Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Currently sorted By last update ascending Sort chronologically: By last update
Cosmic rays | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short definition: Cosmic rays are high energy particles that travel through space at nearly the speed of light. Most cosmic rays are represented by atomic nuclei stripped of their atoms. Detailed definition: Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912. They originate from the Sun, from the Milky Way, and from distant galaxies. Most cosmic rays (89%) are protons of hydrogen, but some of them are nuclei of helium (around 10%) and other, heavier nuclei. Only about 1% of cosmic rays are lone electrons. Once a cosmic ray reaches the Earth’s atmosphere, it collides with other atoms there and bursts them into different particles, namely pions, muons and neutrinos. Etymology: Cosmic comes from Ancient Greek κόσμος (kósmos, “order, proper order of the world”). The term ray likely arose because cosmic rays were initially believed to be electromagnetic radiation. Sample sentence(s): Cosmic rays follow convoluted paths and arrive at the top of the Earth’s atmosphere from all directions. Translations: French: Rayonnement cosmique German: Kosmische Strahlung Italian: Raggi cosmici Polish: Promieniowanie kosmiczne, promienie kosmiczne Swedish: Kosmiska partiklar Links to Videos/Articles:
Cosmic Rays - Introduction. (n.d.). https://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/science/toolbox/cosmic_rays1.html
Vox. (2019, August 30). The mysterious rays shooting at us from space [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/Z9gQLELtbhg | ||
Cosmochemistry | ||
|---|---|---|
Short Definition:The chemistry of cosmic objects or the chemistry of objects in space, such as the chemistry of the Moon, Mars, the Sun, asteroids, quasars, etc. and their effects on each other. Detailed Definition:
Cosmochemistry is the study of the chemical compositions of matter in the universe and the processes that led to those compositions. Cosmochemistry is primarily done by studying the chemical compositions of cosmic objects or the chemistry of objects in space. For example, carbonaceous meteorites were among the earliest formed bodies in the solar system. Their organic carbon is an indicator of chemical processes that occurred before the dawn of life on Earth. By studying carbonaceous meteorites and the origin and fate of their organic compounds, we begin to understand the general process of chemical evolution of organic molecules from interstellar space. Cosmochemistry also advances our knowledge of the physical and chemical processes in the distant past that might have had a significant role in the development of life in the universe.Etymology:Cosmo = kosmos (latin) + Chemistry = Alchemy (Greek), khēmia (Egyptician) Sample Sentence:“The spectral research on sulphur-containing radicals is of great significance in many fields such as atmospheric chemistry, combustion chemistry, cosmochemistry and so on.” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Cosmos | ||
|---|---|---|
Image: Source: Short Definition: The concept of an organized system with pattern and order in the universe. Detailed Definition: The idea of the physical universe as a whole system, one having order and pattern. The understanding of the cosmos has been evolving with new discoveries about the universe. This leads to the definition of cosmology as the history of the study of the cosmos as a whole. Etymology: Cosmos comes from the Latin Kosmos, which means order or world. Sample Sentence(s): The cosmos may now be represented digitally by scientists. Scientists are hunting for hints as to how the universe came into being. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: cosmos German: Kosmos Polish: kosmos Swedish: kosmos Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nationalgeographicla.com/cosmos https://www.researchgate.net/publication/363520256_The_Infinite_Cosmos_Ebo_S | ||
Dusty Vacuum Chamber (Dirty Vacuum Chamber) | ||
|---|---|---|
Source: https://ttu-ir.tdl.org/bitstream/handle/2346/73031/ICES_2017_235.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y Short Definition:An enclosure that constitutes a closed environment developed for the purpose of simulating lunar conditions and allow for the testing of material behaviour in such a space.
Detailed Definition:Sample Sentence(s):Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles: | ||
Ephemeris | ||
|---|---|---|
Source: Short definition: An ephemeris is a table or data file that gives the positions of celestial objects at specific times. Detailed Definition: An ephemeris is a detailed table or data file that provides the positions of celestial objects in the sky at specific times. Ephemerides are used in astronomy to predict the future positions of these objects and to understand their orbits and movements. They can be calculated for any point in time and are usually given for a series of times at regular intervals, such as every day or every hour. Initially ephemerides were written, then printed, nowadays, they are digital. Ephemerides of the Solar System play a crucial role in navigating spacecraft. Etymology: ephemeris (Latin) - diary; ephemeris (Greek) - diary, journal Sample Sentence(s): "I consulted an ephemeris to find out when the next solar eclipse would occur." "The astronomer used an ephemeris to predict when the comet would be visible in the sky." "Ephemerides are widely used in astrology." Translations: French: Éphéméride German: Ephemeriden Polish: Efemeryda Swedish: Efemerid Links to videos/articles: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ephemeris https://www.astro.com/swisseph/swepha_e.htm https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/horizons/ | ||
Equation of time | ||
|---|---|---|
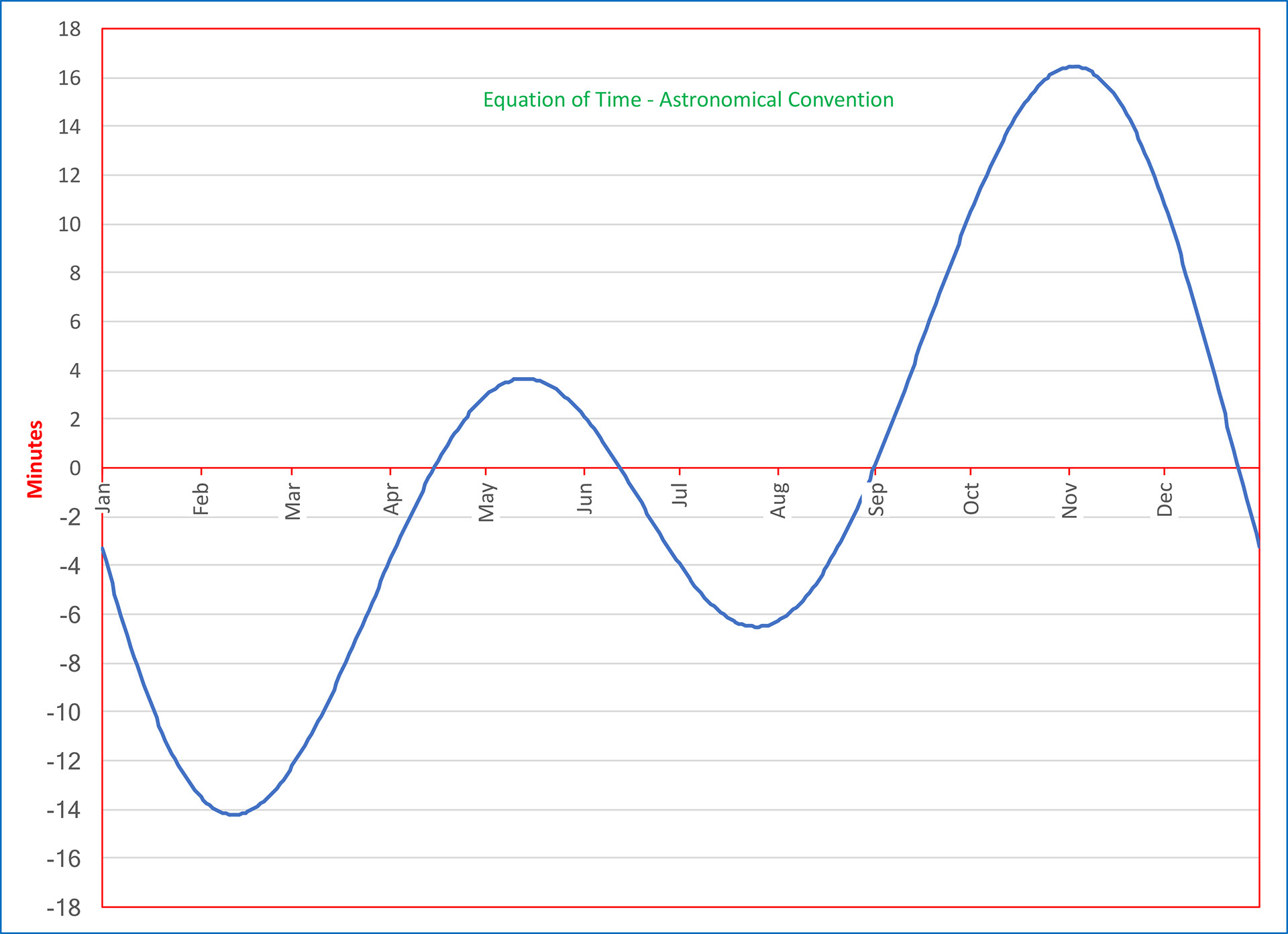 Source: https://pro2-bar-s3-cdn-cf3.myportfolio.com/cf59f354b34391ef9ddbec41a1409bef/ece2a825-e54c-4ea4-a57c-bc1f3e901591_rw_1920.jpg?h=e8d9d5ab3208bd43c08d7702b9ec2c74 Short Definition: The equation of time is a result of the difference between the daytime on Earth and the position of the sun. Detailed Definition: The equation of time exists because the orbit of the Earth around the sun is elliptical (where the orbit is not centered around the sun) and not circular which results in a difference in speed around the elliptical orbit as a difference in the length of the Earth days. The equation is the following: EOT =GHA- GMHA where EOT is the equation of time, GHA is the Greenwich Hour Angle of the apparent sun and GMHA is the Universal Time-Off. As a result, the 21./22. December is the shortest day of a year, the real local time (WOZ) results in uneven long hours and the middle time (MOZ) results in a sun orbit, which is unsymmetrical to the time. Etymology: Equation - latin aequationem (" an equal distribution, a sharing in common") Time - Proto-Germanic Timon-/timi ("Time, proper time") Sample Sentence(s): " The equation of time is the reason a Analemma( a diagramm which shows the position of the sun from one point at a specific time over a year) can be seen" Translation: French: équation du temps German: Zeitgleichung Polish:
Równanie czasu
Swedish:
tidsekvation
Links to Videos/Articles:
https://youtu.be/Mx9AJJSKIL4
https://astro.dur.ac.uk/~ams/users/equation_of_time.html
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hn0js5EzmEc
| ||
Euclid mission | ||
|---|---|---|
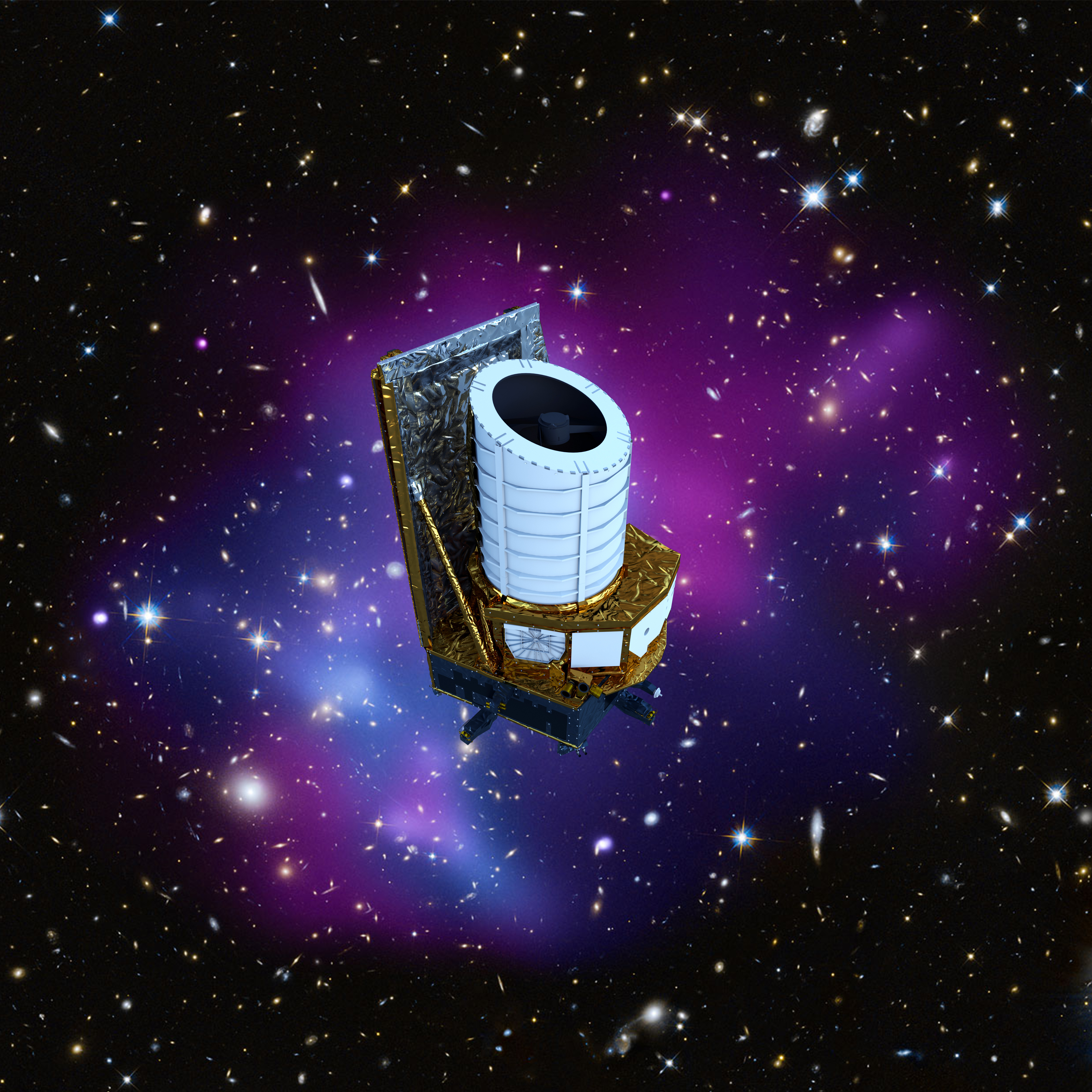 Image source: https://www.esa.int/var/esa/storage/images/esa_multimedia/images/2019/09/euclid_spacecraft/19709645-1-eng-GB/Euclid_spacecraft.jpg Short Definition: The euclid mission is project, being prepared by ESA to investigate dark matter as well as dark energy. At this moment, it is planned to launch the mission in the year 2023 (no specific date is set yet). The planned time the mission will take is set for six years and can be extended, but is limited by the amount of cold gas propulsion. Detailed definition: ESA has started the euclid mission is a project to try to investigate dark matter as well as dark energy. The spacecraft consists of a camera in the visible wavelength and a camera /spectrometer which works in the near-infrared area. It will launch from the Europe'sSpaceport in Kourou, which is located in French Guiana, and will move in an orbit which is halo shaped around the Sun-Earth Lagrange point. Another aspect which will be inspected by the mission is the reason why the expansion of the universe in accelerating and how the evolution of the universe took place, to gain more information about fundamental physics and cosmology. Etymology: Euclid - Greek euclid ("renowned, glorious") mission -Latin missionem ("act of sending a dispatching; a release, a setting at liberty") Sample Sentence: The Euclid mission is expected to bring new knowledge about the history of the universe and dark matter. Translations: French: Mission Euclide German:Euklid-Mission Polish: Misja Euclid Swedish: UppdragEuclid Links to Articles: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/missions/euclid https://sci.esa.int/web/euclid https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/euclid/main/index.html | ||
Expansion of the universe | |||
|---|---|---|---|
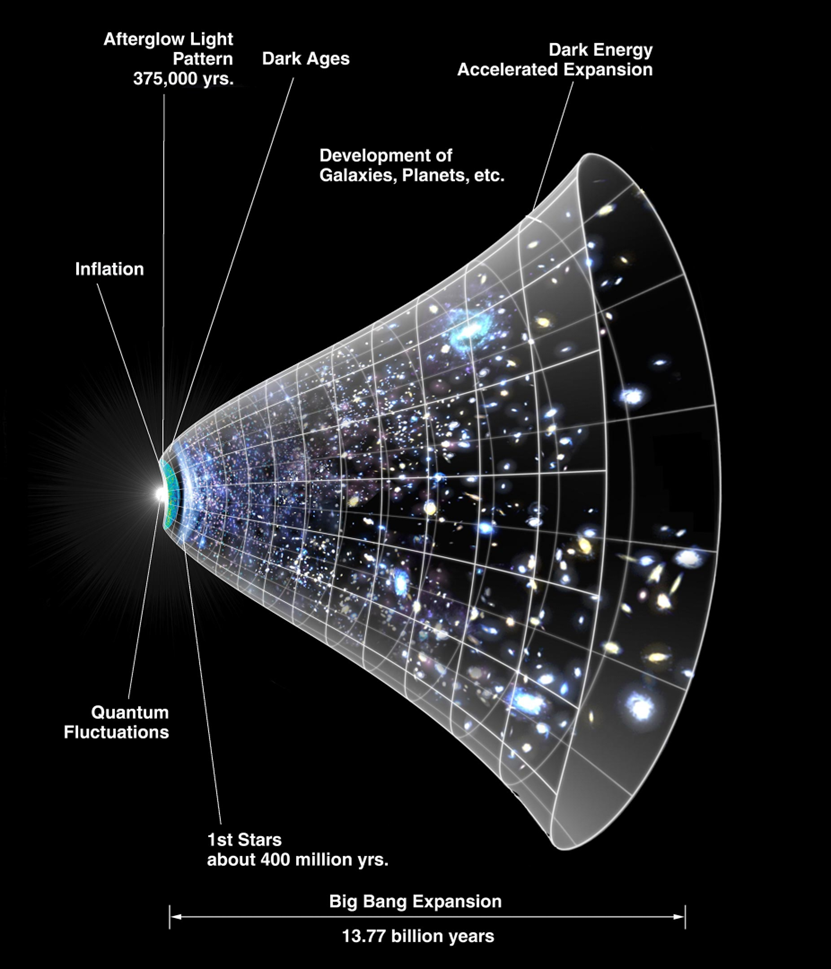 Image/Video/Audio Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Expansion_of_the_universe#/media/File:CMB_Timeline300_no_WMAP.jpg
Short Definition: The expansion of the universe is a phenomenon, which describes the
inherent property of the universe, where two galaxies that are gravitationally unbound
tend to increase the distance to each other and the rate of expansion is even accelerating.
Far away parts of the observable universe will not be observable in the near
future, because the velocity of expansion is higher than light speed from an
outside perspective.
Detailed Definition: The expansion of the universe is a phenomenon, which explains an inherent property of the universe to expand. The fact that the universe seems to expand, was first doubted because of the gravitational force and the fact that releases of energy like the big bang should normally lose power and should slow over time, but the opposite was observed. The elusive culprit was found quite fast. Dark matter is to be responsible for this phenomenon, but since we know even less about dark matter than about the expansion of the universe, details of how and why it expands are still unknown. This expansion occurs at
every location of the universe and only gravitationally bound galaxies will be
able to observe each other, because unbound galaxies will escape our observable
universe at some point. The expansion can in some way be compared to an elastic
rubber band, where the distances also increase when you stretch it, but not
literally and not on a human scale. It is more that at a scale so far zoomed
out, that the universe looks like a cosmic fluid and at this scale it is apparent
that the density is decreasing over time. There are three viable methods to
measure this expansion. One is based on redshifts, while another on the cosmic
distance ladder. Those measurements gave non-matching results, and so 2018 information
from gravitational waves made it possible to determine the rate of expansion
even more precisely.
Etymology:
Expansion à from Latin expandere à spread out Universeà from Old French univers à from Latin universumSample Sentence(s):
In a thought experiment of an ascending civilization in a faraway galaxy in the far future, they would only be able to observe their neighbouring galaxies and will think that this is all there is to the universe and all this due to an expansion of the universe. The rate of expansion of the universe is thought to be accelerating. French: Expansion de l'universGerman: Ausdehnung des Universums
Polish: Ekspansja Wszechświata Swedish: Utvidgning av universum
Links to Videos/Articles:
Expansion of the universe - Wikipedia | |||
Fluid shift in the human body | ||
|---|---|---|
 Image Source: S, M. (2023, June 01). Illustration of fluid distribution. self. self-made The fluid shift in the body is an adaption to the reduced gravitation force in space. This results in a shift of the body fluids from the lower body to the upper body. Detailed Definition: When a human body is placed on the earth surface, it has a hydrostatic (gravitational) blood pressure gradient and every body region has a different arterial pressure. In the reduced gravity of space, the hydrostatic pressure in the arteries and veins is altered to a homogeneous arterial pressure in all regions (which is the original arterial pressure of the hearth), which results in the shifted fluid distribution through the body. The human body reduces the volume of the total fluid and after the space resident, the fluid is shifted because of the returned gravity force. This phenomenon can cause several issues like cardiac arrhytmia, muscular athropy and visual problems (because the globe is flattened, the blood flow is changed slightly and the diamteter of the optical nerve can increase). Etymology: fluid - Latin fluidus ("fluid, flowing, moist") shift - Proto-Germanic skiftan (" to divide, change, seperate") Sample sentence(s): A medical
effect of a space flight may be a fluid shift. Nasa is studying
the effect of the fluid shift and how it affects changes in vision. Translation: French: déplacement du fluide German: Flüssigkeitsverschiebung Polish: Przemieszczenie płynów w ludzkim organizmie Swedish: vätskeförskjutning Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nasa.gov/content/fluid-shifts-study-advances-journey-to-mars https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/20150001888 | ||