Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Venus | |
|---|---|
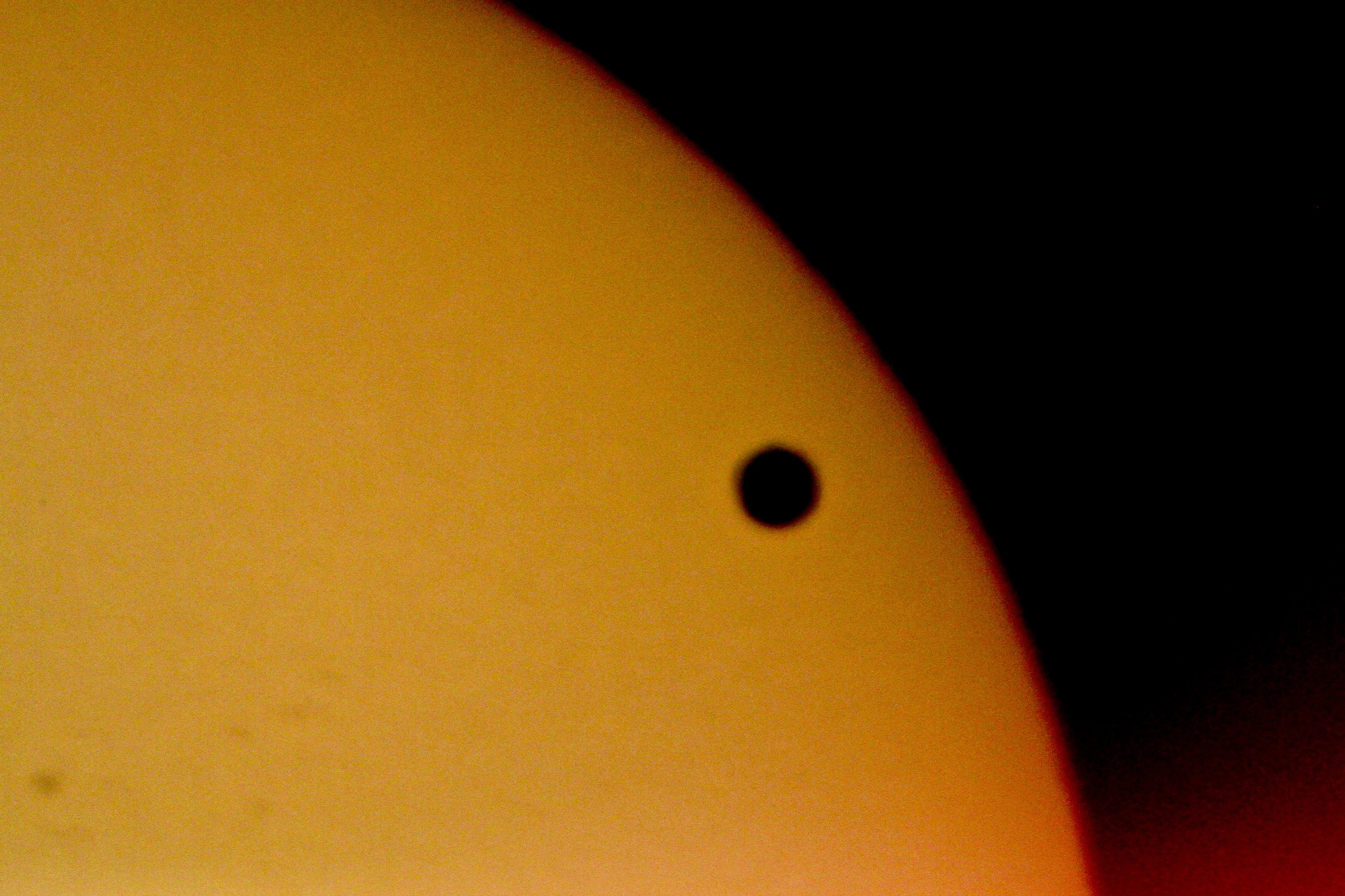 Source: Hecht, M. (2012, June 5). Venus Transit. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/76858203@N04/23105554654 Definition:Venus is the planet with the second closest orbit to the Sun. Venus is our inner neighbor in space in the Solar System. It is a celestial body located just 40 million kilometers far from the Earth. Venus resembles the earth in the main parameters: size, mass, density and internal structure almost match. Etymology:In Roman mythology (= ancient stories), the goddess (= female god) of beauty and love. Translations:
| |
Volcano | |
|---|---|
Image: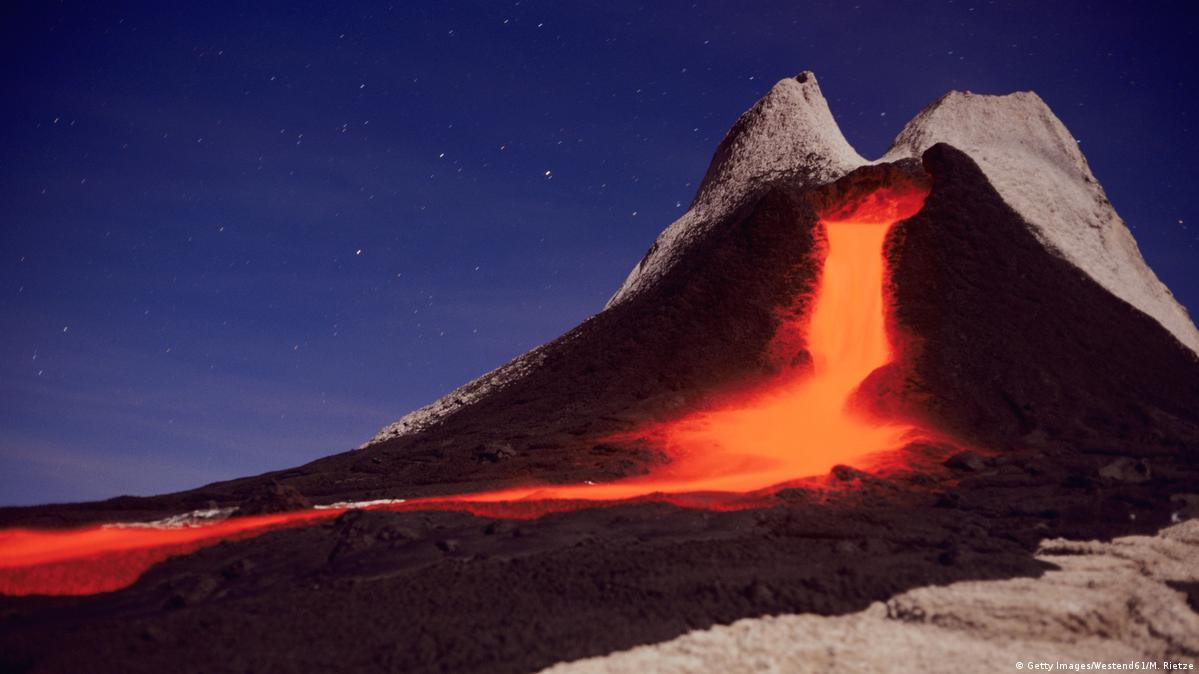  Image: Source: https://www.dw.com/en/volcanic-eruptions-can-cool-the-planet/a-40727123 Short Definition: A volcano is a hill or mountain with a hole where lava, rocks, or gas may be seen erupting from a planet or moon's interior. Detailed Definition: A crack in the earth's crust through which substances such as lava, steam, ashes, etc. are released continually or sporadically. Volcanoes are known to exist on the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, the Moon, Mars, and the moon Io of Jupiter. Only two of these bodies currently have active volcanoes: Earth and Io. However, Venus or Europa, the moon of Jupiter, may have volcanoes erupting. Etymology: Volcano comes from the Latin Vulcanus, which is the name of the fire god. Sample Sentence(s): The volcano's lava was pouring down the mountainside. On the seabed of Jupiter's moon Europa, there has been volcanic activity. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: volcan German: Vulkan Polish: wulkan Swedish: vulkan Links to Videos/Articles: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/topic/volcanoes https://chandra.harvard.edu/press/10_releases/press_081810.html | |
White Dwarf | |
|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio:  Image/Video/Audio: Picture: A white dwarf Image/Video/Audio Source: File:White dwarf.jpg - Wikimedia Commons. (2011, April 5). https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:White_dwarf.jpg Short Definition:
White dwarfs, or cold stars, is a term often used to describe stars in the final stages of their evolution. These stars, which lose their energy sources and cannot perform fusion reactions, are the stars that tend to squeeze into themselves due to the gravitational law. This phenomenon was firstly discovered by the British astronomer 'William Herschel' in 1783.
Detailed Definition:
As one of the densest stellar remnants in space, white dwarfs are stars that have run out of most of their nuclear fuel and tend to collapse inwards. These stars, which are relatively Earth-sized and composed entirely of carbon and oxygen mass, are less than 1.4 solar masses when their cores are stable, but they tend to suffer constant heat and radiation loss because they do not undergo any fusion process. According to NASA's calculations, the core temperatures of white dwarfs can reach up to 100,000 Kelvin. Apart from the carbon and oxygen mass that make up their core, their envelope are surrounded by thin helium and in some cases hydrogen atoms.
Etymology:
White - from Proto-Indo-European (ḱweydós) Dwarf - from Proto-Germanic (dwergaz) (white - Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/white) (dwarf - Wiktionary. (n.d.). https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/dwarf)
Sample Sentence(s):
‘’White dwarfs evolve from stars with an initial mass of up to three or four solar masses or even possibly higher.’’ (The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (1998, July 20). White dwarf star | Definition, Size, Mass, Life Cycles, & Facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/white-dwarf-star) ‘’White
dwarfs reach this incredible density because they are collapsed so
tightly that their electrons are smashed together, forming what is
called "degenerate matter.’’ (Dobrijevic, D., & Tillman, N. T. (2022, March 4). White dwarfs: Facts about the dense stellar remnants. Space.com. https://www.space.com/23756-white-dwarf-stars.html)
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages: French:
Naine blanche German:
Weißer Zwerg Polish:
Biały karzeł Swedish:
Vit dvärg Turkish:
Beyaz Cüce Links to Videos/Articles:
Dobrijevic, D., & Tillman, N. T. (2022, March 4). White dwarfs: Facts about the dense stellar remnants. Space.com. https://www.space.com/23756-white-dwarf-stars.html Kurzgesagt
– In a Nutshell. (2017, May 4). The Last Light Before Eternal
Darkness – White Dwarfs & Black Dwarfs [Video]. YouTube.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qsN1LglrX9s The
Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (1998, July 20). White dwarf
star | Definition, Size, Mass, Life Cycles, & Facts. Encyclopedia
Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/white-dwarf-star White Dwarfs. (2021, May 4). Science. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/white-dwarfs | |
Yuri Gagarin | |
|---|---|
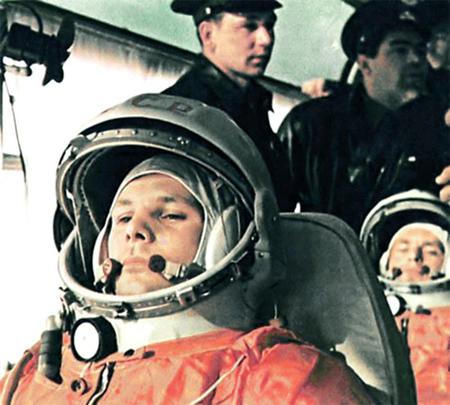 Wikipedia Year: (n.d.) Yuri Gagarin - 1961-04-12. Wikimedia Commons. Retrieved May 29, 2023, from https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/vi/7/7f/Yurigagarin-1961-04-12.jpg
Definitions
Yuri Gagarin was a Soviet cosmonaut and the first human to travel into space. On April 12, 1961, aboard the Vostok 1 spacecraft, Gagarin completed a single orbit around the Earth, marking a significant milestone in human space exploration. His flight lasted 108 minutes and made him an international symbol of space exploration and achievement. Detailed Definition
Sample Sentence(s) 1. Gagarin's flight came at a time when the United States and the Soviet Union were competing for technological supremacy in space. David, L. Year: 2012 First Man in Space: Yuri Gagarin's Historic Vostok 1 Flight. Space.com Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from https://www.space.com/16159-first-man-in-space.html 2. The Gagarin crater on the Moon is named after Yuri Gagarin, in recognition of his achievement as the first human to journey into space. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French German Italian Polish Swedish Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Languages Russian: Юрий Гагарин Links to Videos/Articles: Britannica Year: (n.d.). Yuri Gagarin. Encyclopedia Britannica Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from https://www.britannica.com/biography/Yuri-Gagarin BBC News. 2021. Yuri Gagarin: The first man in space - BBC News. Retrieved Jun 12. 2024 from https://youtu.be/KANuFlelQ5k. | |
Zenith | |
|---|---|
Media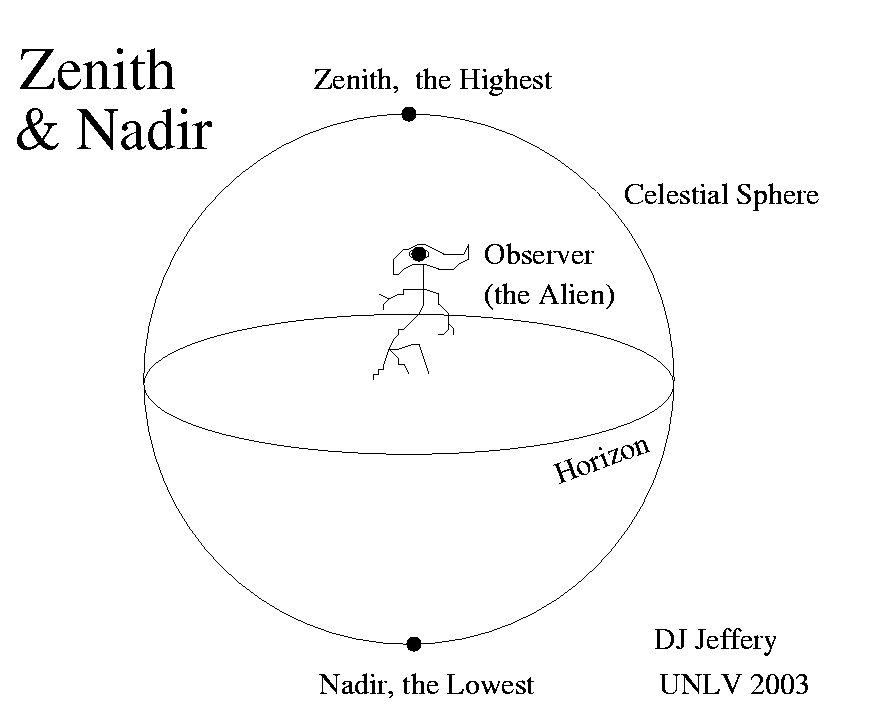 Media Zenith & Nadir, DJ Jeffery, University of Nevada, Las Vegas, 2003. DefinitionsShort Definition Detailed Definition Etymology Sample Sentences Glowing with astral turquoise, the comet dashingly passed zenith and started decelerating as it was approaching the horizon.
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages Frenchle zénith
German
der Zenit
Italian lo zenit
Polish zenit
Swedish zenit
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Languages Russian Ukrainian Links to Videos/Articles: The Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica. (1998, July 20). Zenith | astronomy. Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved [ 06.14.2023 ], from https://www.britannica.com/science/zenith-astronomy
Zenith | COSMOS. (n.d.). Retrieved [ 06.20.2023 ], from https://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/z/Zenith | |
