Dictionary of Space Concepts
What is the Dictionary of Space Concepts?
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) is a project by UNIVERSEH – the European Space University of Earth and Humanity. Starting in 2020, this Alliance of five European Universities decided to launch an online dictionary dealing with terms and concepts related to space sciences. It should be created and used by students, lecturers, researchers and citizens alike.
After an initial planning phase, the DSC was published in spring 2022. It opens up several opportunities for all members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance and interested citizens to contribute to the content of the DSC.
In our course "Terms and Concepts of Space" (to the registration) , students learn how to write a dictionary article and later on contribute several entries to the DSC. Students and other members of the UNIVERSEH Alliance can also submit articles for the DSC via an entry in here . Interested citizens can contribute in this entry platform.
Once submitted, these articles are reviewed by UNIVERSEH Alliance staff and, if necessary, edited before their publication in the Dictionary.
In this way, the DSC is a dynamic project that is constantly expanding in content and quality through constant contributions from students, staff and citizens.
NEO (Near-Earth Object) | |
|---|---|
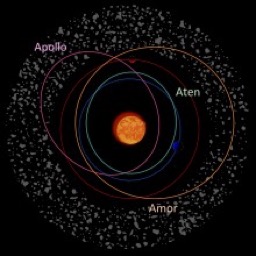 Source: Video from NASA explaining NEO: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r-OCcFnp2RA Short Definition:NEO, or near-Earth object, is a celestial body which is in the size range of meters to tens of kilometres, that orbits the sun and approaches the earth within the distance of 1.3 AU (astronomical units). Detailed Definition:Among the 600,000 known asteroids, only 20,000 of them are NEOs. To be classified as such, the object must be natural and cannot be manmade. Some of them could potentially hit the earth and for this reason, some organisation keep track of them everyday. Historically speaking, NEOs have had an impact of the earths geological and biological history. Most of the NEOs are Apollo asteroids (55.4%), meaning that they come from the Apollo asteroid group. The second most common are Amor asteroids (36.4%), and third most common are Aten asteroids (7.7%). Etymology:Acronym of "near-Earth object." Sample Sentence:An astronomer would for example say during a lecture: “The Amor asteroid, 433 Eros, was the first NEO discovered in 1898, by D. Witt of Berlin, Germany, using a photographic plate to record its position.” Translations:
Links to Articles/Videos: | |
Dusty Vacuum Chamber (Dirty Vacuum Chamber) | |
|---|---|
Source: https://ttu-ir.tdl.org/bitstream/handle/2346/73031/ICES_2017_235.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y Short Definition:An enclosure that constitutes a closed environment developed for the purpose of simulating lunar conditions and allow for the testing of material behaviour in such a space.
Detailed Definition:Sample Sentence(s):Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles: | |
Falcon 9 | |
|---|---|
 Source : SpaceX (2016, January 16). Falcon 9 vertical at Vandenberg Air Force Base. wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=64851825 Definition:Falcon 9 is the world's first orbital class reusable rocket, created and manufactured by SpaceX. It is a reusable, two-stage rocket capable of transporting both people and payloads into Earth's orbit and beyond. Reusability allows to reuse the most expensive parts of the rocket, which diminishes the cost of space access. The standard parameters of the rocket are: Height - 70 m / 229.6 ft Diameter - 3.7 m / 12 ft Mass - 549,054 kg / 1,207,920 lb The engine used in production of Falcon 9 is the Merlin, which uses grade kerosene (RP-1) and liquid oxygen as rocket propellants in a gas-generator power cycle. The Merlin engine was originally designed for recovery and reuse. Falcon 9 has already been used in numerous missions or tests (Crew-1 Mission, Crew-2 Mission, Crew-3 Mission, DART Mission) and is planned to be launched in the next ones (for example Polaris Dawn in the last quarter of 2022). Sample Sentence(s):"This rocket is the Falcon 9 that successfully reached orbit after 9 minutes and 38 seconds on its maiden test flight." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.spacex.com/updates/ | |
Biomining | |
|---|---|
 Source: Midjourney (2023, May 24). AI illustration of microorganisms on ore. midjourney. midjourney.com Short Definition:A process involving the extraction of a resource using biological tools. For example, with bacteria or algea. Detailed Definition:Biomining is an environmentally friendly and energy efficient way of extracting useful elements by using microbes to break down rocks to make soil or provide nutrients. Microbes are tiny organisms, such as bacteria and fungi, that have a wide variety of functions. Some microbes have abilities that could be beneficial to humans, such as biomining. Etymology:Bio: From Ancient Greek βίο- (bo-), combining form and stem of βίος (bíos, “life”). Mining: Any activity that extracts or unearths minerals. Sample Sentence:You can use biomining to extract minerals from asteroids using bacteria or fungi." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.sciencedirect.com/referencework/9780080885049/comprehensive-biotechnology | |
Orbital Manufacturing | |
|---|---|
The concept of orbital manufacturing visualized by a primate building space mission components with blocks. Source: Short Definition:Orbital manufacturing refers to the production of various components required for space missions in orbit. Detailed Definition:
In orbital manufacturing, parts, materials, and tools needed for space missions are manufactured in orbit around planets. This manufacturing capability provides a solution for sustainable, flexible missions and enables on-demand repair, fabrication, and recycling on critical systems. These capabilities provide tangible cost savings by reducing launch mass, as well as significant risk mitigation by reducing dependence on spare parts and/or oversizing systems for reliability. There are several advantages of manufacturing in space: The effects of microgravity and vacuum in space enable the study and manufacturing of products that would otherwise be impossible to make on Earth. When compared to launching all essential resources from Earth, the harvest and processing of raw materials from other astronomical bodies, commonly known as In-Situ Resource Utilisation (ISRU), could enable more sustainable space research missions at a lower cost. Raw materials might be transferred to low Earth orbit and processed into products before being delivered back to Earth. This aims to preserve the Earth by replacing terrestrial production on the planet. Etymology:
Orbit - Latin - orbita “course, track, impression, mark” Manu - Latin - manus “Hand” Facture – Latin - factura “Making” Sample Sentence(s):
“Was this arm made using orbital manufacturing?” “Orbital manufacturing is particularly suitable for long space missions.” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles: | |
Twins Study | |
|---|---|
Definition:A study aiming to investigate the effects of spaceflight on the human organism. The study was organized by NASA with the support of 8 universities across the USA. It was conducted in 2015-2016 and involved two identical twin brothers: Scott and Mark Kelly. Scott Kelly served on a year-long mission aboard the International Space Station, while his brother Mark Kelly, a former NASA employee, remained on Earth. The twins study included an array of biochemical, neurological and other types of medical tests conducted before, during and after the spaceflight, i.e. over the span of 27 months. The results confirmed the robustness and resilience of human health, since 91,3% of Scott Kelly’s medical parameters returned to baseline six months after the spaceflight. The remaining changes were to be used for development of personalized measures to predict and overcome possible adverse consequences of spaceflight. Translations:French: German: Polish: Eksperyment z bliżniakami Swedish: Article:https://www.science.org/doi/pdf/10.1126/science.aau8650 Other sources:https://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasa-s-twins-study-results-published-in-science https://www.nasa.gov/twins-study/about
| |
ExoMars Programme | |
|---|---|
 DefinitionA programme created in cooperation between ESA and Roscosmos, which is trying to find signs of biological processes on Mars indicating whether life has ever existed on that planet. The programme includes two missions:
The Trace Gas Orbiter’s task is to look for trace atmospheric gases, including methane, which would indicate the presence of biological processes, whereas the Rosalind Franklin rover is supposed to look for evidence of life on the surface and underground. Etymology:“Exo” in ExoMars refers to “exobiology”, a branch of sciences investigating life beyond Earth. A rover involved in this mission is named after Rosalind Franklin, who was an English chemist known in particular for her contribution to DNA research. The platform Kazachok is named after a Russian folk dance. Sources:https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Exploration/ExoMars More about the mission:https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Exploration/ExoMars/ExoMars_Factsheet | |
Gravity Assist | |
|---|---|
Source: http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/multimedia/display.cfm?IM_ID=2143, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=18049439 Short Definition:Gravity assistance describes the intentional use of the gravitational attraction of a celestial body, in order to modify the trajectory of a space vehicle. This maneuver allows the spacecraft to save rocket fuel. Detailed Definition:Etymology:1. Gravity (Noun.), originating from the Latin word gravitatem, with the meaning of “weight, heaviness, pressure” 2. Assist (Verb.), originating from Latin word assistere, which means “standing by, help” Sample Sentence(s): “The global minimum velocity increments of direct transfer trajectory and gravity-assist trajectories are obtained for each candidate target.” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:
| |
RemoveDEBRIS Mission | |
|---|---|
Definition:A mission under the supervision of the Surrey Space Centre of the University of Surrey (supported by Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd., Airbus Defense and Space, Innovative Solutions in Space, CSEM, Inria and Stellenbosch University) that aimed to find the best method of capturing and removing space debris. The project was based on a satellite containing several pieces of equipment (a net, a harpoon, a drag sail and vision-based navigation equipment, as well as a set of targets simulating space debris), which remained in orbit between 2018 and 2021. The satellite platform for the project RemoveDEBRIS was launched using SpaceX Falcon 9, was delivered to the International Space Station and later deployed into orbit, where a series of experiments on debris removal were conducted, using several pieces of equipment:
Translations:
Links to Videos:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XLuHk5gWx3k https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_QUhCLTfXf0 Articles:https://www.surrey.ac.uk/surrey-space-centre/missions/removedebris https://www.airbus.com/en/products-services/space/in-space-infrastructure/removedebris https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/r/removedebris | |
Twins Study | |
|---|---|
Definition:A study aiming to investigate the effects of spaceflight on the human organism. The study was organized by NASA with the support of 8 universities across the USA. It was conducted in 2015-2016 and involved two identical twin brothers: Scott and Mark Kelly. Scott Kelly served on a year-long mission aboard the International Space Station, while his brother Mark Kelly, a former NASA employee, remained on Earth. The twins study included an array of biochemical, neurological and other types of medical tests conducted before, during and after the spaceflight, i.e. over the span of 27 months. The results confirmed the robustness and resilience of human health, since 91,3% of Scott Kelly’s medical parameters returned to baseline six months after the spaceflight. The remaining changes were to be used for development of personalized measures to predict and overcome possible adverse consequences of spaceflight. Translations:French: German: Polish: Eksperyment z bliżniakami Swedish: Article:https://www.science.org/doi/pdf/10.1126/science.aau8650 Other sources:https://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasa-s-twins-study-results-published-in-science https://www.nasa.gov/twins-study/about
| |
Kalpana Chawla | |
|---|---|
Source: http://lk.astronautilus.pl/astros/366.htm Definition:Kalpana Chawla, born in Karnal, India, in 1962, is first astronaut with an Indian descent. In her early years, her father took her to local flying clubs, where she developed her passion for flying. She moved to the U.S. to pursue degrees in engineering (Ph.D. in aerospace engineering from the University of Colorado) and eventually after graduation, she did research, focusing on vertical take-off and landing concepts. Her area was the development and implementation of efficient techniques for performing aerodynamic optimization. In 1994, Chawla was chosen as an astronaut candidate and took part in 2 space flights. The second flight ended tragically in 16.01.2003, as Space Shuttle Columbia exploded while being on the way back to the Earth, after 15 days and 22 hours spent in space. The explosion while re-entrng into Earth's atmosphere killed all seven astronauts on board, including Kalpana Chawla. Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/atoms/files/chawla_kalpana.pdf https://www.space.com/17056-kalpana-chawla-biography.html | |
Valentina Tereshkova | |
|---|---|
Illustration: http://www.astronaut.ru/as_rusia/lady62/foto/tereshkova02.jpg Definition:The first female cosmonaut, the 10th person in the world to be sent into space. Valentina Tereshkova flew into space alone aboard Vostok-6 on June 16, 1963. The duration of the flight amounted to 2 days, 22 hours and 50 minutes, during which the spacecraft orbited the Earth 48 times. Valentina Tereshkova was born in 1937 in the village of Bolshoye Maslennikovo in Yaroslavl Oblast, USSR. In 1960, she graduated from Yaroslavl Light Industry Training School as a cotton spinning technician, and in 1969 received a qualification from Zhukovsky Air Force Engineering Academy as a pilot, cosmonaut and engineer. She enjoyed parachuting, which later turned out to be one of the criteria for cosmonaut selection. Following the spaceflight, she worked as a cosmonaut instructor until reaching mandatory retirement age in 1997. Later she continued working as a politician, which she had already been doing since 1966. Her daughter Elena is said to be the first child in the world whose parents are both cosmonauts. Translation:
Links to Videos/Articles:http://www.astronaut.ru/crossroad/010.htm https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Терешкова,_Валентина_Владимировна
| |
Barycenter | |
|---|---|
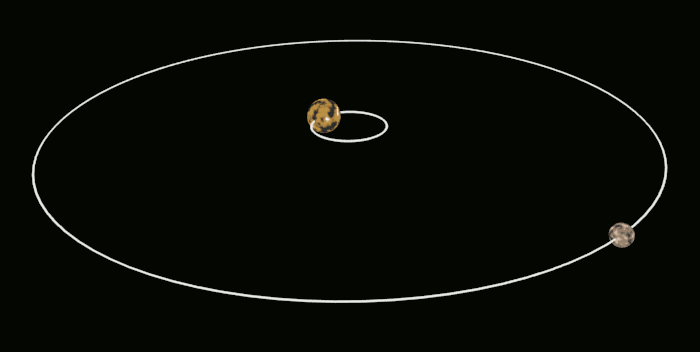 Source: Hoover, S. (2013, July 21). wikimedia commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=28974343 Short Definition:
Barycenter is a theoretical point that has several meanings according to the field in which it is employed:
Detailed Definition:The barycenter is a theoretical point usually with a mathematical value, which has different meanings depending on the field to which it is applied. From its etymology, Barycenter is usually used to express the center or average of a distribution of objects, values or data.
Originally, the mathematician and physicist Archimède introduced and described the notion of barycenter around 300 B.C.E. He first approached it from a physical perspective by stating: “Every heavy body has a well-defined centre of gravity in which all the weight of the body can be considered concentrated." In astronomy, this notion describes the point around which a celestial body and its/their satellite(s) rotate. The illustration below depicts the barycenter with the red cross in the middle as well as the two bodies of different mass orbiting around it. Etymology:Barycenter comes from ancient Greek. Bary: βάρος (báros, “weight”) + center which comes from the Latin of centrum or even earlier from ancient Greek as kentron, κέντρον (single point). Sample Sentence:"How well we understand the Solar System’s barycenter is critical as we attempt to sense even the smallest tingle to the web.” Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://youtu.be/7hMfCCqSdFc
| |
Dark energy | |
|---|---|
Source: https://astronomy.com/news/2020/03/whats-the-difference-between-dark-matter-and-dark-energy Definition:Dark energy (not to be mistaken with dark matter) makes up approximately 68% of the universe, and it is distributed evenly not only in space, but also in time (therefore it has a global effect on the universe as a whole). This is a repulsive force, that accelerates the expansion of the universe. The rate of expansion and its acceleration can be measured by observations based on the Hubble law. The existence of dark energy is proven and its role in the universe can be described thanks to Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity. Example Sentence(s):"Dark energy is generally accepted as contributing to the increased acceleration of the expanding universe, so understanding this relationship will help to refine how physicists and astrophysicists understand it." "And there are still no final answers to the questions surrounding dark energy." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://home.cern/science/physics/dark-matterhttps://astronomy.com/news/2020/03/whats-the-difference-between-dark-matter-and-dark-energy | |
Dark matter | |
|---|---|
Source: https://astronomy.com/news/2020/03/whats-the-difference-between-dark-matter-and-dark-energy Definition:Dark matter (not to be mistaken with dark energy) makes up about 27% of the universe. Unlike normal matter, dark matter does not interact with electromagnetic forces. This means it does not absorb, reflect or emit light, therefore it can't be seen, but researchers can detect it and map it by measuring gravitational lensing. Because of these properties, it works like an attractive force, holding the universe together. In the 1930s, astronomer Fritz Zwicky studied images of around 1,000 galaxies that make up the Coma Cluster and speculated that some kind of matter must be keeping them together. Astronomers Vera Rubin and Kent Ford found a similar phenomenon when they studied the rotation rates of individual galaxies, with even more evidence of the features mentioned above. The existence of dark matter is so widely accepted that it’s part of the "standard model of cosmology", although there is no solid evidence that it is real. There are many theories suggesting that physics beyond the Standard Model, such as supersymmetry and extra dimensions, exist. If other parallel universes exist, then physical features of each universe would be different, therefore the amount of dark matter in each universe would be different. Dark matter helps scientists gain a better understanding of the composition of our universe and how galaxies are held together. Sample Sentence(s):"You can see the galaxy clusters that Professor Zwicky studied to discover Dark Matter." "Dr. Shepherd's work enhances our profile in the area of Dark Matter exploration significantly." Translations:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://home.cern/science/physics/dark-matterhttps://astronomy.com/news/2020/03/whats-the-difference-between-dark-matter-and-dark-energy | |
Inflation | |
|---|---|
Sources: https://wmap.gsfc.nasa.gov/universe/bb_cosmo_infl.html https://www.space.com/42261-how-did-inflation-happen-anyway.html Definition:Rapid expansion of the universe at its early stages of development (at around 10-36 seconds after the Big Bang). The Inflation Theory was developed in 1980 by Alan Guth, Andrei Linde, Paul Steinhardt, and Andy Albrecht and attempted to account for phenomena that could not be explained by the Big Bang Theory (the Horizon Problem, the Flatness Problem and the Monopole Problem). Nowadays, the Inflation Theory is considered to be an extension of the Big Bang Theory. Translation
| |
Great Red Spot | |
|---|---|
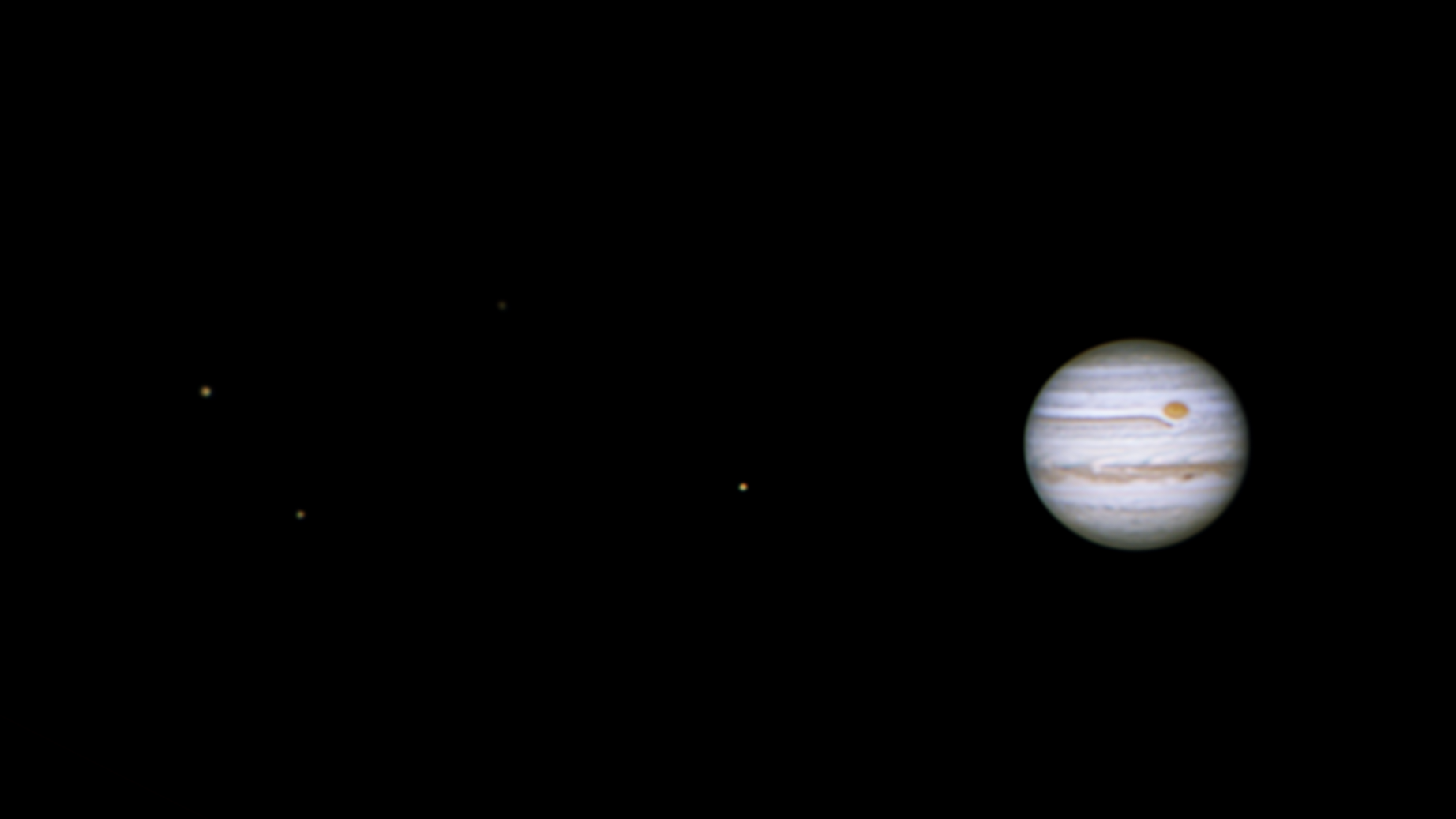 Sources: Stewart, P. (2018, June 8). Jupiter. flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/106648653@N05/42658035711 Definition:A persistent large anticyclonic storm in the atmosphere of Jupiter, 22° south from its equator, which has been continuously observed since the 19th century.As of 2021, the Great Red Spot is reported to be about 10,000 miles across and 300 miles deep into the atmosphere of Jupiter. However, according to NASA observations, it is shrinking and becoming taller, and it is not yet clear whether the Great Red Spot will stabilize or disappear completely. Translation:
Links to Videos/Articles:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JDi4IdtvDVE | |
