Dictionary of Space Concepts
Welcome to the Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space", students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
B |
|---|
Big Bang | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 24). Artistic AI Illustration of the Big Bang. midjourney. midjourney.com Definition:
According to the Big Bang Theory, this is the starting point of the known, observable universe, when a rapid expansion of matter took place. According to the standard cosmological model (Big Bang Theory), the Big Bang occurred about 13.8 billion years ago. The model describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature, and offers an explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, like the lighter elements, such as hydrogen and helium. Etymology:From English big “of considerable size or extent” and bang “to (cause something to) make a sudden very loud noise or noises.” The term was introduced in 1948 by the British astronomer Fred Hoyle. In a radio broadcast, Mr Hoyle made disparaging remarks about the hypothesis of the expanding universe and mocked its starting point as the "big bang", without suspecting that he was giving birth to a term that would become part of humankind's common vocabulary. Translations:
| |||
Binary stars | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Sources: Center for High Angular Resolution Astronomy (2008, August 21). Beta Lyrae - CHARA (inverted colors). wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=86270181 Short Definition: A system composed of two stars in which both share a common centre of revolution or one revolves around the other. Detailed Definition: A binary star is a pair of stars in orbit around their common centre of gravity. The term is different from a double star, which refers to any two stars close together in the sky. If components in binary star systems are close enough, they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stellar atmospheres. In some cases, binary systems can exchange mass, evolving in a way which is unattainable for single stars. Etymology: The term binary was first used in the context of space terminology by Sir William Herschel in 1802, in one of his works regarding the observation of double stars. Binary - "dual, twofold, double," mid-15c., from Late Latin binarius Sample Sentence(s): One of the examples of a binary star is Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Étoile binaire German: Doppelstern Polish: Gwiazdy podwójne Swedish: Binär Stjärna Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pIFiCLhJmig https://www.scienceabc.com/nature/universe/what-are-binary-stars.html | |||
Biomining | ||
|---|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 24). AI illustration of microorganisms on ore. midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition:A process involving the extraction of a resource using biological tools. For example, with bacteria or algea. Detailed Definition:Biomining is an environmentally friendly and energy efficient way of extracting useful elements by using microbes to break down rocks to make soil or provide nutrients. Microbes are tiny organisms, such as bacteria and fungi, that have a wide variety of functions. Some microbes have abilities that could be beneficial to humans, such as biomining. Etymology:Bio: From Ancient Greek βίο- (bo-), combining form and stem of βίος (bíos, “life”). Mining: Any activity that extracts or unearths minerals. Sample Sentence:You can use biomining to extract minerals from asteroids using bacteria or fungi." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.sciencedirect.com/referencework/9780080885049/comprehensive-biotechnology | ||
Black Hole | ||
|---|---|---|

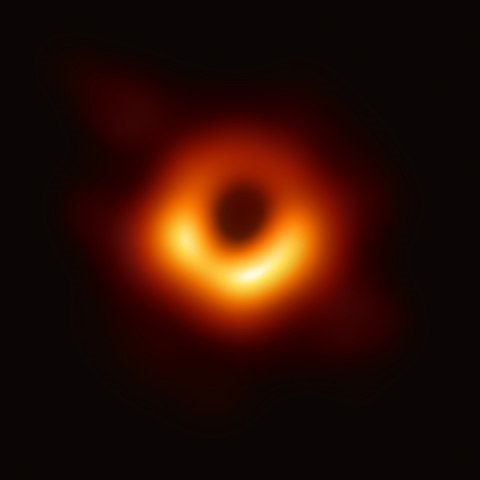
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Black_hole_-_Messier_87_crop_max_res.jpg Short definition: A Black Hole is a region of spacetime where the gravitational field is so strong that nothing, not even light or other electromagnetic waves can escape its event horizon. An event horizon is “the point of no return”, meaning the boundary beyond which nothing can escape. Detailed definition: Since Black Holes can’t be observed directly with telescopes, they’re usually detected by other means, such as observing their gravitational influence on their surroundings. Most Black Holes are formed from large stars that die in a supernova explosion - these Black Holes are usually around 20 times as massive as the Sun. However, there also exist Black Holes that are incredibly large, called Supermassive Black Holes, which can be millions or even billions times as massive as the Sun. Scientists believe that at the centre of almost every big galaxy lies a Supermassive Black Hole, for example Sagittarius A* at the centre of the Milky Way. Etymology: Presumably in December 1967, a student suggested the phrase "black hole" at a lecture by John Wheeler; Wheeler adopted the term for its brevity and "advertising value", and it quickly caught on. (Source: Siegfried, T. (2019, August 9). 50 years later, it’s hard to say who named Black Holes. Science News. https://www.sciencenews.org/blog/context/50-years-later-its-hard-say-who-named-black-holes) Sample sentence(s): Some Black Holes apparently have nonstellar origins. (Source: Lohnes, K. (n.d.). How Do Black Holes Really Work? Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/story/how-do-black-holes-really-work ) Translations: French: Trou noir German: Schwarzes Loch Italian: buco nero Polish: Czarna dziura Swedish: Svart hål Links to Videos/Articles:
The Economist. (2022, July 12). Black holes: why they matter [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/qqMAFtIGaq4 Black Holes | Science Mission Directorate. (n.d.). https://science.nasa.gov/astrophysics/focus-areas/black-holes | ||
Black hole Horizon | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Black_hole_-_Messier_87_crop_max_res.jpg Short Definition: The horizon of a black hole is called event horizon and is an astrophysical phenomenon, which describes the “point of no return” where matter and even light can not cross back according to our understandings of physics. The event horizon is a boundary in spacetime, where the gravitational pull becomes absolute. Detailed Definition: The astrophysical phenomenon of the event horizon defines the boundary of spacetime, where the ability of mass to deform spacetime is absolute. Near this event horizon time seems to work differently, because of gravitational time dilation, which appears to slow down clocks near the horizon more than those farther away and the clock would take an infinite amount of time to reach the black hole in itself. The huge amounts of gravitational pull causes any light to redshift in a process called gravitational redshift. A clock that is falling into a black hole would change from being visible from an outside perspective, to the light of it red shifting and then finally it would disappear from view and all this in a mere minute. On the contrary an indestructible observer that falls into a black hole would experience time normally and it would fall into the black hole in a finite amount of time.
Etymology: Black hole term was coined in astronomy in 1964 Horizon Greekhorizon (kyklos) àboundary
Sample Sentence(s): From an outside perspective an object falling into the black hole horizon would take an infinite amount of time to reach it.
The black hole horizon is the point of no
return, where matter or light are not able to cross back.
French:
Horizon du trou noir
German:
Schwarzes Loch-Horizont
Polish:
Horyzont czarnej dziury
Swedish:
Horisont för svarta hål
Links to Videos/Articles: | |||
Blazar | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Sloan Digital Sky Survey image of blazar Markarian 421. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Markarian_421#/media/File:SDSS_Mrk_421.jpg Short Definition: A blazar is a type of active galaxy nucleus with a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light, which direction is nearly towards an observer. Due to the jet almost directly shooting towards Earth, a blazar appears much brighter on observations than in case of facing another direction. Blazars are a source of powerful radiation in all electromagnetic spectrum, especially in high-energy gamma rays. Blazars are among the most energetic phenomena in the universe and are an important subject to research. Detailed Definition: Blazars are an extremely bright, starlike object characterized by rapid changes in luminosity and a flat spectrum caused by a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light directed at the observer. Blazars emit electromagnetic radiation over a very wide range of frequencies, but mostly distinguished by amount of radio and gamma rays. Due to blazar's instabilities its properties change over time, specifically the variability and intensity of their observable brightness, which is distinguishing blazars from another class of active galactic nucleus, quasars. Blazars are important topics of research in astronomy and astrophysics. Blazar research includes investigation of the properties of accretion disks and jets, the central supermassive black holes and surrounding host galaxies, and the emission of high-energy photons, cosmic rays, and neutrinos. Etymology: Coined by 1978 by astronomer Edward Spiegel from BL Lac object and quasar. Sample Sentence(s): "Blazars are thought to be active galactic nuclei, with relativistic jets oriented close to the line of sight with the observer." Translations: French: Blazar German: Blazare Polish: Blazar Swedish: Blazar Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/blazar | |||
UNIVERSEH is an alliance of:
All rights reserved. Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Education and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA). Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.