Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Currently sorted By last update ascending Sort chronologically: By last update
Kuiper Belt | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image: 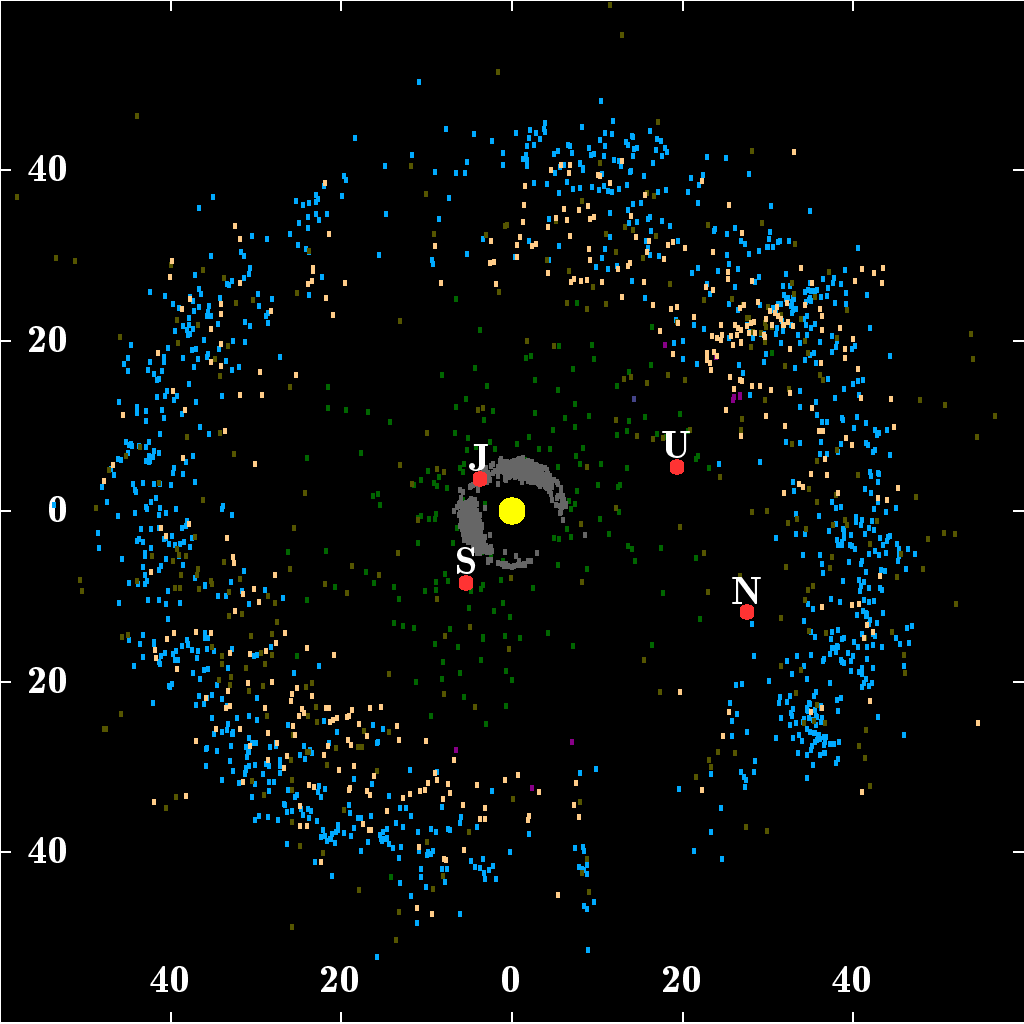 Image: Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=38097918 Short Definition:
Detailed Definition:
Etymology:
Sample Sentence(s):
French:
German:
Polish:
Swedish:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||||||||||
Launch escape system | ||
|---|---|---|
 NASA. (1965, June). Apollo Pad Abort Test #2. Retrieved from https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/17/Apollo_Pad_Abort_Test_-2.jpg Short Definition: Launch escape system (LES) or launch abort system (LAS) is a system in rockets that will separate a capsule with crew and move it away from the rocket in case of emergency such as pending rocket explosion. This is a safety measure necessary to evacuate the crew when their presence in the rocket is life-threatening. Detailed Definition: LES is attached to the capsule and usually has thrusters and a little fuel. It is just enough to propel it for a short time and send the capsule away from the rocket. It can be placed above capsule as a tower (as in Apollo) or be a part of capsule (as in Crew Dragon). LES doesn't have to be detachable from the capsule with crew, but if it is (as towers), it will be separated as soon as it runs out of fuel or when it is no longer needed. When LES finished working, capsule can land or splash with its own parachutes. Nowadays all crewed missions are equipped with some kind of launch escape system. Etymology: Launch – from Old French lancier– to fling, hurl, throw, castEscape – Old French eschaper– free oneself from confinementSystem – from Late Latin or Greek systema– an arrangement, organized whole, a whole compounded of parts Sample Sentences: The launch escape system provided a critical safety measure for astronauts in case of a rocket malfunction. Translations: French: Tour de sauvetageGerman: Rettungsrakete Italian: Sistema di fuga di lancio Polish: Rakietowy System Ratunkowy Swedish: Starta utrymningssystem Russian: Система аварийного спасения Ukrainian: Система аварійного порятунĸу References: McHale, S. (2014, February). Soyuz launch escape system. Retrieved from https://web.archive.org/web/20140221212224/http://suzymchale.com/ruspace/soyescape.html Clark, S. (2010, February). Orbital sees bright future for Orion launch abort system. Retrieved from https://spaceflightnow.com/news/n1002/18orionlas/ | ||
Light Pollution | |||
|---|---|---|---|
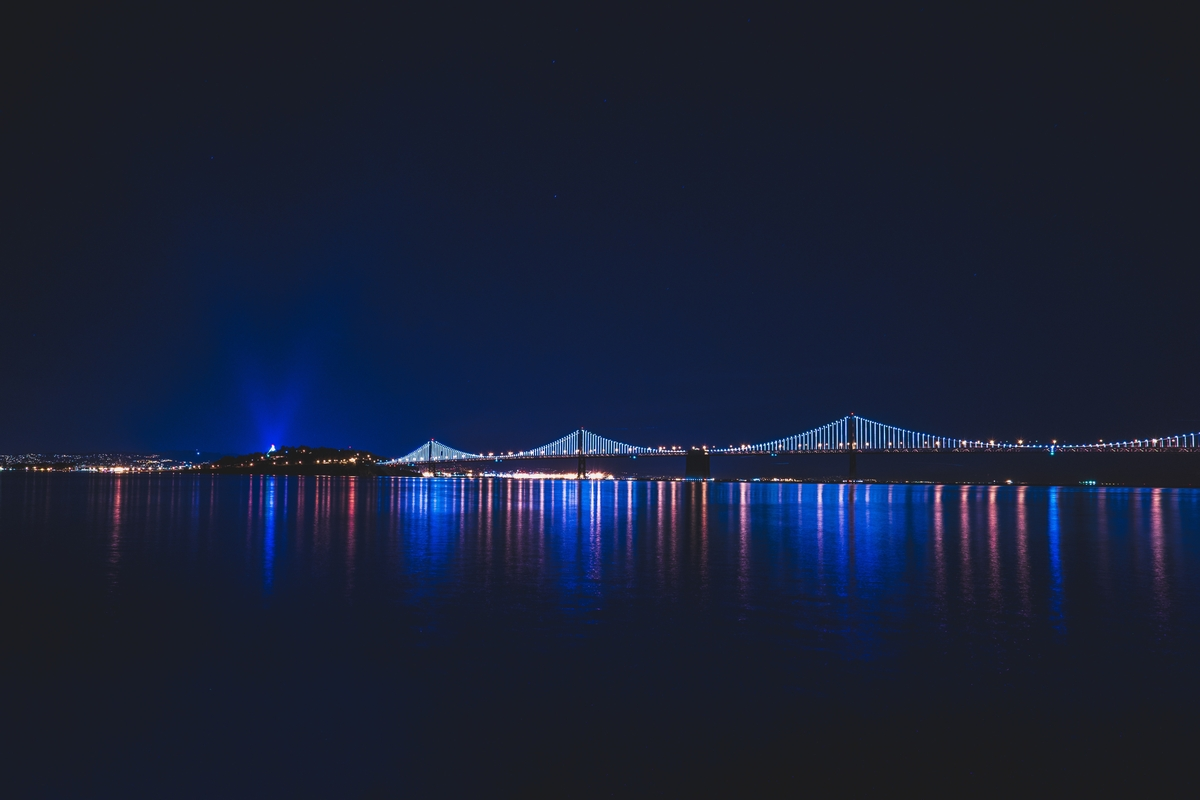 Source: Law, L. (2015, February 25). Night sky with light pollution from Coachella Valley. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/115357548@N08/16026201013 Short Definition: Light pollution is the effect of excessive or poor use of artificial outdoor light sources. There are several negative impacts from it: it disrupts both the human sleep and natural patterns of wildlife, it is a factor in the increase in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, and obscures the celestial bodies in the night sky. Detailed Definition: Light pollution, also referred to as luminous pollution, is the negative consequence of excess of artificial light and its misuse. There are several major repercussions to the increasing amounts of light in the night sky, such as sky glow, disruption of natural body rhythms in both human and animals, and the obscured ability of celestial object observation. The sky glow is the over presence of artificial light in densely populated areas after sunset, which results in disruptions of melatonin hormone in humans, causing sleep deprivation, fatigue, headaches, stress, and anxiety. Studies indicate a connection between the low melatonin levels and cancer. Light pollution also impacts the behaviour of animals, such as migration patterns, wake-sleep habits and habitat formation. Sky glow impairs the research of the night sky, obscuring stars and other celestial bodies. Etymology: "light" - Old English leht, West Saxon leoht, German Licht - brightness, radiant energy, that which makes things visible "pollution" - Late Latin pollutionem, Latin polluere - defilement, to soil, defile, contaminate Sample Sentence(s): "Light pollution disrupts astronomers in their study of space." "It is increasingly difficult to appreciate the beauty of the evening sky, as the light pollution obscures the visibility of stars." Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Pollution lumineuse German: Lichtverschmutzung Polish: Zanieczyszczenie światłem Swedish: Ljusförorening Links to Videos/Articles: https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/light-pollution https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/mapmaker-light-pollution https://planetfacts.org/light-pollution/ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UdIGJNVUwmE | |||
Liu Yang | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short
Definition
Soon
after, on June 16, 2012, Liu Yang launched into space, accompanied by commander
Jing Haipeng and operator Liu Wang.
This milestone
mission marked China's first successful crewed space docking with the Tiangong
1 space module. During the mission, Liu Yang took charge of conducting medical
experiments. Etymology Sample Sentence(s) "[…] having Liu Yang on board will not only help the country's aspiring space program test equipment designed for women in preparation for the building of an orbiting space station, but it will also expand the social impact of human space missions." Wolchover, N. (2012, June 15). Who Is China’s First Female Astronaut? livescience.com. https://www.livescience.com/34002-china-female-astronaut.html
Links to Videos/Articles:
● Wolchover, N. (2012, June 15). Who Is China’s First Female Astronaut? livescience.com. https://www.livescience.com/34002-china-female-astronaut.html ● China’s first female astronaut ready for new space mission. (2022, June 4). CGTN. https://news.cgtn.com/news/2022-06-04/China-s-first-female-astronaut-ready-for-new-space-mission-1aAKaX706GI/index.html ● Gregersen, E. (Invalid Date). Liu Yang. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/biography/Liu-Yang ●
CGTN. (2022, September 6). Liu Yang: No preferential treatment for being
a woman in space [Video]. YouTube.
| ||
Low Earth orbit | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Orbitalaltitudes.svg Short Definition: The Low Earth Orbit (in short, LEO) is an orbit that is relatively low compared to typical space orbits. An object orbiting Earth above 100 km and below 2000 km can be described as orbiting on Low Earth Orbit. In terms of orbiting time, a low Earth orbit have an orbiting period of 128 minutes or less. Low Earth Orbit is often used as temporary orbit for spacecrafts travelling further into space. Detailed Definition: The Low Earth Orbit (LEO in short) is a zone around Earth from a 100 km (Kármán line) to about 2000 km above Earth's surface. Due to orbits shape varying from circles to ellipses, better description is done using time. A body orbiting at the Low Earth Orbit has an orbiting time around 128 minutes or less. The pull of gravity in the LEO is only slightly less than on the Earth's surface, and the orbiting body still encounters atmospheric drag from present gas particles. Due to this, the LEO is often used as a transitive stage for spaceships traveling further into space, as the mean orbital velocity needed to maintain a stable low Earth orbit is about 7.8 km/s, rather than being used as a stable orbit due to constant need of course correction. The most famous spacecraft orbiting in the LEO is the International Space Station, orbiting at around 400 km above Earth’s surface. Etymology: Low - From Middle English lowe, lohe, lāh, from Old Norse lágr (“low”) Sample Sentence(s): "The International Space Station is the largest modular space station currently in the Low Earth Orbit." Translations: French: Orbite terrestre basse German: Niedrige Erdumlaufbahn Polish: Niska orbita okołoziemska Swedish: Låg omloppsbana Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2020/03/Low_Earth_orbit | |||
Meridian | ||
|---|---|---|
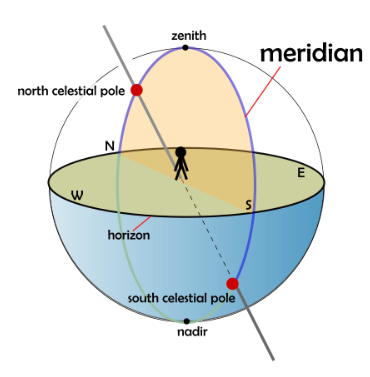 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Meridian_(astronomy) Short definition: An imaginary line in the sky running from due north to due south through the observer's location and the zenith.Detailed Definition:
In astronomy, a meridian is an imaginary line in the sky that runs from due north to due south, passing through the observer's location and the zenith. The zenith is the point in the sky that is directly overhead. The meridian is used to measure the altitude of objects in the sky, as well as their right ascension and declination. The meridian also marks the boundary between the eastern and western halves of the sky, with objects east of the meridian being in the morning sky and those west of the meridian being in the evening sky. Etymology: Latin - medius ‘middle’ + dies ‘day’. Sample Sentence(s):
"The planet Venus will cross the meridian at 8:00 pm tonight." "The altitude of the North Star above the horizon can be measured relative to the observer's meridian." "The meridian passage of a celestial object is the time it crosses the observer's meridian." Translations: French: Le Meridien German: Höhepunkt Polish: Południk Links to videos/articles: https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/m/meridian https://www.britannica.com/science/celestial-meridian | ||
Meteorite | ||
|---|---|---|
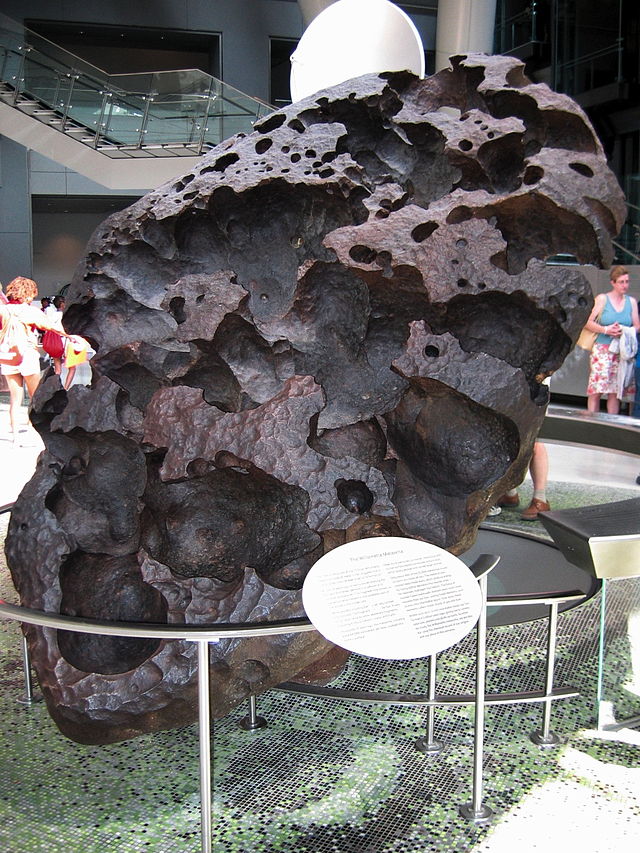 Short definition: A meteorite is a piece of rock or metal originating from space that has landed on the Earth’s surface. Before a meteorite enters the Earth’s atmosphere, it’s called a meteoroid. The phenomenon of a meteoroid burning up and leaving a glowing trail behind is called a meteor. Detailed definition: A meteorite is a piece of debris, usually of a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that has survived its passage through the Earth’s atmosphere and reached the surface. Meteorites vary greatly in size: some, that are called micrometeorites, are less than 1mm in size, and very few are large enough to leave an impact crater. The biggest meteorite ever found - the Hoba meteorite in Namibia - weighs about 60 tons. Most meteorites are stony, and only about 6% of meteorites are iron meteorites or a mix of stone and metal. Etymology: meteor (from Greek ta meteōra"the celestial phenomena, things in heaven above") + -ite Sample sentence(s): Commonly, chondrules can make up 75% of the volume of the meteorites in which they occur. (Source: Cambridge English Corpus | Cambridge University Press | ELT. (n.d.). Cambridge.es. https://www.cambridge.es/en/) Translations: French: météorite German: Meteorit Italian: meteorite Polish: Meteoryt Swedish: Meteorit Links to Videos/Articles: Alexander, C. M., & Wetherill, G. W. (2023, May 11). Meteorite | Definition, Types, Identification, & Facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/meteorite meteorite. (n.d.). https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/meteorite/ Science with Thomas Stevenson. (2022, August 9). What is a Meteorite? [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/Cv82yiksbl8 | ||
Meteoroid | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short definition: A meteoroid is a small rocky or metallic body in space that has not yet entered the Earth's atmosphere. When a meteoroid enters the Earth’s atmosphere at a high speed and burns up, it leaves a glowing trail, which is called a meteor. Detailed definition: Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than meteoroids are called micrometeoroids or space dust. Most meteoroids are fragments from comets or asteroids, containing extraterrestrial nickel and iron. Etymology: Meteoroid comes from meteor + -oid. -oid is a suffix coming from Ancient Greek εἶδος (eîdos, “form, likeness”), which means “resembling; having the likeness of”. Sample sentence(s): It was found that meteoroids from cometary sources were typically of porous, aggregate compositions with relatively low densities. (Source: Cambridge English Corpus | Cambridge University Press | ELT. (n.d.). https://www.cambridge.es/en/) Translations: French: Météoroïde German: Meteoroid Italian: Meteoroide Polish: Meteoroid Swedish: Meteoroid Links to Videos/Articles:Atkinson, N. (2018, April 8). What Is The Difference Between Asteroids and Meteorites? - Universe Today. Universe Today. https://www.universetoday.com/36398/what-is-the-difference-between-asteroids-and-meteorites/ Meteors & Meteorites. (n.d.). NASA Solar System Exploration. https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/asteroids-comets-and-meteors/meteors-and-meteorites/overview/?page=0&per_page=40&order=id+asc&search=&condition_1=meteor_shower%3Abody_type Encyclopaedia Britannica. (2019, January 2). DEMYSTIFIED: What’s the difference — meteoroids, meteors, & meteorites | Encyclopaedia Britannica [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/tXfjUxdzqBY | ||
Milky Way | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Milchstraße#/media/Datei: Artist's_impression_of_the_Milky_Way_(updated_-_annotated).jpg 5th November 2021 Definition:A large spiral galaxy consisting of several hundred billion stars, dust and gas.The galaxy that includes our solar system, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. Etymology:The term Milky Way is a translation of the Latin via lactea, from the Greek γαλακτικός κύκλος (galaktikos kýklos), meaning "milky circle”. Translations:
| |||

