Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
E |
|---|
ExoMars Programme | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 DefinitionA programme created in cooperation between ESA and Roscosmos, which is trying to find signs of biological processes on Mars indicating whether life has ever existed on that planet. The programme includes two missions:
The Trace Gas Orbiter’s task is to look for trace atmospheric gases, including methane, which would indicate the presence of biological processes, whereas the Rosalind Franklin rover is supposed to look for evidence of life on the surface and underground. Etymology:“Exo” in ExoMars refers to “exobiology”, a branch of sciences investigating life beyond Earth. A rover involved in this mission is named after Rosalind Franklin, who was an English chemist known in particular for her contribution to DNA research. The platform Kazachok is named after a Russian folk dance. Sources:https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Exploration/ExoMars More about the mission:https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Exploration/ExoMars/ExoMars_Factsheet | |||
Expansion of the universe | |||
|---|---|---|---|
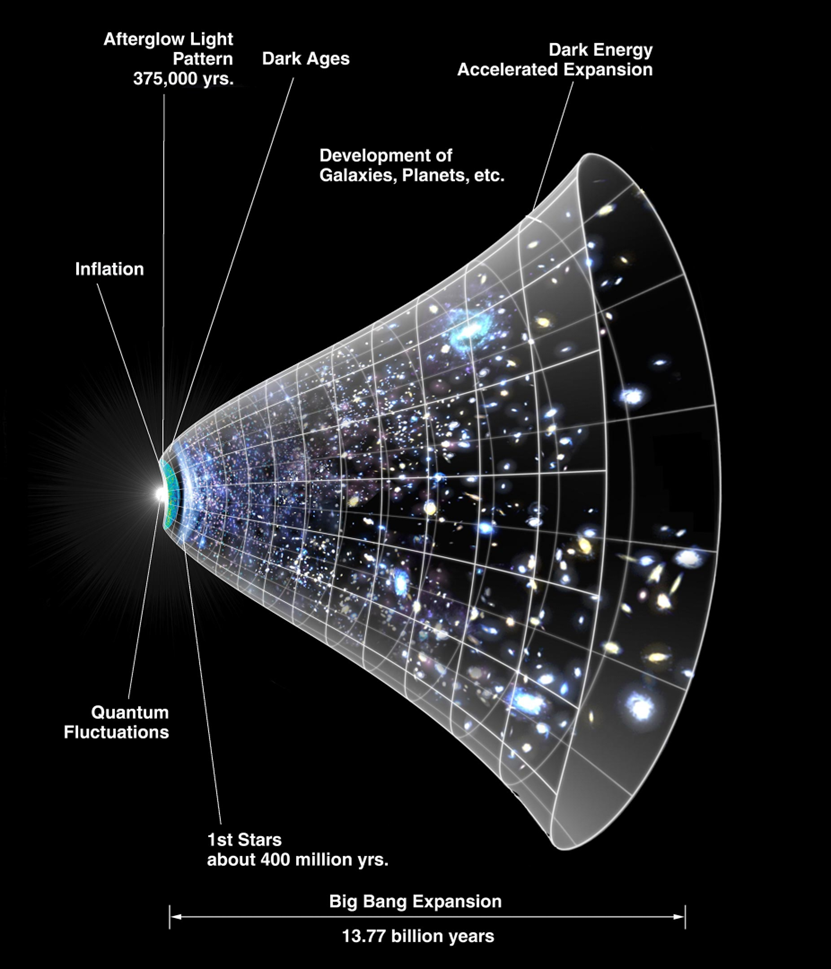 Image/Video/Audio Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Expansion_of_the_universe#/media/File:CMB_Timeline300_no_WMAP.jpg
Short Definition: The expansion of the universe is a phenomenon, which describes the
inherent property of the universe, where two galaxies that are gravitationally unbound
tend to increase the distance to each other and the rate of expansion is even accelerating.
Far away parts of the observable universe will not be observable in the near
future, because the velocity of expansion is higher than light speed from an
outside perspective.
Detailed Definition: The expansion of the universe is a phenomenon, which explains an inherent property of the universe to expand. The fact that the universe seems to expand, was first doubted because of the gravitational force and the fact that releases of energy like the big bang should normally lose power and should slow over time, but the opposite was observed. The elusive culprit was found quite fast. Dark matter is to be responsible for this phenomenon, but since we know even less about dark matter than about the expansion of the universe, details of how and why it expands are still unknown. This expansion occurs at
every location of the universe and only gravitationally bound galaxies will be
able to observe each other, because unbound galaxies will escape our observable
universe at some point. The expansion can in some way be compared to an elastic
rubber band, where the distances also increase when you stretch it, but not
literally and not on a human scale. It is more that at a scale so far zoomed
out, that the universe looks like a cosmic fluid and at this scale it is apparent
that the density is decreasing over time. There are three viable methods to
measure this expansion. One is based on redshifts, while another on the cosmic
distance ladder. Those measurements gave non-matching results, and so 2018 information
from gravitational waves made it possible to determine the rate of expansion
even more precisely.
Etymology:
Expansion à from Latin expandere à spread out Universeà from Old French univers à from Latin universumSample Sentence(s):
In a thought experiment of an ascending civilization in a faraway galaxy in the far future, they would only be able to observe their neighbouring galaxies and will think that this is all there is to the universe and all this due to an expansion of the universe. The rate of expansion of the universe is thought to be accelerating. French: Expansion de l'universGerman: Ausdehnung des Universums
Polish: Ekspansja Wszechświata Swedish: Utvidgning av universum
Links to Videos/Articles:
Expansion of the universe - Wikipedia | |||
F |
|---|
Falcon 9 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source : SpaceX (2016, January 16). Falcon 9 vertical at Vandenberg Air Force Base. wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=64851825 Definition:Falcon 9 is the world's first orbital class reusable rocket, created and manufactured by SpaceX. It is a reusable, two-stage rocket capable of transporting both people and payloads into Earth's orbit and beyond. Reusability allows to reuse the most expensive parts of the rocket, which diminishes the cost of space access. The standard parameters of the rocket are: Height - 70 m / 229.6 ft Diameter - 3.7 m / 12 ft Mass - 549,054 kg / 1,207,920 lb The engine used in production of Falcon 9 is the Merlin, which uses grade kerosene (RP-1) and liquid oxygen as rocket propellants in a gas-generator power cycle. The Merlin engine was originally designed for recovery and reuse. Falcon 9 has already been used in numerous missions or tests (Crew-1 Mission, Crew-2 Mission, Crew-3 Mission, DART Mission) and is planned to be launched in the next ones (for example Polaris Dawn in the last quarter of 2022). Sample Sentence(s):"This rocket is the Falcon 9 that successfully reached orbit after 9 minutes and 38 seconds on its maiden test flight." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.spacex.com/updates/ | |||
Fluid shift in the human body | ||
|---|---|---|
 Image Source: S, M. (2023, June 01). Illustration of fluid distribution. self. self-made The fluid shift in the body is an adaption to the reduced gravitation force in space. This results in a shift of the body fluids from the lower body to the upper body. Detailed Definition: When a human body is placed on the earth surface, it has a hydrostatic (gravitational) blood pressure gradient and every body region has a different arterial pressure. In the reduced gravity of space, the hydrostatic pressure in the arteries and veins is altered to a homogeneous arterial pressure in all regions (which is the original arterial pressure of the hearth), which results in the shifted fluid distribution through the body. The human body reduces the volume of the total fluid and after the space resident, the fluid is shifted because of the returned gravity force. This phenomenon can cause several issues like cardiac arrhytmia, muscular athropy and visual problems (because the globe is flattened, the blood flow is changed slightly and the diamteter of the optical nerve can increase). Etymology: fluid - Latin fluidus ("fluid, flowing, moist") shift - Proto-Germanic skiftan (" to divide, change, seperate") Sample sentence(s): A medical
effect of a space flight may be a fluid shift. Nasa is studying
the effect of the fluid shift and how it affects changes in vision. Translation: French: déplacement du fluide German: Flüssigkeitsverschiebung Polish: Przemieszczenie płynów w ludzkim organizmie Swedish: vätskeförskjutning Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nasa.gov/content/fluid-shifts-study-advances-journey-to-mars https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/20150001888 | ||
G |
|---|
Galactic disk | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short Definition: A galactic disc is a component of disc galaxies. An example are spiral galaxies and the Milky Way. The set-up of Galactic discs are a stellar component (these encompass the majority of the galaxy's stars) as well as a gaseous component (simply largely composed of cold gas and dust). Detailed Definition: The stellar disc of our Galaxy is divided into two components because the vertical density profile determined from star counts can be explained by a superposition of two exponentials, but not by a single exponential. (Gilmore & Reid, 1983). Further study found a thick-disc component with high-velocity dispersion, significant enrichment, and ancient age. Many writers believe that the thick disc was a relic of a turbulent period in Galactic history when the thick disc developed from accreted satellites or a thin disc heated the substance at high temperatures by one or more merger events (for a discussion, see Reddy Lambert, and Allende Prieto 2006). This structure was first observed in external edge-on galaxies and later proposed as a distinct part of the Milky Way in a 1983 article by Gilmore and Reid. It is separate from both the thin disk and the halo. The thick disk is a structural component of approximately two-thirds of all disk galaxies, including the Milky Way. It was initially detected in external edge-on galaxies. Soon later, in the 1983 article by Gilmore and Reid, it was proposed as a galactic structure in the Milky Way, distinct from the thin disk and the halo.Etymology The term galaxy was derived from the Greek word galaxas (kklos) (o), which means "milky (circle)," and was called by its appearance in the sky as a milky ring of light. Sample Sentence(s): 1. It would take two billion years for the changes caused by a Galactic Battle to be realized. 2. It glows on the galactic scale. 3. The galactic disk is the Milky Way's disk component. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages Polish: dysk galaktyczny French: disque galactique German: galaktische Scheibe Italian: disco galattico Swedish: galaktisk skiva | ||
Galaxy | ||
|---|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio Source: Short Definition: Detailed Definition: Etymology: Sample Sentence(s): Translations: German: Polish: Swedish: Spanish: Links to Videos/Articles: | ||
Galaxy cluster | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short Definition
Sample Sentence(s) Galaxy clusters can consist of thousands of galaxies. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: amas de galaxies German: Galaxienhaufen Italian: mmasso di galassie Polish: gromada galaktyk Swedish: galaxhop Links to Videos/Articles:
| ||
Galaxy Evolution | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Picture: Model of Evolution of Galaxy Image/Video/Audio Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/a3/Evolution_in_slow_motion.jpg Short Definition: Galaxy evolution or evolution of galaxy is a term that we have used for understanding the formation process and changes of galaxies since the beginning that made up the known universe. The term galaxy evolution also represents the models we form about the universe filled by the observed photons and the expansion since the big bang. At this point, the sizes, shapes and contents of all galaxies give us an idea about the formation and evolution of the universe. Detailed Definition: Galaxy evolution is a term used to understand the structure of the universe and the ongoing formation processes by comparing the morphology, brightness and content of galaxies with each other. The term galaxy evolution here studies galaxies in four main groups. These are Elliptical Galaxies, Lenticular Galaxies, Spiral Galaxies, and Irregular galaxies. The evolution process of galaxies in these four groups is examined under three main headings. These are Passive evolution (The state where the galaxy does not interact with any other galaxy [interactions or mergers] and thus does not produce star formations.), Interactions and Mergers (The state in which galaxies are affected by interacting with other galaxies), Secular Evolution (Situation in which processes by internal changes of galaxies affect their colour, luminosity and shape.) Etymology: From Latin ‘Galaxias’ and From Latin ‘ēvolūtiōnis’ (Unrolling/Unfolding) Sample Sentence(s): ‘’Radio telescopes have played a pivotal role in the understanding of galactic evolution.’’ (Galaxy Evolution, Cosmology and Dark Energy. (2018, May 30). Public Website. https://www.skatelescope.org/galaxyevolution/) ‘’Understanding how black holes shape their host galaxies is part of the study of galactic structure and evolution.’’ (Galaxy Formation and Evolution | Center for Astrophysics. (n.d.). https://www.cfa.harvard.edu/research/topic/galaxy-formation-and-evolution) Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French: Évolution de la galaxie German: Galaxienentwicklung Polish: Ewolucja galaktyki Swedish: Utveckling av galaxer Turkish: Galaksi Evrimi Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.britannica.com/science/galaxy/Evolution-of-galaxies-and-quasars https://www.jwst.nasa.gov/content/science/galaxies.html https://www.skatelescope.org/galaxyevolution/ https://www.cfa.harvard.edu/research/topic/galaxy-formation-and-evolution https://sites.astro.caltech.edu/~george/ay20/eaa-galevol.pdf https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/E/evolution+of+galaxies https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rdd9KAUcvgQ&ab_channel=TakayukiSaitoh https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_WtvU4Xn2UE&ab_channel=CaltechAstro | |||
Galaxy Merger | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: https://www.eso.org/public/images/1016-galaxy_formation_merger/ Short Definition: A galaxy merger is the phenomenon of two or more galaxies colliding with each other, resulting in the formation of a new, enlarged galaxy. Detailed Definition: A galaxy merger occurs when two or more galaxies collide with each other, leading to the creation of a larger galaxy. Galaxy mergers are the most violent type of galaxy interaction. When a collision of several galaxies occurs, the stars and dark matter in each of them become affected, which has influence on both the orbits of the stars and the shape of the newly formed galaxy. During a merger, an increase in star formation can be observed, as the friction interaction of gas and dust contributes to the raise of energy in the resulting system. Galaxy mergers provide astronomers with the merger rate, which is a fundamental measurement of galaxy evolution and sheds some light on how galaxies have increased in size over time. Etymology: merge - Latin mergere"to dip, dip in, immerse, plunge" galaxy - Late Latin galaxias - Greek galaxías Sample Sentence(s): Galaxy mergers can be simulated in computers, to learn more about galaxy formation. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Fusion de galaxies German: Galaxienfusion Polish: Fuzja galaktyk, połączenie się galaktyk Swedish: Galaxsammanslagning Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.eso.org/public/images/1016-galaxy_formation_merger/ https://www.thoughtco.com/interacting-galaxies-have-interesting-results-3072045 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4disyKG7XtU | |||
