Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
I |
|---|
Inflation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Sources: https://wmap.gsfc.nasa.gov/universe/bb_cosmo_infl.html https://www.space.com/42261-how-did-inflation-happen-anyway.html Definition:Rapid expansion of the universe at its early stages of development (at around 10-36 seconds after the Big Bang). The Inflation Theory was developed in 1980 by Alan Guth, Andrei Linde, Paul Steinhardt, and Andy Albrecht and attempted to account for phenomena that could not be explained by the Big Bang Theory (the Horizon Problem, the Flatness Problem and the Monopole Problem). Nowadays, the Inflation Theory is considered to be an extension of the Big Bang Theory. Translation
| |||
Infrared | ||
|---|---|---|
Image:
Source: Short Definition: Light with wavelength from 800 nanometers to 1 millimiter. Detailed Definition: Electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from 800 nanometers to one millimeter. It is next to the red end of the visible spectrum, hereby the name. Also called IR, it is a kind of electromagnetic radiation that has qualities like both a wave and a particle, the photon, and propagates energy and momentum as well as exerting radiation pressure. Etymology: Infrared comes from Latin: infra, which means below. Sample Sentence(s): To keep an eye on workplace activities, they used infrared cameras. Without disturbing the bats, an infrared camera records them. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: infrarouge German: Infrarot Polish: podczerwień Swedish: infraröd Links to Videos/Articles: https://science.nasa.gov/ems/07_infraredwaves https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/infrared-vision | ||
International Asteroid Warning Network | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short
Definition
Sample Sentence(s): IAWN includes members from all over the world that are creating a response in case of meteorite impact. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French: International Asteroid Warning Network
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
International Space Station | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:A research facility that was launched in 1998, is orbiting around the Earth and is operated by multinational groups of astronauts sent regularly by five space agencies participating in the project – NASA (the USA), Roscosmos (Russia), ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan) and CSA (Canada). Translations:
| |||
Interstellar Medium | ||
|---|---|---|
 webteam@eso.org. (n.d.). ESO - The Planet, the Galaxy and the Laser. 1999- 2008 ESO. https://web.archive.org/web/20081121184421/http://www.eso.org/gallery/v/ES OPIA/Paranal/phot-33a-07.tif.html Short Definition: The interstellar medium (ISM) is a composition of radiation and matter which occurs between star systems, which are compositions of stars orbiting each other. The medium is usually created from various gasses, mostly hydrogen and helium. This matter is a filler between the stars. Detailed Definition: The interstellar medium (ISM) is a region filled with gas and dust in between stars. The medium is created when a star dies. As the star collapses into itself, it releases huge amounts of energy and matter at high velocity and high temperature. When this mix encounters patches of interstellar gas, the visible nebulas of interstellar medium are created. The gas is ionized, and space dust blocks certain light waves which. Contrary to common belief, space is not completely empty and is not a full vacuum but is filled with matter such as gas and space dust. The interstellar medium is impactful in formations it is in. Stars which are positioned in the denser areas of ISM supply it with matter and energy through stellar winds or supernovae (the explosion of a star). The inter-influence of stars and ISM formations helps scientists determine the lifespan of given star formations. Etymology: This phrase is a conjunction between the words 'interstellar' and 'medium'. The word 'interstellar' comes from combining the prefix 'inter' from Latin for "between" and the word 'stellar' from Latin 'stellaris' meaning "pertaining to a star". The word 'medium' from Latin medium "the middle, midst, center; interval" Sample Sentence(s): 1. The interstellar medium can be visible with long exposure astrological
photography. Translations: French: milieu interstellaire German: interstellares Medium Italian: mezzo interstellare Polish: ośrodek międzygwiazdowy Swedish: interstellärt medium | ||
J |
|---|
James Webb Space Telescope | ||
|---|---|---|
Source: Short Definition: The James Webb Space Telescope is a large telescope in space that conducts infrared
astronomy. The cutting edge telescope technology aims to shine light on stars or
galaxies, that were previously hidden in “plain” sight. Many people think this
is the successor to the Hubble telescope, but in reality, it is more of a
successor for the Spitzer space telescope, which also is an infrared telescope.
The property of light to shift to red makes this a helpful telescope to look at
the oldest galaxies. Detailed Definition: The James Webb Space Telescope is a visualizing device for away structures or phenomenons that work in the infrared range. The biggest telescope in space had to overcome many difficulties to even be transported to space. The telescope had to be folded to even fit in the rocket, and so they used Origami techniques to transport it safely to its place. JWST is not an all-rounder telescope like Hubble is. JWST aims to discover secrets from almost the beginning of time with the most sophisticated infrared sensors, cameras and lenses that were used till now, but looking at the oldest stars and galaxies is not its only job. JWST will also be used to identify fitting exoplanets by scanning the atmospheres of those planets for the right gas composition.Etymology: Latin- spatiumà Old French -espaceà Middle English – space Modern latin– tele and modern latin -scopiumà Modern latin – Telescopiumà English telescopeSample Sentence(s): Webb will be the largest telescope ever placed in space; 100 times more powerful than Hubble. So big it has to fold origami-style to fit in the rocket and will unfold like a "Transformer" in space (NASA) NGC 346, one of the most dynamic star-forming regions in nearby galaxies, is full of mystery. Now, it is less mysterious with new findings from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. (NASA)French: télescope
spatial james webb German: James Webb Weltraumteleskop Polish: Kosmiczny Teleskop Jamesa Webba Swedish: James Webb rymdteleskop Links to Videos/Articles: https://webb.nasa.gov/ https://webbtelescope.org/ | ||
Jet engine | ||
|---|---|---|
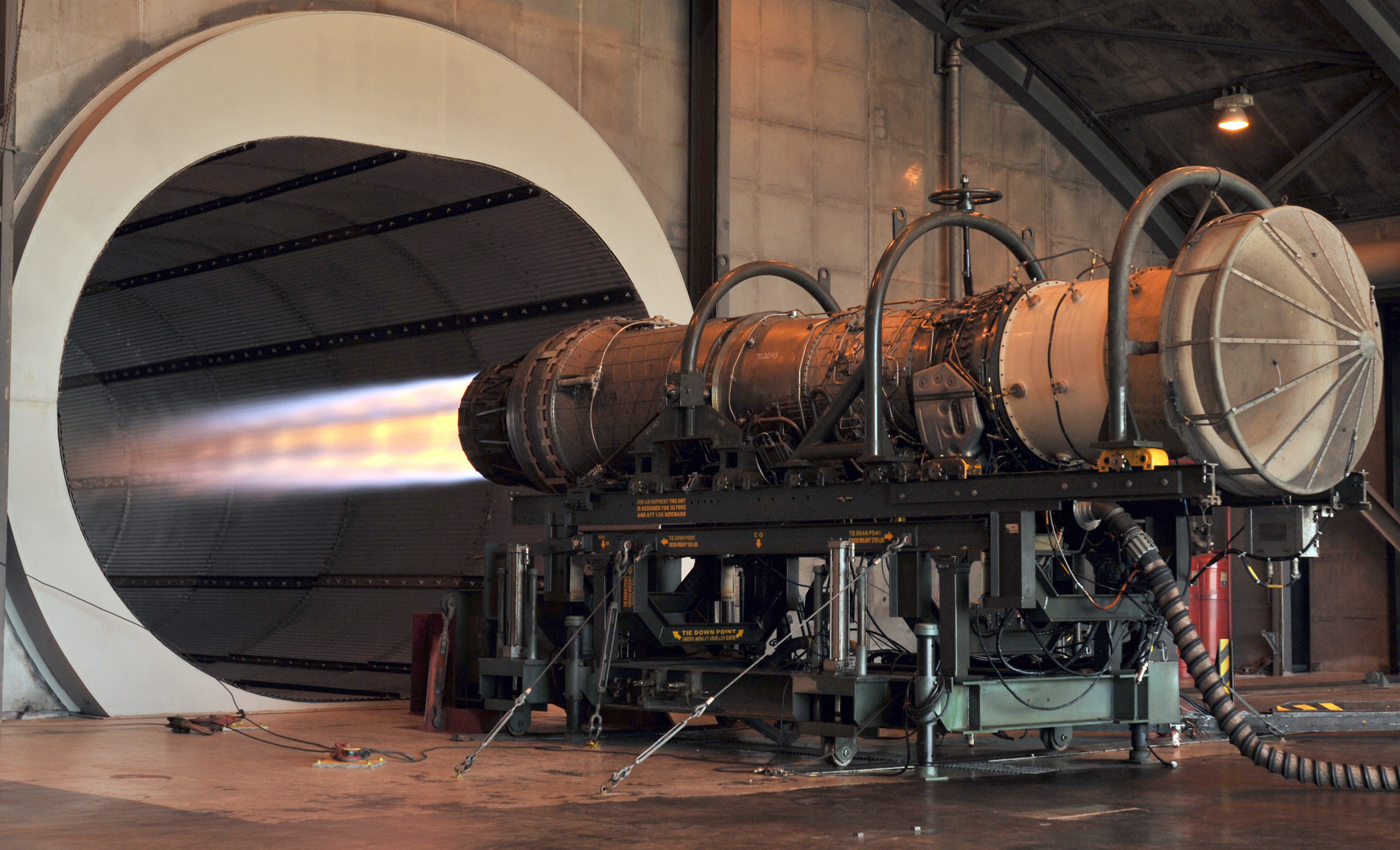 U.S. Air Force. (2010, November). F100 F-15 engine. Retrieved from https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/69/F100_F-15_engine.JPG Photograph of a jet engine in operation, with a long converging plume of hot gas streaming out from the nozzle Short Definition: A jet engine is a reaction engine that produces a jet of heated gas to be discharged from the engine as a reaction mass. The Propelling gas is usually air, especially when the engine is used in the atmosphere on flying vehicles, but can be other gas or liquid. Detailed Definition: A jet engine is a reaction engine that discharges a fast-moving (often supersonic) jet of hot gas (usually air, if the engine is used in the atmosphere) and to generate thrust. Jet engines are usually internal combustion engines and used everywhere: on planes, boats and rockets. Etymology: Jet – from French jet– throw, cast, gush, spurtEngine – from Middle English engyn or Anglo-Norman engine or Old French engin– skill, cleverness, war machine Sample Sentences: The jet engine roared as the airplane accelerated down the runway. Translations French: Moteur à réactionGerman: Turbinen-Strahltriebwerk Italian: Esoreattore Polish: Silnik odrzutowy Swedish: Jetmotor Russian: Реаĸтивный двигатель Ukrainian: Реаĸтивний двигун References: SKYbrary Aviation Safety. (2019, December). Jet engine. Retrieved from https://www.skybrary.aero/articles/jet-engine Airbus. (2016, November). Flight operations briefing notes – Supplementary techniques : Handling engine malfunctions. Retrieved from https://web.archive.org/web/20161022181226/http://www.airbus.com/fileadmin/media_gallery/files/safety_library_items/AirbusSafetyLib_-FLT_OPS-SUPP_TECH-SEQ07.pdf | ||
Jupiter | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Stewart, P. (2018, June 8). Jupiter. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/106648653@N05/42658035711 Definition
Etymology:The planet is named after Jupiter, the highest ancient Roman deity, the god of sky and thunder. Translations:
| |||
K |
|---|
Kalpana Chawla | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: http://lk.astronautilus.pl/astros/366.htm Definition:Kalpana Chawla, born in Karnal, India, in 1962, is first astronaut with an Indian descent. In her early years, her father took her to local flying clubs, where she developed her passion for flying. She moved to the U.S. to pursue degrees in engineering (Ph.D. in aerospace engineering from the University of Colorado) and eventually after graduation, she did research, focusing on vertical take-off and landing concepts. Her area was the development and implementation of efficient techniques for performing aerodynamic optimization. In 1994, Chawla was chosen as an astronaut candidate and took part in 2 space flights. The second flight ended tragically in 16.01.2003, as Space Shuttle Columbia exploded while being on the way back to the Earth, after 15 days and 22 hours spent in space. The explosion while re-entrng into Earth's atmosphere killed all seven astronauts on board, including Kalpana Chawla. Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/atoms/files/chawla_kalpana.pdf https://www.space.com/17056-kalpana-chawla-biography.html | |||