Dictionary of Space Concepts
Welcome to the Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space", students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
N |
|---|
National Aeronautics and Space Administration | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source: https://www.nasa.gov/audience/forstudents/5-8/features/symbols-of-nasa.html Definition:National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency responsible for America’s civil space program, which aims to research areas of space for the benefit of humanity. National Aeronautics and Space Administration is a global leader in space exploration. It has 20 centres and facilities across the United States. Basic activities of the agency are studying the Earth, climate, Sun, Solar System and beyond. It conducts research (missions), testing and development to advance and develop space technologies. NASA's work also includes cooperation with U.S. industry, international partners, as well as with academia. Sample Sentence(s):National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) unveiled its newest supercomputer, the Columbia, which is powered by 10,240 Intel Itanium 2 processors." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.nasa.gov/ | |||
Nebula | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source : Kirk, A. (2015, April 25). The Mighty Orion Nebula from New Zealand. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/67481624@N05/17243621226 Short Definition: Any kind of giant cloud that includes miscellaneous gas and dust; especially hydrogen, cosmic dust, and helium located in outer space. Detailed Definition: As the basic components of galaxies, nebulae were stars before they formed. During the formation phase of these stars, the gases released into space initiate a fusion reaction with hydrogen atoms and form the foundations of a new star. Thus, the universe continues to expand. Etymology: Ancient Greek (νεφέλη - nephélē): Cloud Sample Sentences: 'Today the term nebula generally refers exclusively to the interstellar medium.' 'A nebula that is visible to the human eye from Earth would appear larger, but no brighter, from close by.' Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French: Nébuleuse Italian: Nebulosa German: Nebel Polish: Mgławica Turkish: Nebula Links to Videos/Articles: https://spacecenter.org/what-is-a-nebula/ https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/nebula/en/ https://www.space.com/nebula-definition-types https://www.britannica.com/science/nebula | |||
Neil Armstrong | ||
|---|---|---|
 Short
Definition
After earning a degree in aeronautical engineering from Purdue University in 1955, Armstrong began working as a civilian research pilot for the organization that would later evolve into the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). In 1962, Armstrong joined NASA's space program and 7 years later, on July 20, 1969, he made history by stepping onto the surface of the moon, saying his iconic words, "That's one small step for [a] man, one giant leap for mankind." Following this achievement, Armstrong resigned from NASA in 1971. He then dedicated himself to teaching in the Department of Aerospace Engineering at the University of Cincinnati until 1979. He passed away in 2012 at the age of 82.
Etymology Sample Sentence(s) "Neil and Buzz's footprints will be on the Moon for millions of years, because there is no wind to blow them away.” Who was Neil Armstrong? (2022). BBC Bitesize. https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/zhpchbk/articles/z4w3mfr
Links to Videos/Articles:
● Who was Neil Armstrong? (2022). BBC Bitesize. https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/zhpchbk/articles/z4w3mfr ● Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia (Invalid Date). Neil Armstrong. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/biography/Neil-Armstrong ●
NTD. (2012, August 25). Neil Armstrong - First Moon Landing 1969
[Video]. YouTube. ● Banijay History. (2018, October 10). First Man on the Moon: The Real Neil Armstrong | History Documentary | Reel Truth History [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fXTML_0DBDM | ||
NEO (Near-Earth Object) | ||
|---|---|---|
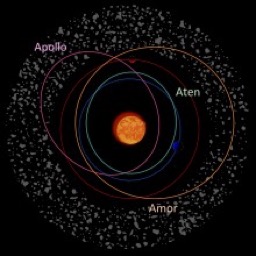 Source: Video from NASA explaining NEO: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r-OCcFnp2RA Short Definition:NEO, or near-Earth object, is a celestial body which is in the size range of meters to tens of kilometres, that orbits the sun and approaches the earth within the distance of 1.3 AU (astronomical units). Detailed Definition:Among the 600,000 known asteroids, only 20,000 of them are NEOs. To be classified as such, the object must be natural and cannot be manmade. Some of them could potentially hit the earth and for this reason, some organisation keep track of them everyday. Historically speaking, NEOs have had an impact of the earths geological and biological history. Most of the NEOs are Apollo asteroids (55.4%), meaning that they come from the Apollo asteroid group. The second most common are Amor asteroids (36.4%), and third most common are Aten asteroids (7.7%). Etymology:Acronym of "near-Earth object." Sample Sentence:An astronomer would for example say during a lecture: “The Amor asteroid, 433 Eros, was the first NEO discovered in 1898, by D. Witt of Berlin, Germany, using a photographic plate to record its position.” Translations:
Links to Articles/Videos: | ||
Neptune | ||
|---|---|---|
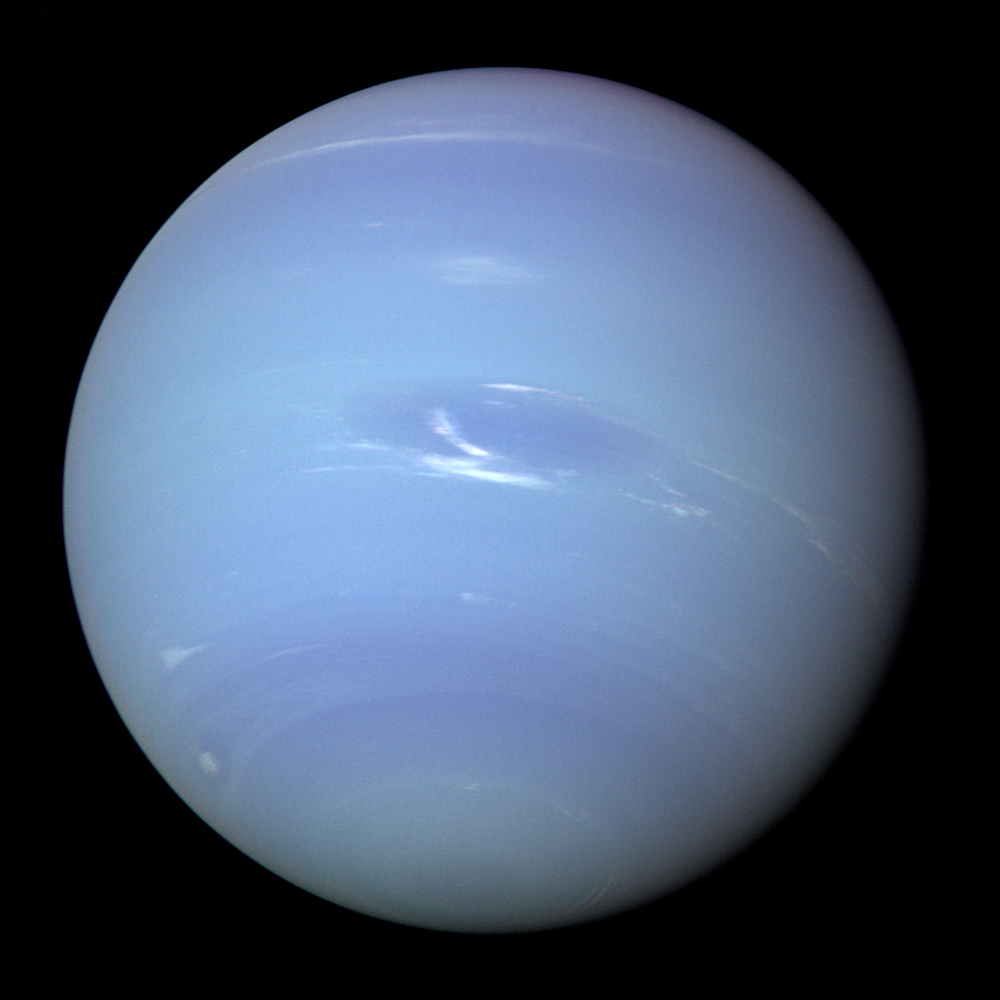 Short
Definition
Sample Sentence(s)
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
French
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Lang... Dutch Neptunus Turkish Neptün Spanish Neptuno Links to Videos/Articles: ● Miner, E. D. (Invalid Date). Neptune. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/place/Neptune-planet · Moses, J. A., Cavalié, T., Fletcher, L. N., & Roman, M. R. (2020). Atmospheric chemistry on Uranus and Neptune. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 378(2187), 20190477. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2019.0477 ● In Depth | Neptune – NASA Solar System Exploration. (n.d.). NASA Solar System Exploration. https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/neptune/in-depth/ ● National Geographic. (2019, March 28). Neptune 101 | National Geographic [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NStn7zZKXfE ●
Astrum. (2016, October 13). Our Solar System’s Planets: Neptune [Video].
YouTube.
| ||
Neutron star | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Short Definition: A Neutron star is a celestial body
and is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star that had a total mass of
about 10-25 solar masses. Compared to other stellar objects, they are much
smaller and much denser. Not counting black holes or hypothetical stellar
objects, they are the densest stellar object in the universe. Detailed Definition: A Neutron stars is a stellar object, which is only a few kilometres in
diameter, but has the mass of a star. So even compared to others stellar objects they have a mind-boggling density and are even so dense, that they are on the
cusp of becoming a black hole. Stars hold an equilibrium between the force of
gravity forcing plasma inwards, which in turn enables fusion of hydrogen to
helium, and this releases energy that pushes outwards. So the equilibrium is
directly linked to the amount of hydrogen available in stars. Breaking this equilibrium
in our sun would result in it transforming to a red giant and then to a white
dwarf. In those massive supergiant stars, gravity will prevail and will
compress the core to the density of an atomic nucleus, which in turn forces
heavier elements to fuse, and thus the outer layer will get bigger by a factor
of x100. After a time the heavier elements are fused to iron and can not be fused any more, so the fusion activity will cease, and the star will collapse to its
core. Electrons and Protons will be forced into each other and form Neutrons as
dense as in atomic nuclei, where nuclei are so densely packed, they form a
layer that is called nuclear pasta. Another interesting property is that they
are spinning really fast, which empowers their magnet fields and gives them the
strongest magnet field in our universe. Etymology: Neutron from Ne and uterà neutral +on ending from ion subatomic particle suffix Star from Proto-Indo-European rooth₂stḗrSample Sentence(s): The physics in the core of the Neutron stars are still largely unknown and are still subject of speculation. Scientists were able to detect gravitational
waves of two merging Neutron stars and confirmed the theory of Albert Einstein. French: Étoile à neutrons German: Neutronenstern Polish: Gwiazda neutronowa Swedish: Neutronstjärna Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=udFxKZRyQt4&list=PLFs4vir_WsTwEd-nJgVJCZPNL3HALHHpF&index=16 https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/science/neutron_stars.html | |||
Nicolaus Copernicus | ||
|---|---|---|
 https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Nicolaus_Copernicus#/media/File:Nikolaus_Kopernikus.jpg Author : Unknown Year: (n.d.) Title: Nicolaus Copernicus Description: Portrait of Nicolaus Copernicus Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nikolaus_Kopernikus.jpg
Definitions
Etymology Sample Sentence(s) 1. Before Nicolaus Copernicus published his heliocentric theory, people generally agreed that the Moon and the Sun orbited the motionless Earth and that Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn were beyond the Sun in that order. Author : Britannica Year: (n.d.) Title: Nicolaus Copernicus Source: Encyclopedia Britannica Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from https://www.britannica.com/biography/Nicolaus-Copernicus
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French German Italian Polish Swedish Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Lang... Russian : Николай Коперник Links to Videos/Articles: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/7740908.stm Author : BBC News Year: 2008 Title: Poland honours Copernicus Source: BBC News Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/7740908.stm https://www.britannica.com/biography/Nicolaus-Copernicus
| ||
UNIVERSEH is an alliance of:
All rights reserved. Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Education and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA). Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.