Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
Nicolaus Copernicus | |
|---|---|
 https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Nicolaus_Copernicus#/media/File:Nikolaus_Kopernikus.jpg Author : Unknown Year: (n.d.) Title: Nicolaus Copernicus Description: Portrait of Nicolaus Copernicus Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nikolaus_Kopernikus.jpg
Definitions
Etymology Sample Sentence(s) 1. Before Nicolaus Copernicus published his heliocentric theory, people generally agreed that the Moon and the Sun orbited the motionless Earth and that Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn were beyond the Sun in that order. Author : Britannica Year: (n.d.) Title: Nicolaus Copernicus Source: Encyclopedia Britannica Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from https://www.britannica.com/biography/Nicolaus-Copernicus
Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French German Italian Polish Swedish Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other Lang... Russian : Николай Коперник Links to Videos/Articles: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/7740908.stm Author : BBC News Year: 2008 Title: Poland honours Copernicus Source: BBC News Retrieved Date: May 29, 2023, from http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/7740908.stm https://www.britannica.com/biography/Nicolaus-Copernicus
| |
Orbit | |
|---|---|
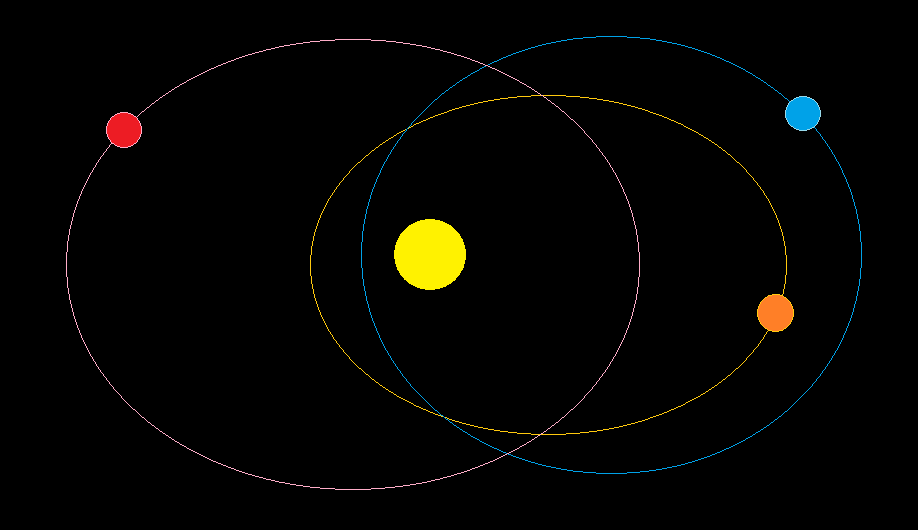 Image Source: MS Paint (2023, May 25). MS Paint Illustration of orbits. ms paint. ms paint Short Definition: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6cUe4oMk69E&list=TLGG8tIphgpDAHkxMzA0MjAyMw&t=1s | |
Orbit (entry exists but has poor description) | |
|---|---|
Image source: Short Definition: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6cUe4oMk69E&list=TLGG8tIphgpDAHkxMzA0MjAyMw&t=1s | |
Orbital Manufacturing | |
|---|---|
The concept of orbital manufacturing visualized by a primate building space mission components with blocks. Source: Short Definition:Orbital manufacturing refers to the production of various components required for space missions in orbit. Detailed Definition:
In orbital manufacturing, parts, materials, and tools needed for space missions are manufactured in orbit around planets. This manufacturing capability provides a solution for sustainable, flexible missions and enables on-demand repair, fabrication, and recycling on critical systems. These capabilities provide tangible cost savings by reducing launch mass, as well as significant risk mitigation by reducing dependence on spare parts and/or oversizing systems for reliability. There are several advantages of manufacturing in space: The effects of microgravity and vacuum in space enable the study and manufacturing of products that would otherwise be impossible to make on Earth. When compared to launching all essential resources from Earth, the harvest and processing of raw materials from other astronomical bodies, commonly known as In-Situ Resource Utilisation (ISRU), could enable more sustainable space research missions at a lower cost. Raw materials might be transferred to low Earth orbit and processed into products before being delivered back to Earth. This aims to preserve the Earth by replacing terrestrial production on the planet. Etymology:
Orbit - Latin - orbita “course, track, impression, mark” Manu - Latin - manus “Hand” Facture – Latin - factura “Making” Sample Sentence(s):
“Was this arm made using orbital manufacturing?” “Orbital manufacturing is particularly suitable for long space missions.” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles: | |
Parabolic flight | |
|---|---|
Source: https://www.esa.int/Education/Fly_Your_Thesis/Parabolic_manoeuvres Definition:Flight manoeuvre in which the aircraft alternatingly ascends and descends to achieve weightlessness or to simulate reduced gravity. Parabolic flights are performed to train astronauts in zero-g manoeuvres, giving them about 25 seconds of weightlessness out of 65 seconds of flight in each parabola. During such training, the airplane typically flies about 40–60 parabolic manoeuvres. Initially, the aircraft climbs with a pitch angle of around 45 degrees, the sensation of weightlessness is achieved by reducing thrust and lowering the nose such that the aircraft follows a ballistic trajectory. Weightlessness begins while ascending and lasts all the way "up-and-over the hump", until the craft reaches a downward pitch angle of around 40 degrees. Etymology:from Ancient Greek παραβολικός /parabolikós/ “of or pertaining to a parable” Translations:
| |
Parallax | |
|---|---|
Media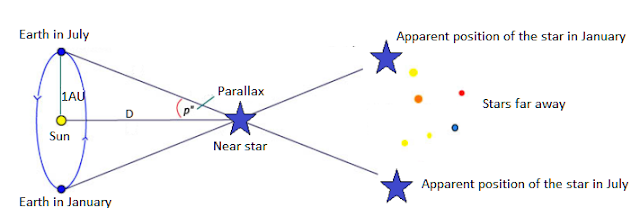 Insight Observatory (n.d.). Star Parallax. DefinitionsShort Definition Detailed Definition Etymology Sample Sentences Eyes of live creatures with binocular sight, humans included, exploit parallax to perceive depth and measure distances. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages Frenchla parallaxe
German
die Parallaxe
Italian la parallasse
Polish paralaksa
Swedish parallax
Additional Translations of Terms/Concepts into Other LanguagesRussian Ukrainian Links to Videos/Articles:
| |
Parsec | |
|---|---|
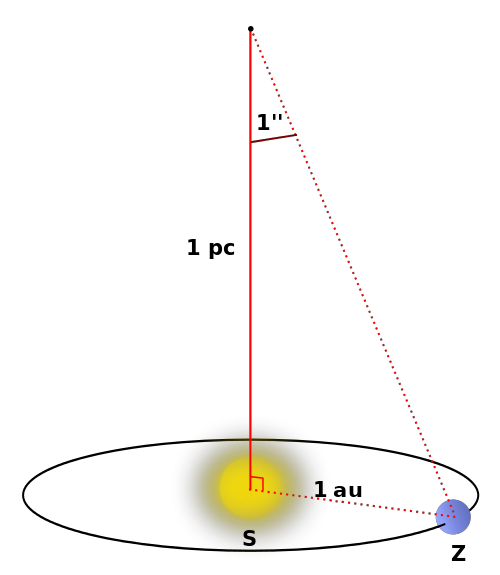 Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Parsek_pl.png Short Definition: The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System. Parsec is approximately equal to 3.26 light-years or 206,000 astronomical units (symbol: AU), or 30.9 trillion kilometers. As an example, the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is about 1.3 parsecs from the Sun. Most stars visible to the naked eye are within a few hundred parsecs of the Sun, with the most distant at a few thousand. Detailed Definition: A Parsec is the distance for which the annual parallax of the position of the Earth, viewed perpendicular to the plane of the orbit, is 1 arc second (arcsec). A parsec can equally be described as the distance from which half of the Earth's orbital major axis (equal to 1 AU) is visible as an arc of 1 arcsecond. Although distance equal to one parsec is tremendous still, multiples of parsecs are required for the larger scales in the universe, including kiloparsecs (kpc) for the more distant objects within and around the Milky Way, megaparsecs (Mpc) for mid-distance galaxies, and gigaparsecs (Gpc) for many quasars and the most distant galaxies. The term parsec is a combination of "parallax" and "arcsecond," which derives from the use of triangulation when measuring the distance between two stars. Etymology: Combination of words parallax and arcsecond Sample Sentence(s): "Distance to the nearest star is about 1.3 parsecs." Translations: French: Parsec German: Parsec Polish: Parsek Swedish: Parsec Links to Videos/Articles: https://earthsky.org/space/what-is-a-parsec/ | |
Perihelion | |
|---|---|
Diagram of a body's direct orbit around the Sun, with its nearest (perihelion) and farthest (aphelion) points. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apsis#/media/File:Perihelion-Aphelion.svg Short Definition: Perihelion is the farthest point in the orbit of a planetary body about the Sun. This point is present in every Solar System orbiting body orbit due to the fact all orbits are elliptical. Detailed Definition: Perihelion is the farthest point in the orbit of a planetary body about the Sun in the Solar System. In case of describing generic star orbiting system, such point is called an apsis as the farthest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For bodies moving around the Sun in a stable elliptical orbit, the perihelion is crossed at regular intervals, every orbital period. At perihelion, the Earth is 147.1 million km (0.9833 au) from the Sun. This usually takes place between 2nd and 4th January and occurs at a slightly different time each year due to interference from other celestial bodies. Etymology: From Proto-Indo-European *per- (“before, in front; first”) + ἥλιος (hḗlios, “sun”) + -on (suffix forming nouns) (from Ancient Greek -ον (-on)) Sample Sentence(s): "If the comet's perihelion (its closest point to the sun) coincides with the shower's peak, a rare meteor storm can occur, creating thousands of meteor showers per hour." - Skyler Caruso, Peoplemag, 4 Oct. 2022 "Earth makes its closest past on Jan. 4, which is called perihelion." - Dave Epstein, BostonGlobe.com, 4 July 2022 Translations: French: Périhélie German: Perihel Polish: Peryhelium Swedish: Perihelium Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.space.com/what-is-perihelion | |
Perseids Meteor Shower | |
|---|---|
 Source: Sutton, B. (2015, August 19). Perseid Meteor Shower over the Ocotillo Patch; 8/12/15. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/115357548@N08/20713070995 Definition:A meteor shower that recurs annually between the July 17th, and August 24th, with a peak of shooting stars in the days around August 12th. They have a high velocity (60 km/s) and, as so-called fireballs, can even reach the brightness of Venus. The radiant, apparent origin of this shower, lies in the eponymous constellation Perseus, near its border with Cassiopeia. Etymology:from Greek Περσείδαι “Perseidai”, the sons of Perseus in Greek mythology Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:Perseid meteor shower on NASA TV 2015 (4 hours)https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DIvVLyltJe8 | |
Phobos | |
|---|---|
Definition:
Etymology:Named after Phobos, the ancient Greek god of fear, twin brother of Deimos, son of Ares (the equivalent of the Ancient Roman god of war Mars). Translations:
| |
