Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Currently sorted By last update ascending Sort chronologically: By last update
Falcon 9 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source : SpaceX (2016, January 16). Falcon 9 vertical at Vandenberg Air Force Base. wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=64851825 Definition:Falcon 9 is the world's first orbital class reusable rocket, created and manufactured by SpaceX. It is a reusable, two-stage rocket capable of transporting both people and payloads into Earth's orbit and beyond. Reusability allows to reuse the most expensive parts of the rocket, which diminishes the cost of space access. The standard parameters of the rocket are: Height - 70 m / 229.6 ft Diameter - 3.7 m / 12 ft Mass - 549,054 kg / 1,207,920 lb The engine used in production of Falcon 9 is the Merlin, which uses grade kerosene (RP-1) and liquid oxygen as rocket propellants in a gas-generator power cycle. The Merlin engine was originally designed for recovery and reuse. Falcon 9 has already been used in numerous missions or tests (Crew-1 Mission, Crew-2 Mission, Crew-3 Mission, DART Mission) and is planned to be launched in the next ones (for example Polaris Dawn in the last quarter of 2022). Sample Sentence(s):"This rocket is the Falcon 9 that successfully reached orbit after 9 minutes and 38 seconds on its maiden test flight." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.spacex.com/updates/ | |||
Absolute Magnitude | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio:
Short Definition:
Absolute magnitude is the measurement of the brightness of celestial bodies using inverse logarithmic calculations in astronomical calculations and expressed as a mathematical value. This process involves mathematically expressing their luminosity, as a hypothesis, by placing objects at an equal distance from the observer (10 parsecs that equals to 32.6 light years).
Detailed Definition:
Absolute magnitude is also called absolute visual magnitude, which is a hypothesis that predicts the mathematical calculation of the luminosity of different celestial bodies, taking into account fixed distances, and comparing the luminosities of these objects. The mathematical formula used to calculate this luminosity is as follows; Mv: Absolute magnitude m: Apparent magnitude d: Distance in 10 parsecs Mv = m – 2.5 log [d/10]² The apparent magnitude here, on an inverse scale, indicates how bright celestial objects appear to our eyes. Because it's an inverted scale, high numbers indicate dim objects and low numbers indicate bright objects. The brightest object known and measured on this scale has a value of -10, while the star Sirius has a luminosity of 1.4, and our sun has a luminosity of 4.8.
Etymology:
Absolute -from old Latin (absolūtus) (Absolute – Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/absolute) Magnitude -from old Latin (Magnus) (Magnitude – Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/magnitude)
Sample Sentence(s):
‘’When comet 289P/Blanpain was discovered in 1819, its absolute magnitude was estimated as {\displaystyle M_{1}=8.5}{\displaystyle M_{1}=8.5}’’ (Wikipedia contributors. (2023, January 13). Absolute magnitude. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Absolute_magnitude) ‘’Colour–magnitude diagram, in astronomy, graph showing the relation between the absolute magnitudes (brightnesses) of stars and their colours, which are closely related to their temperatures and spectral types.’’ (The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (1998, July 20). Colour–magnitude diagram | astronomy. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/colour-magnitude-diagram) Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages:
French:
Magnitude absolue German:
Absolute Helligkeit Polish:
wielkość absolutna Swedish:
Absolut magnitud Turkish: Mutlak Kadir
Links to Videos/Articles:
Absolute magnitude | astronomy. (n.d.-a). Encyclopaedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/absolute-magnitude Absolute Magnitude | COSMOS. (n.d.-a). https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/a/Absolute+Magnitude Apparent and Absolute Magnitudes. (n.d.-b). https://www.phys.ksu.edu/personal/wysin/astro/magnitudes.html Michel van Biezen. (2014, April 9). Astronomy - Measuring Distance, Size, and Luminosity (18 of 30) Absolute Magnitude [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yfsUhOPCMaM | |||
Galaxy cluster | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short Definition
Sample Sentence(s) Galaxy clusters can consist of thousands of galaxies. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: amas de galaxies German: Galaxienhaufen Italian: mmasso di galassie Polish: gromada galaktyk Swedish: galaxhop Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Geosynchronous orbit | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Projection of the path traced by geosynchronous satellites of different inclinations. Source: Wikipedia Short Definition: | |||
Great Red Spot | |||
|---|---|---|---|
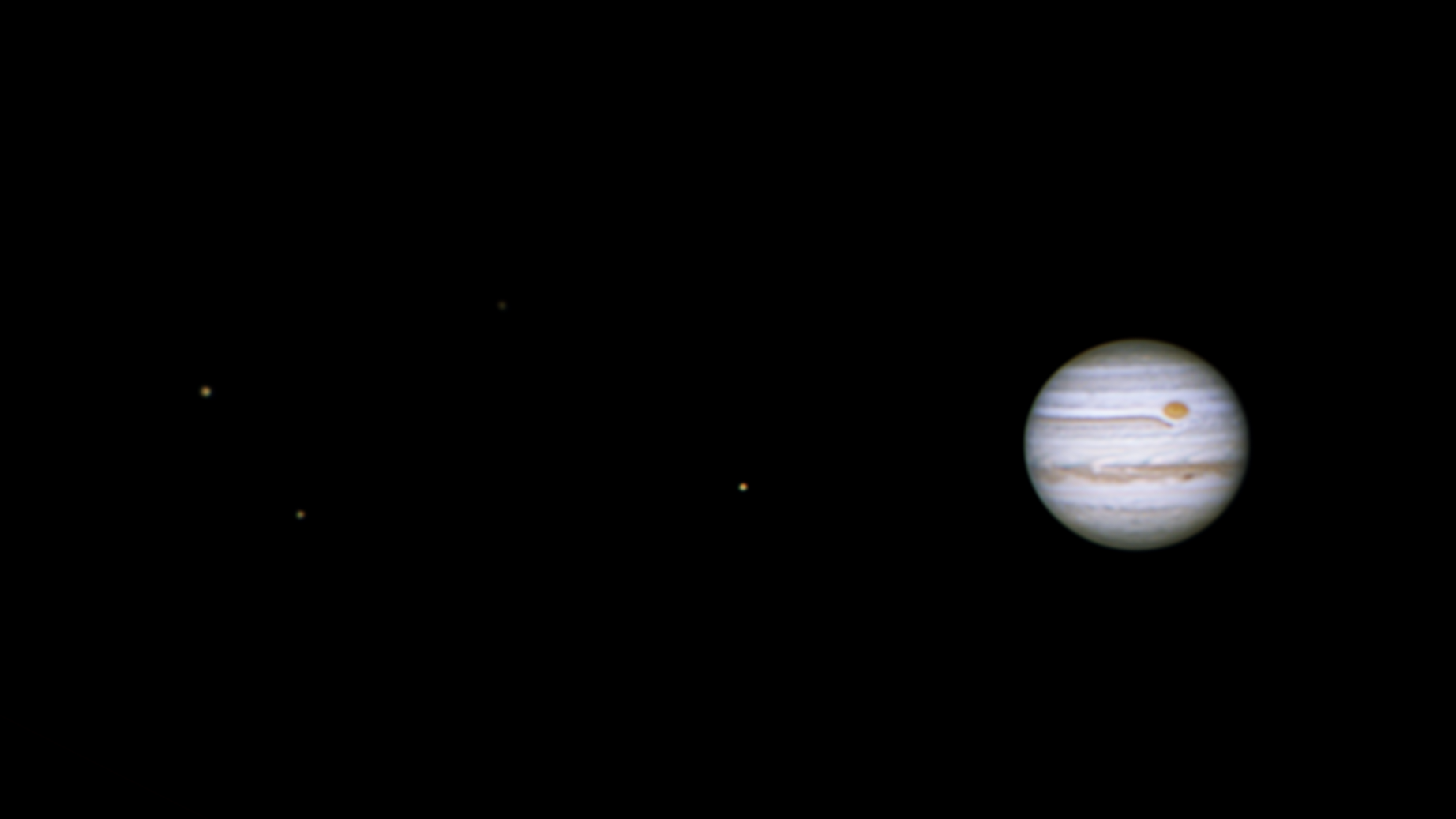 Sources: Stewart, P. (2018, June 8). Jupiter. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/106648653@N05/42658035711 Definition:A persistent large anticyclonic storm in the atmosphere of Jupiter, 22° south from its equator, which has been continuously observed since the 19th century.As of 2021, the Great Red Spot is reported to be about 10,000 miles across and 300 miles deep into the atmosphere of Jupiter. However, according to NASA observations, it is shrinking and becoming taller, and it is not yet clear whether the Great Red Spot will stabilize or disappear completely. Translation:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JDi4IdtvDVE | |||
Heavy Element | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Image/Video/Audio: Image: Periodical Table Image/Video/Audio Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ionization_energy_periodic_table.svg
Short Definition:
Heavy elements are the general name for elements containing atomic numbers greater than 92. Above these, elements with atomic numbers 112 and above are called superheavy elements. The state that creates the atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of the element. Detailed Definition:
Heavy elements, which are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of the element (this called atomic number) are elements with atomic number greater than 92. One row above them there is superheavy elements with atomic numbers greater than 112. The first artificially produced heavy and superheavy elements were first produced during the Cyclotron experiments. One of the most important issues about heavy elements is the concept of 'island of stability'. This concept refers to the region in the table of nucleides where elements with half-lives longer than some other super heavy elements are found. However, it should be noted that we are ona narrow time scale, from minutes to micro/nano seconds at most. The term was first coined in 1998 with the discovery of the super heavy element 114 (Flerovium).
Etymology:
Heavy – From Proto Germanic (hafiga) Element – From Latin (elementum) (origin and meaning of heavy. (n.d.). Etymonline. https://www.etymonline.com/word/heavy) (element - Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/element)
Sample Sentence(s):
‘’The heaviest element known at the end of the 19th century was uranium, with an atomic mass of approximately 240 (now known to be 238) amu.’’ (Wikipedia contributors. (2022, December 31). Superheavy element. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Superheavy_element) ‘’Although the scientific community has assigned these heaviest elements to their own spots on the periodic table, there is still a lot we don’t know about them.’’ (Exploring the superheavy elements at the end of the periodic table. (n.d.). cen.acs.org.)
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French:
Élément lourd German:
Schweres element Polish:
Ciężki pierwiastek Swedish:
Tungt element Turkish: Ağır Element
Links to Videos/Articles:
Cookie Absent. (n.d.). https://physicstoday.scitation.org/action/cookieAbsent Discovery of Elements 113 and 115. (n.d.). https://pls.llnl.gov/research-and-development/nuclear-science/project-highlights/livermorium/elements-113-and-115 Seeker. (2019, November 10). This Superheavy Atom Factory Is Pushing the Limits of the Periodic Table [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kg0AN8bZ4us Wikipedia contributors. (2022, December 31). Superheavy element. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Superheavy_element | |||
Hubble Space Telescope | ||
|---|---|---|
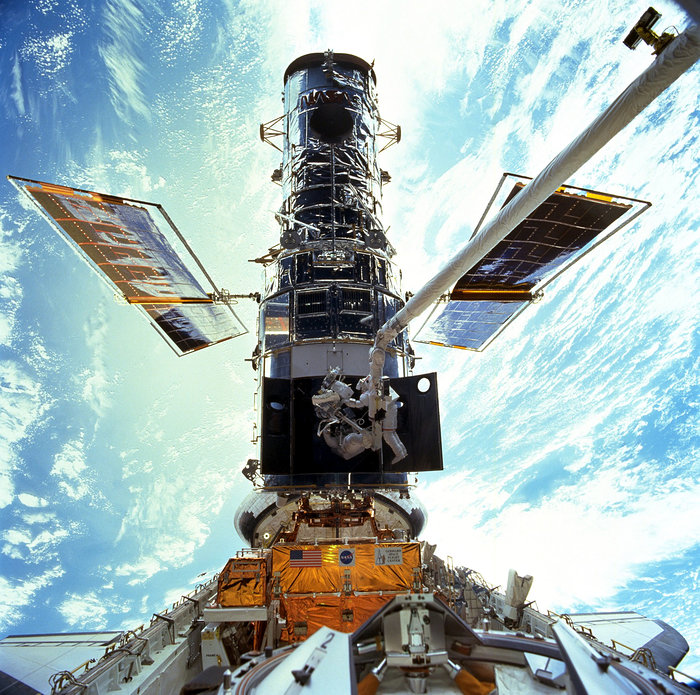 Short Definition
Sample Sentence(s):
Hubble
Space Telescope helped researchers make new discoveries.
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French: Hubble German: Hubble-Weltraumteleskop Italian: telescopio spaziale Hubble Polish: Kosmiczny Teleskop Hubble’a Swedish: Hubbleteleskopet Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
ClearSpace-1 | ||
|---|---|---|
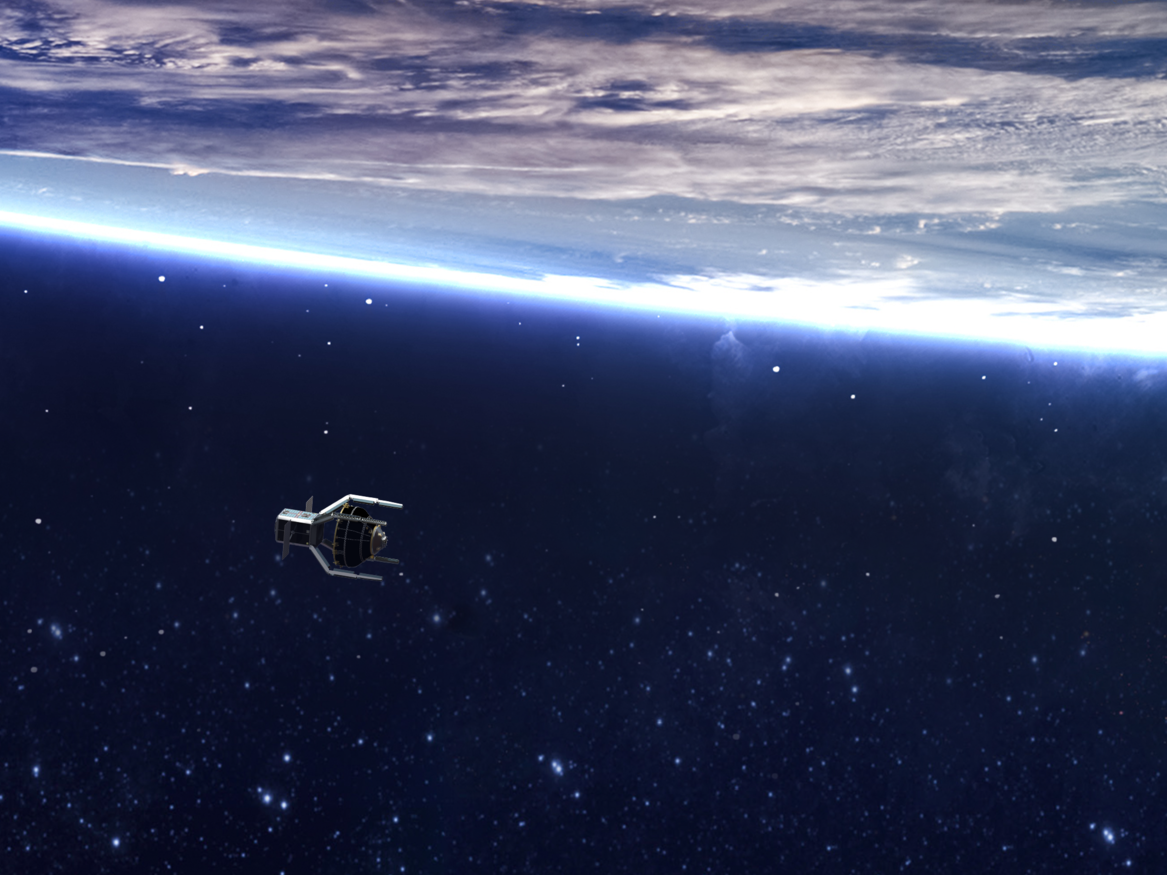 Source: ESA - ESA commissions world’s first space debris removal Definition:ClearSpace-1 is a mission targeting the removal of the Vega Secondary Payload Adapter (Vega) which is planned for launch in 2025. The mission is brought forward as a service contract with a startup-led commercial consortium, to help establish a new market for in-orbit servicing, as well as debris removal. The ClearSpace-1 ‘chaser’ will be launched into a lower 500-km orbit for commissioning and critical tests before being raised to the target orbit for rendezvous and capture using a quartet of robotic arms under ESA supervision. The combined chaser plus Vespa will then be deorbited to burn up in the atmosphere. Etymology:Sample Sentences(s):Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:ESA - ESA commissions world’s first space debris earth observation for sustainable development (esa.int) removal | ||
Copernicus Programme | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Definition:A European Earth observation programme aiming at monitoring land, atmosphere and the marine environment, supporting emergency management, ensuring civil security and mitigating the consequences of climate change. The programme was officially established in 2014 by the European Commission and the European Space Agency, serving as a successor of the project GMES (Global Monitoring of Environmental Security), which has existed since 1998. Copernicus Programme utilizes the Sentinel missions for surveillance and observation of land, ocean and atmosphere, as well as a range of contributing missions organized by various countries.Etymology:The programme is named after Nicolaus Copernicus, who was a Renaissance scientist and the author of the heliocentric model of the Universe. Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:
https://www.esa.int/Applications/Observing_the_Earth/Copernicus/Europe_s_Copernicus_programme https://www.copernicus.eu/en/copernicus-services | |||

