translations:
| |||
Aurora | ||
|---|---|---|
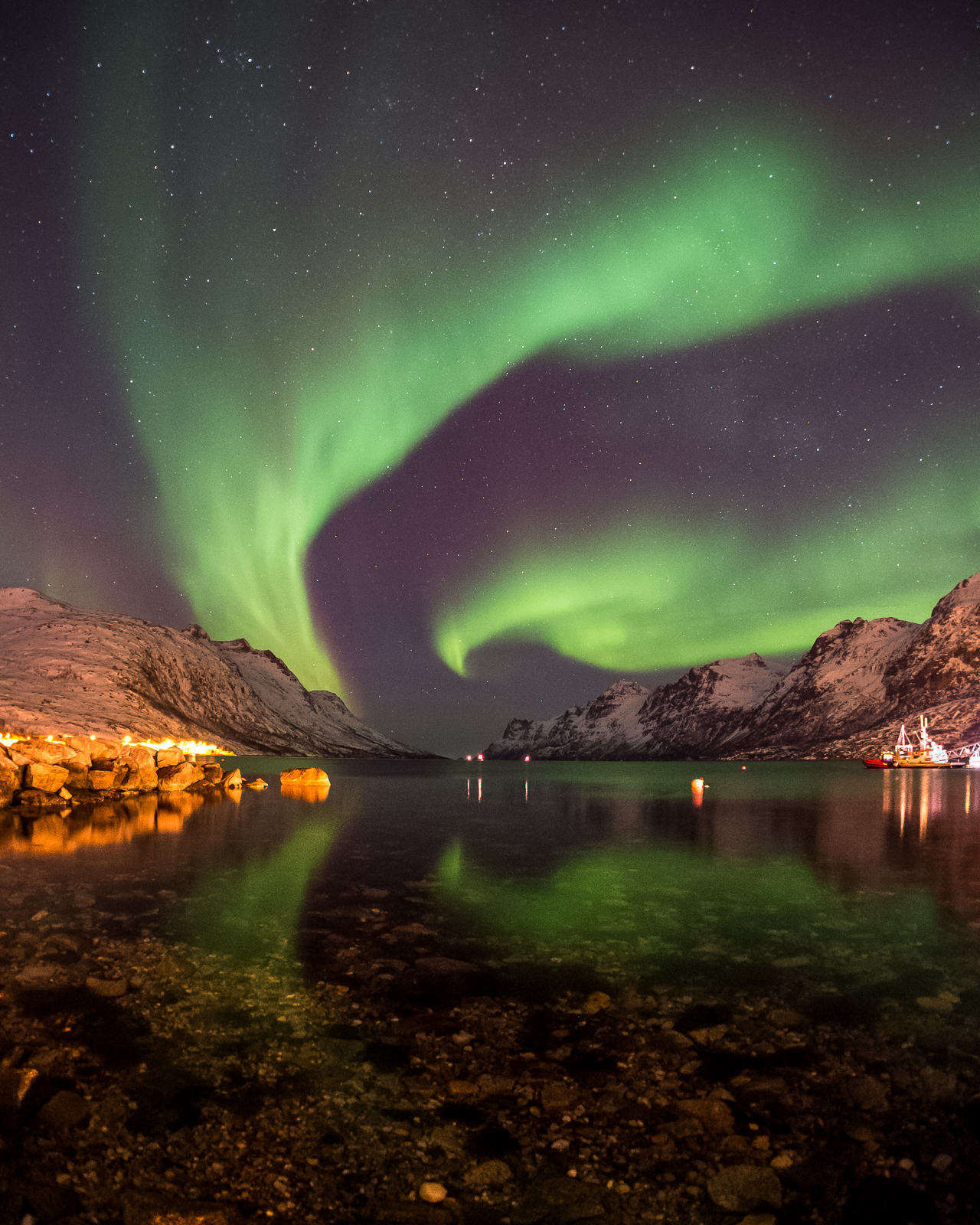 Image/Video/Audio Source: Hemmingsen, J.A. (2016, January 8). aurora borealis in Ersfjordbotn. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/64104971@N02/24226248576 Short Definition: An aurora is a phenomenon caused by the Sun (star). A bust of electrified gas (solar wind) from the star approaches planets. Small particles travel down the magnetic field lines towards both poles. Particles from the star interact with gas particles in the atmosphere, causing the creation of the light in the sky. Depending on the atmosphere composition, the colour of the aurora might be different. Oxygen glows green and red, nitrogen blue and purple. Auroras can appear on every celestial object that has an atmosphere and magnetic field. On Earth, the aurora near the North Pole is called an aurora borealis (northern light) and one near the South Pole is called an aurora australis (southern light). Etymology: “Aurorae are considered to be one of the seven natural wonders of the world.” (source: https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/a/Aurora) Translations: French: German: Polish: Swedish: Spanish: Links to Videos/Articles: | ||
B |
|---|
Barycenter | ||
|---|---|---|
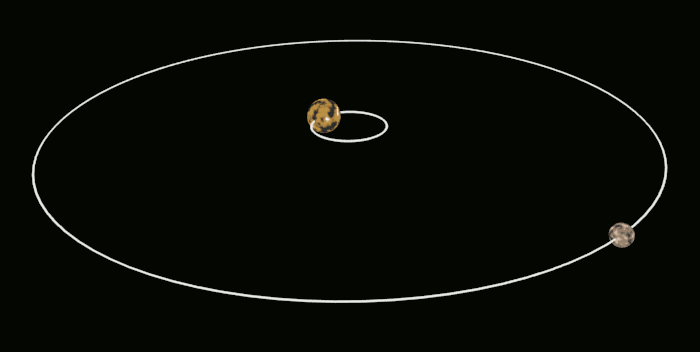 Source: Hoover, S. (2013, July 21). wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=28974343 Short Definition:
Barycenter is a theoretical point that has several meanings according to the field in which it is employed:
Detailed Definition:The barycenter is a theoretical point usually with a mathematical value, which has different meanings depending on the field to which it is applied. From its etymology, Barycenter is usually used to express the center or average of a distribution of objects, values or data.
Originally, the mathematician and physicist Archimède introduced and described the notion of barycenter around 300 B.C.E. He first approached it from a physical perspective by stating: “Every heavy body has a well-defined centre of gravity in which all the weight of the body can be considered concentrated." In astronomy, this notion describes the point around which a celestial body and its/their satellite(s) rotate. The illustration below depicts the barycenter with the red cross in the middle as well as the two bodies of different mass orbiting around it. Etymology:Barycenter comes from ancient Greek. Bary: βάρος (báros, “weight”) + center which comes from the Latin of centrum or even earlier from ancient Greek as kentron, κέντρον (single point). Sample Sentence:"How well we understand the Solar System’s barycenter is critical as we attempt to sense even the smallest tingle to the web.” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://youtu.be/7hMfCCqSdFc
| ||
Big Bang | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 24). Artistic AI Illustration of the Big Bang. midjourney. midjourney.com Definition:
According to the Big Bang Theory, this is the starting point of the known, observable universe, when a rapid expansion of matter took place. According to the standard cosmological model (Big Bang Theory), the Big Bang occurred about 13.8 billion years ago. The model describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature, and offers an explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, like the lighter elements, such as hydrogen and helium. Etymology:From English big “of considerable size or extent” and bang “to (cause something to) make a sudden very loud noise or noises.” The term was introduced in 1948 by the British astronomer Fred Hoyle. In a radio broadcast, Mr Hoyle made disparaging remarks about the hypothesis of the expanding universe and mocked its starting point as the "big bang", without suspecting that he was giving birth to a term that would become part of humankind's common vocabulary. Translations:
| |||
Binary stars | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Sources: Center for High Angular Resolution Astronomy (2008, August 21). Beta Lyrae - CHARA (inverted colors). wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=86270181 Short Definition: A system composed of two stars in which both share a common centre of revolution or one revolves around the other. Detailed Definition: A binary star is a pair of stars in orbit around their common centre of gravity. The term is different from a double star, which refers to any two stars close together in the sky. If components in binary star systems are close enough, they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stellar atmospheres. In some cases, binary systems can exchange mass, evolving in a way which is unattainable for single stars. Etymology: The term binary was first used in the context of space terminology by Sir William Herschel in 1802, in one of his works regarding the observation of double stars. Binary - "dual, twofold, double," mid-15c., from Late Latin binarius Sample Sentence(s): One of the examples of a binary star is Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Étoile binaire German: Doppelstern Polish: Gwiazdy podwójne Swedish: Binär Stjärna Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pIFiCLhJmig https://www.scienceabc.com/nature/universe/what-are-binary-stars.html | |||
Biomining | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 24). AI illustration of microorganisms on ore. midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition:A process involving the extraction of a resource using biological tools. For example, with bacteria or algea. Detailed Definition:Biomining is an environmentally friendly and energy efficient way of extracting useful elements by using microbes to break down rocks to make soil or provide nutrients. Microbes are tiny organisms, such as bacteria and fungi, that have a wide variety of functions. Some microbes have abilities that could be beneficial to humans, such as biomining. Etymology:Bio: From Ancient Greek βίο- (bo-), combining form and stem of βίος (bíos, “life”). Mining: Any activity that extracts or unearths minerals. Sample Sentence:You can use biomining to extract minerals from asteroids using bacteria or fungi." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.sciencedirect.com/referencework/9780080885049/comprehensive-biotechnology | ||

