Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
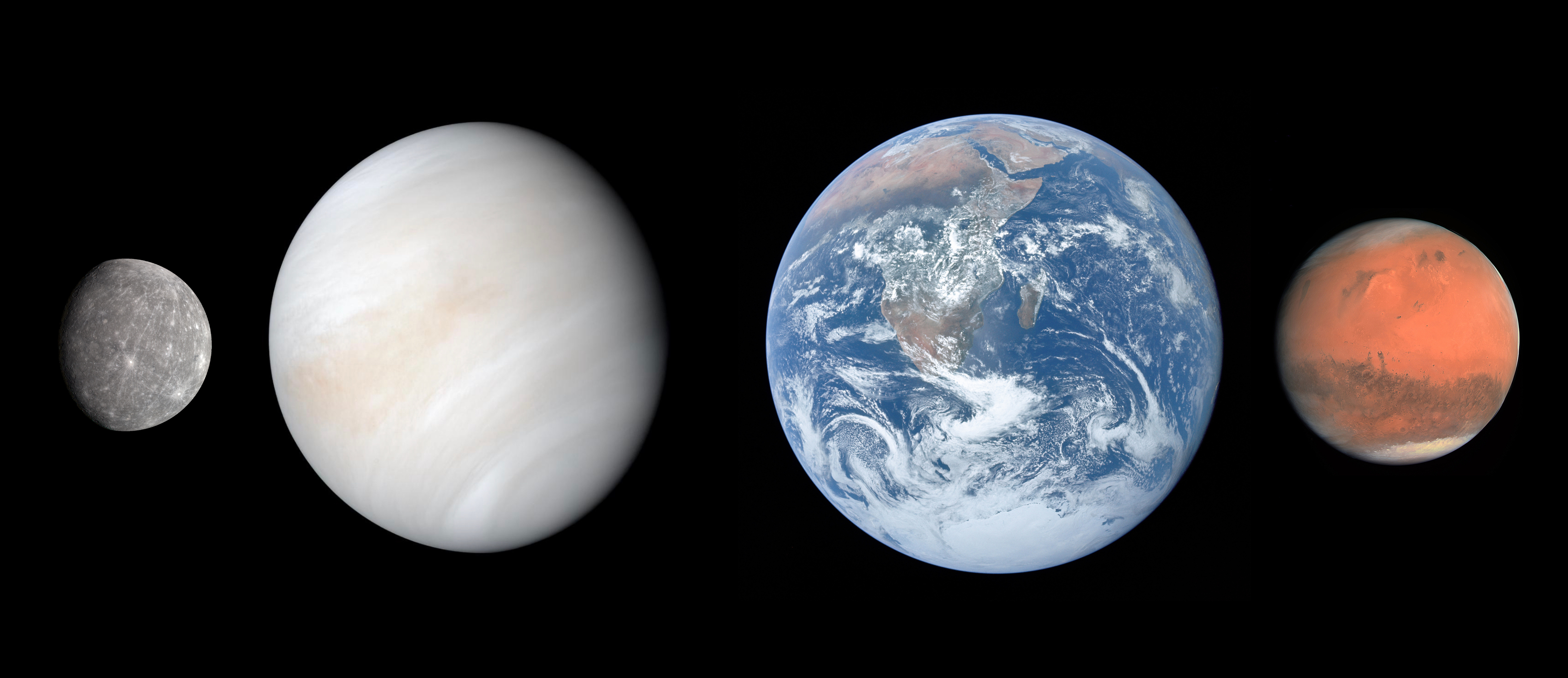
Terrestrial Planets | |
|---|---|
 Short
Definition
The word "planet" has its roots in ancient Greek. It comes from the
Greek term "planētēs," which means "wanderer" or
"wandering star." Sample Sentence(s) "It's unclear what the dividing line is between a rocky planet and a terrestrial planet."
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages
French
German
Italian
Polish
Swedish
Additional Translations Spanish Planeta terrestre Turkish Karasal gezegen Dutch Aardse planeten
Links to Videos/Articles
Dutfield, S., & Gammon, K. (2022). Terrestrial planets: Definition & facts about the inner planets and beyond. Space.com. https://www.space.com/17028-terrestrial-planets.html Morbidelli, A., Lunine, J. I., O’Brien, D. P., Raymond, S. N., & Walsh, K. J. (2012). Building Terrestrial Planets. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 40(1), 251–275. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-earth-042711-105319 Terrestrial | Planet Types – Exoplanet Exploration: Planets Beyond our Solar System. (n.d.). Exoplanet Exploration: Planets Beyond Our Solar System. https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/what-is-an-exoplanet/planet-types/terrestrial/ Cornerstone Television Network. (2015, October 8). Origins: The
Terrestrial Planets [Video]. YouTube.
MooMooMath and Science. (2019, August 22). Terrestrial Planets in Order
[Video]. YouTube. | |
The Kuiper belt | |
|---|---|
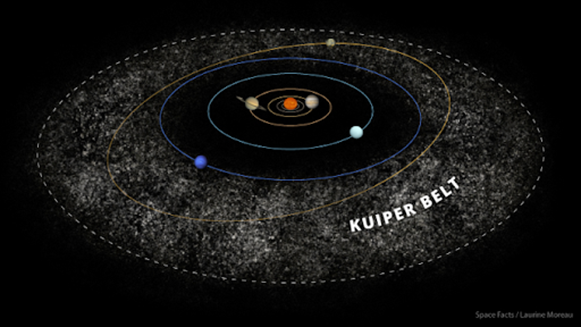 Image Source: https://theplanets.org/kuiper-belt/
Short Definition:
Detailed Definition: Etymology: Kuiper – Dutch
– Kuiper - cooper – from the name of the scientist Gerard Kuiper
Sample Sentence(s): French: German: Polish: Swedish: Spanish
Links to Videos/Articles: https://theplanets.org/kuiper-belt/ | |
The Solar System | |
|---|---|
Image Source: Short Definition: Detailed Definition: Etymology: Sample Sentence(s): French: Système solaire German: Układ Słoneczny Swedish: Solsystem Spanish:El sistema solar Links to Videos/Articles: | |
Time Dilation | |
|---|---|
Media:  Media: File:Nonsymmetric velocity time dilation.gif - Wikimedia Commons . (2006, January 28). https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nonsymmetric_velocity_time_dilation.gif Short Definition: Time Dilation is a phenomenon observable through the change of measuring of elapsed time by two clocks. The change usually occurs due to the difference in velocity or gravitational potential. The faster you move relative to some object, the slower time seems to flow. Detailed Definition: Time Dilation is an occurrence which takes place due to the difference in velocity or gravitational potential of a given object. It occurs when one of the objects has higher velocity than the other (commonly called a reference frame). The reference frame is a coordinate system defined by certain characteristic points, this frame is stable while the other object travels with a certain velocity, different from the frame. What can be then observed is that the travelling object experiences time slower, than the reference frame (observer). This phenomenon is strictly connected to Einstein's theory of relativity, as the time passes differently, relative to the state (either gravitational or velocity) of the object. Time dilation has been observed and calculated on the International Space Station. The differences in time perception are virtually insignificant (in milliseconds) at small distances, but might increase to even years in difference. Etymology: Time, from Old English "tima" defined as limited space of time. Dilation from Late Latin "dilatationem" meaning widening of something. Sample Sentence(s) 1. The astronauts on the ISS experienced time dilation of around 20 milliseconds, compared to earth. 2. The time on ISS is lagging by about 0.01 seconds for every 12 months on earth, due to time dilation. Translation: French - dilatation du temps German- Zeitdilatation Italian - dilatazione del tempo Polish - dylatacja czasu Swedish - Tidsdilatation | |
Twilight | |
|---|---|
Image/Video/Audio Source: Short definition: Twilight is the period after sunset when the Earth is illuminated by sunlight diffused in the atmosphere. The following twilight phases are distinguished: civil twilight, nautical twilight and astronomical twilight. The only difference between twilight phases is where the Sun is located, which makes the sky gets darker. When the Sun is up to 6° below the horizon, it is considered a civil twilight. When the Sun is between 6° and 12° below the horizon, it is said to be a nautical twilight. An astronomical twilight is when the Sun is located from 12° to 18° below the horizon. When Sun position is over 18° below the horizon line, it is considered as night. Etymology: late Middle
English: from Old English twi- ‘two’ (used in an obscure sense in this
compound) Sample Sentence(s): French: Le crépuscule German: Zmierzch Swedish: Skymning Spanish: El crepúsculo Links to Videos/Articles: | |
Twins Study | |
|---|---|
Definition:A study aiming to investigate the effects of spaceflight on the human organism. The study was organized by NASA with the support of 8 universities across the USA. It was conducted in 2015-2016 and involved two identical twin brothers: Scott and Mark Kelly. Scott Kelly served on a year-long mission aboard the International Space Station, while his brother Mark Kelly, a former NASA employee, remained on Earth. The twins study included an array of biochemical, neurological and other types of medical tests conducted before, during and after the spaceflight, i.e. over the span of 27 months. The results confirmed the robustness and resilience of human health, since 91,3% of Scott Kelly’s medical parameters returned to baseline six months after the spaceflight. The remaining changes were to be used for development of personalized measures to predict and overcome possible adverse consequences of spaceflight. Translations:French: German: Polish: Eksperyment z bliżniakami Swedish: Article:https://www.science.org/doi/pdf/10.1126/science.aau8650 Other sources:https://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasa-s-twins-study-results-published-in-science https://www.nasa.gov/twins-study/about
| |
Universe | |
|---|---|

Source:Cajina, I. (2017, September 17). Milky Way from Max Patch. unsplash. https://unsplash.com/photos/asuyh-_ZX54 DefinitionThe totality of all existing matter, energy, space and time. The universe is approximately 13,8 years old and has emerged as a result of the Big Bang, in which it emerged from a single point and continues to expand. Translation
Links to Videos/Articles:https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/what-is-an-exoplanet/what-is-the-universe/ | |
Vacuum | |
|---|---|
Image:
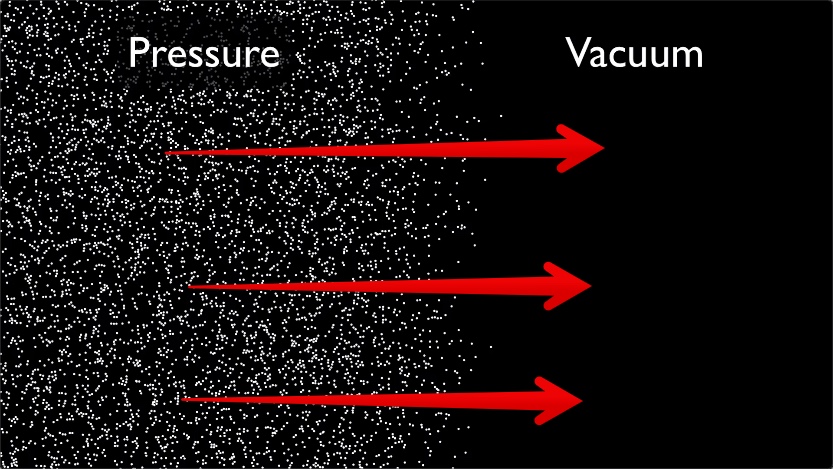 Image: Source: https://www.metabunk.org/attachments/metabunk-2018-10-31-08-37-23-jpg.34929/ Short Definition: A vacuum is a space in which there is no matter such as gas or particles. It is found in space or can be generated by machines. Detailed Definition: Space that does not contain any gas inside its boundaries. However, it is also required that there is not any matter in general in either state such as gas, liquid, or solid, among other complex definition states. Even though the vacuum is found naturally in space, it is used on earth for different machines such as vacuum pumps, and vacuum chambers, among others. Etymology: Vacum comes from the latin Vacuus, which means empty. Sample Sentence(s): Life cannot be found or developed in the vacuum of space. The dead body astronaut rambled in the vacuum of space. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: vide German: Vakuum Polish: próżnia Swedish: svenska Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/365382138_A_Review_of_Research_on_the_Vacuum_Plume DOI: 10.3390/aerospace9110706 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E43-CfukEgs&ab_channel=BBC | |
Valentina Tereshkova | |
|---|---|
Illustration: http://www.astronaut.ru/as_rusia/lady62/foto/tereshkova02.jpg Definition:The first female cosmonaut, the 10th person in the world to be sent into space. Valentina Tereshkova flew into space alone aboard Vostok-6 on June 16, 1963. The duration of the flight amounted to 2 days, 22 hours and 50 minutes, during which the spacecraft orbited the Earth 48 times. Valentina Tereshkova was born in 1937 in the village of Bolshoye Maslennikovo in Yaroslavl Oblast, USSR. In 1960, she graduated from Yaroslavl Light Industry Training School as a cotton spinning technician, and in 1969 received a qualification from Zhukovsky Air Force Engineering Academy as a pilot, cosmonaut and engineer. She enjoyed parachuting, which later turned out to be one of the criteria for cosmonaut selection. Following the spaceflight, she worked as a cosmonaut instructor until reaching mandatory retirement age in 1997. Later she continued working as a politician, which she had already been doing since 1966. Her daughter Elena is said to be the first child in the world whose parents are both cosmonauts. Translation:
Links to Videos/Articles:http://www.astronaut.ru/crossroad/010.htm https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Терешкова,_Валентина_Владимировна
| |
