Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
G |
|---|
Geosynchronous orbit | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Projection of the path traced by geosynchronous satellites of different inclinations. Source: Wikipedia Short Definition: | |||
Gravity | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| |||||||||||
Gravity Assist | ||
|---|---|---|
Source: http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/multimedia/display.cfm?IM_ID=2143, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=18049439 Short Definition:Gravity assistance describes the intentional use of the gravitational attraction of a celestial body, in order to modify the trajectory of a space vehicle. This maneuver allows the spacecraft to save rocket fuel. Detailed Definition:Etymology:1. Gravity (Noun.), originating from the Latin word gravitatem, with the meaning of “weight, heaviness, pressure” 2. Assist (Verb.), originating from Latin word assistere, which means “standing by, help” Sample Sentence(s): “The global minimum velocity increments of direct transfer trajectory and gravity-assist trajectories are obtained for each candidate target.” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Great Red Spot | |||
|---|---|---|---|
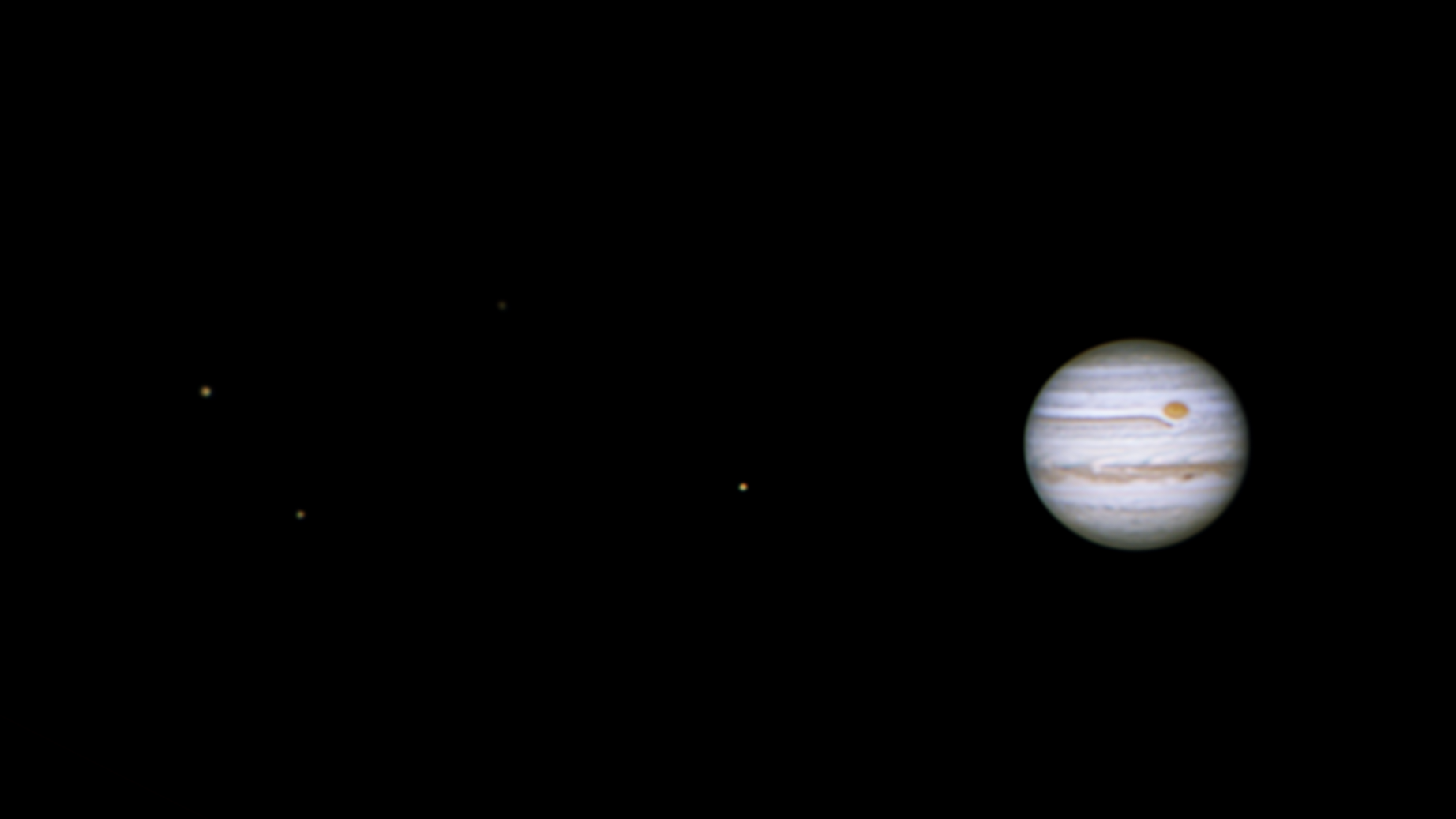 Sources: Stewart, P. (2018, June 8). Jupiter. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/106648653@N05/42658035711 Definition:A persistent large anticyclonic storm in the atmosphere of Jupiter, 22° south from its equator, which has been continuously observed since the 19th century.As of 2021, the Great Red Spot is reported to be about 10,000 miles across and 300 miles deep into the atmosphere of Jupiter. However, according to NASA observations, it is shrinking and becoming taller, and it is not yet clear whether the Great Red Spot will stabilize or disappear completely. Translation:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JDi4IdtvDVE | |||
H |
|---|
Heavy Element | |||
|---|---|---|---|
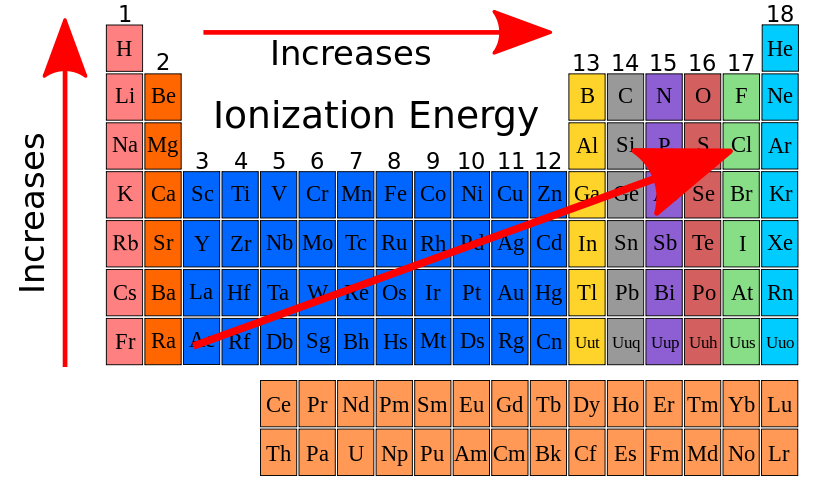 Image/Video/Audio: Image: Periodical Table Image/Video/Audio Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ionization_energy_periodic_table.svg
Short Definition:
Heavy elements are the general name for elements containing atomic numbers greater than 92. Above these, elements with atomic numbers 112 and above are called superheavy elements. The state that creates the atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of the element. Detailed Definition:
Heavy elements, which are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of the element (this called atomic number) are elements with atomic number greater than 92. One row above them there is superheavy elements with atomic numbers greater than 112. The first artificially produced heavy and superheavy elements were first produced during the Cyclotron experiments. One of the most important issues about heavy elements is the concept of 'island of stability'. This concept refers to the region in the table of nucleides where elements with half-lives longer than some other super heavy elements are found. However, it should be noted that we are ona narrow time scale, from minutes to micro/nano seconds at most. The term was first coined in 1998 with the discovery of the super heavy element 114 (Flerovium).
Etymology:
Heavy – From Proto Germanic (hafiga) Element – From Latin (elementum) (origin and meaning of heavy. (n.d.). Etymonline. https://www.etymonline.com/word/heavy) (element - Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/element)
Sample Sentence(s):
‘’The heaviest element known at the end of the 19th century was uranium, with an atomic mass of approximately 240 (now known to be 238) amu.’’ (Wikipedia contributors. (2022, December 31). Superheavy element. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Superheavy_element) ‘’Although the scientific community has assigned these heaviest elements to their own spots on the periodic table, there is still a lot we don’t know about them.’’ (Exploring the superheavy elements at the end of the periodic table. (n.d.). cen.acs.org.)
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French:
Élément lourd German:
Schweres element Polish:
Ciężki pierwiastek Swedish:
Tungt element Turkish: Ağır Element
Links to Videos/Articles:
Cookie Absent. (n.d.). https://physicstoday.scitation.org/action/cookieAbsent Discovery of Elements 113 and 115. (n.d.). https://pls.llnl.gov/research-and-development/nuclear-science/project-highlights/livermorium/elements-113-and-115 Seeker. (2019, November 10). This Superheavy Atom Factory Is Pushing the Limits of the Periodic Table [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kg0AN8bZ4us Wikipedia contributors. (2022, December 31). Superheavy element. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Superheavy_element | |||
Heliosphere | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Term/Concept: Heliosphere Image/Video/Audio: Image/Video/Audio Source: Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages [Multiple fields for entering the translation of the term in each partner language, additional languages can potentially be added, e.g. Russian, Chinese, Portuguese] French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| |||||||||||
Hubble Space Telescope | ||
|---|---|---|
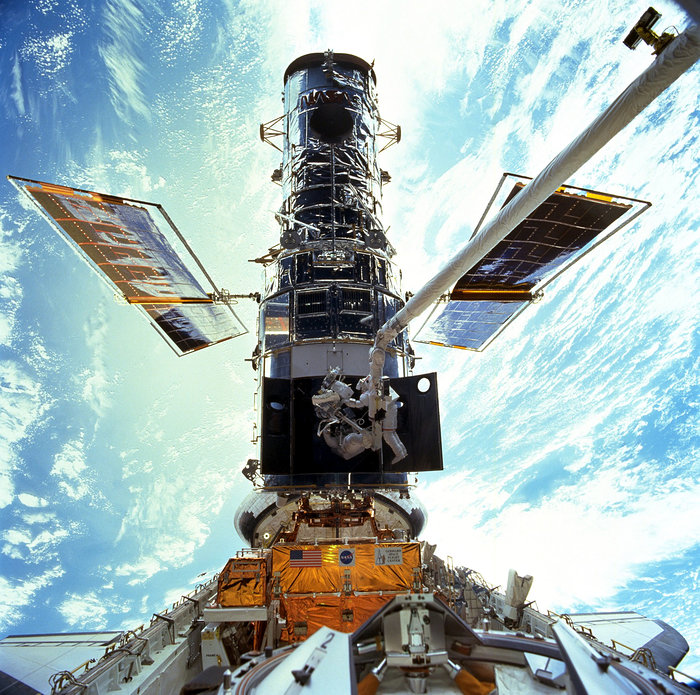 Short Definition
Sample Sentence(s):
Hubble
Space Telescope helped researchers make new discoveries.
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French: Hubble German: Hubble-Weltraumteleskop Italian: telescopio spaziale Hubble Polish: Kosmiczny Teleskop Hubble’a Swedish: Hubbleteleskopet Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Hubble's Law | ||
|---|---|---|
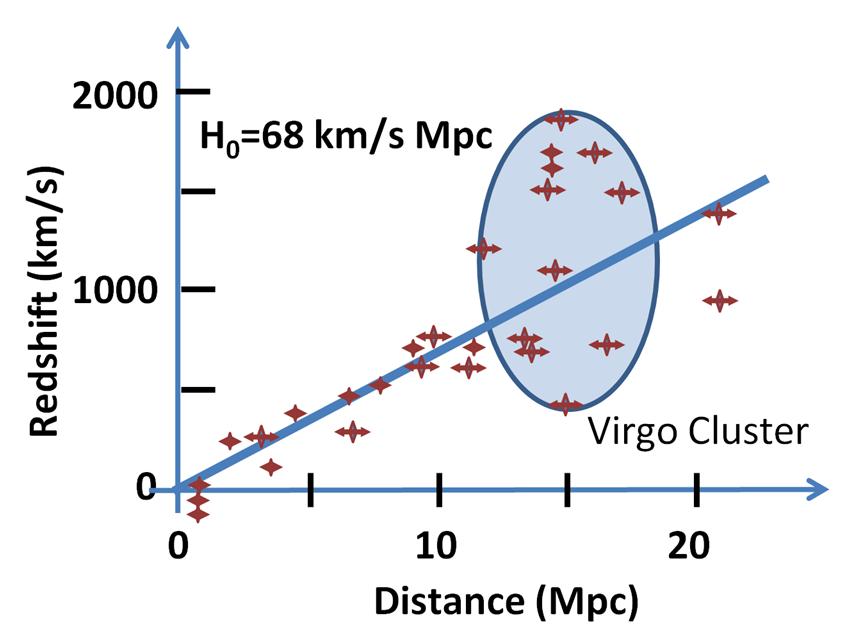
Wikipedia contributors. (n.d.). File:Hubble constant.JPG - Wikipedia. https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/2c/Hubble_constant.JPG Short Definition: Hubble's Law is a concept formed by Edwin Hubble, defining a positive relation between the distance and the speed of galaxies moving away from earth. The further they are, the faster they move away. This theory was a base to observe the expansion of universe. Detailed Definition: Hubble's law defines a relation between distance of galaxies and their speed of moving away from each other. The concept was observed through detection of redshift emitted by these galaxies, visible from earth. In simpler terms, the galaxies emit light on a spectrum further towards the red extreme, which can be observed by comparing measurements from different times, to calculate that the light has changed its wavelength and frequency, thus shifting on the visible light spectrum. The theory proves that the universe is constantly expanding, and thus it contributes to the Big Bang Theory. The constant movement of galaxies away from earth and each other, points to the increase of space in the universe. The theory also derives a so called, Hubble's constant which is a measure of how fast a given galaxy moves away at a given distance, and it comes out to around 70 (km/s)/Mpc which translates to expansion of 70 kilometres per second for every megaParsec of distance from the galaxy. Thus, for a galaxy 1 megaParsec away from earth, the structure moves away at a speed of 70 km/s. Etymology: Hubble's Law comes from the last name of the physicist Edwin Hubble. Sample Sentence(s): 1. Hubble's Law contributed largely to the theory of relativity. Translations: French - Loi de Hubble German - Hubbles Gesetz Italian - Legge di Hubble Polish - Prawo Hubble'a Swedish - Hubbles lag | ||
I |
|---|
Ilmenite | ||
|---|---|---|
Short Definition:A usually massive iron-black mineral that consists of an oxide of iron and titanium and that is a major titanium ore. Detailed Definition:Ilmenite is named after the Ilmenski mountains in Russia, where the mineral was first discovered. It is slightly magnetic, which means that magnets can be used to separate it from other minerals in sand deposits. Ilmenite is also a common accessory mineral in igneous rocks, sediments, and sedimentary rocks in many parts of the world. Also, it is a black iron-titanium oxide with a chemical composition of FeTiO3. Etymology:
Named after Ilmen Mountains in Russia + -ite in 1827. The suffix –ite is used to form nouns denoting rocks or minerals, from Latin -ītēs, and from Ancient Greek -ῑ́της. Sample Sentences:
"Ilmenite is an economically important and interesting mineral." "Ilmenite is the most important ore of titanium and the main source of titanium dioxide, which is used in paints, printing inks, fabrics, plastics, paper, sunscreen, food and cosmetics." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
